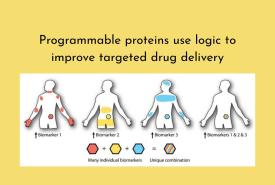
National Pharmacovigilance Week 2025 celebration organized by Saveetha College of Pharmacy
Saveetha College of Pharmacy, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS) Chennai, in collaboration with the Indian Pharmaceutical Association (IPA) Hospital Pharmacy Division, celebrated National Pharmacovigilance Week (NPW 2025).
This initiative aimed to raise awareness among healthcare professionals, regulators, researchers, and the general public about the importance of actively reporting adverse drug reactions (ADRs) using simplified digital platforms.