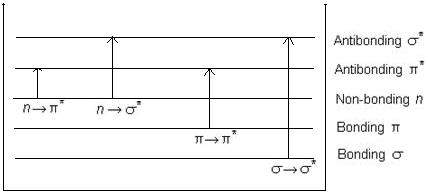
Applications of Absorption Spectroscopy (UV, Visible)
1. Detection of Impurities
UV absorption spectroscopy is one of the best methods for determination of impurities in organic molecules. Additional peaks can be observed due to impurities in the sample and it can be compared with that of standard raw material. By also measuring the absorbance at specific wavelength, the impurities can be detected.
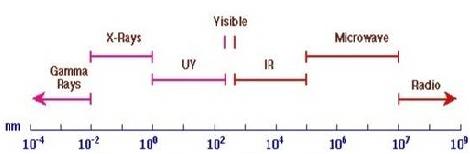
Benzene appears as a common impurity in cyclohexane. Its presence can be easily detected by its absorption at 255 nm.