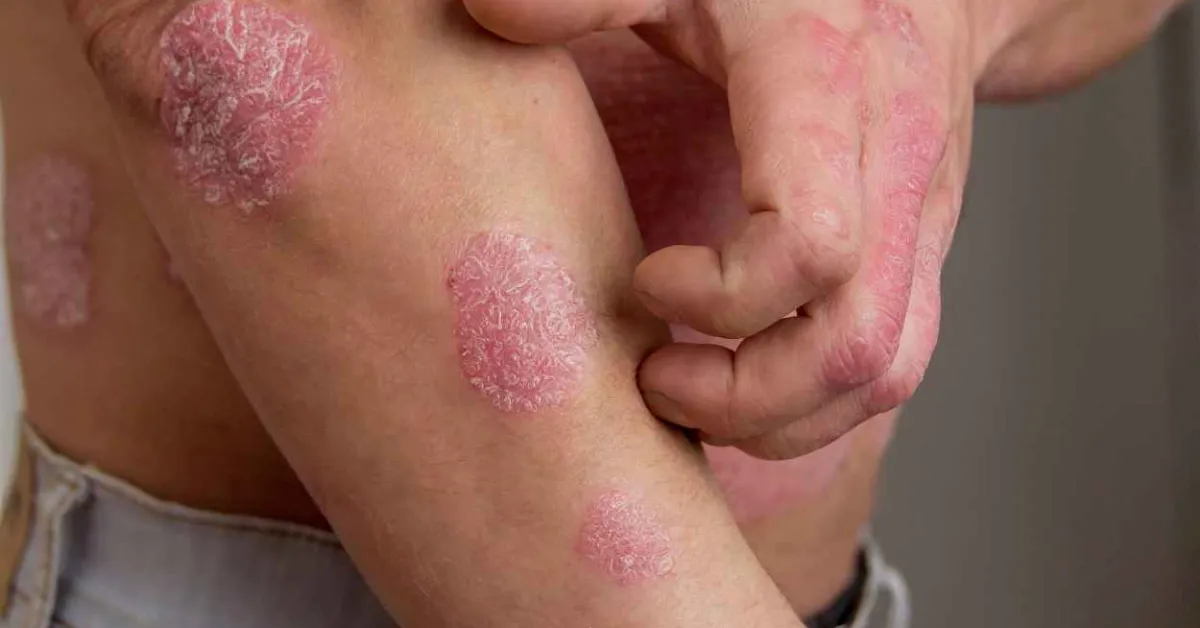
Psoriasis - a chronic skin condition - is not caused or spread by spontaneous genetic mutations in the skin, new research suggests. The team, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and collaborators, sequenced skin samples from 111 people with psoriasis. They didn’t find any mutated genes in the psoriatic patches that weren’t also mutated in the individual’s unaffected skin tissue.
The study, published today (26 October) in Nature Genetics, suggests that unlike other inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease or chronic liver disease, somatic mutations were not responsible for the start or spread of psoriasis.
Confirming that psoriasis is not caused by any somatic mutations enables researchers to continue to explore other avenues.
Over time, all cells in our bodies will accumulate mutations, known as somatic mutations. These can arise from replication errors, chemicals, or environmental factors. While some of these mutations can lead to cancer, many are harmless. When a mutation gives the cell an advantage over its neighbours, it is known as a driver mutation, and this allows the mutated cells to grow and spread.
Recently, research has begun to explore the possibility of driver mutations causing non-cancerous diseases by impacting the function of the tissue or influencing the spread of disease through the body.
In previous work by Wellcome Sanger Institute scientists, these mutations have been shown to have an impact on diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease. In this new study, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and collaborators, explored if the same was true for psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory immune-mediated disease that causes patches of skin to become flaky or sore. The current cause of the condition is unknown and it is estimated that 125 million people worldwide — 2 to 3 per cent of the total population — have psoriasis. This team took skin samples from the forearms of 111 people with psoriasis, taking samples from psoriasis patches and healthy skin. They used laser capture microdissection to isolate 1,182 samples, which were then analysed by whole genome or exome sequencing.
They found minimal differences in the types of mutations seen in healthy skin versus psoriasis patches and only a slight increase in the number of mutations. In addition to this, no functional differences were seen between psoriasis and non-psoriasis tissue, suggesting that the condition is not linked to a specific somatic mutation in the skin.
The team identified four new driver mutations that gave skin cells an advantage over their neighbours, all found in both psoriasis patches and other skin tissue. They also found a mutational signature linked with the use of psoralens, a compound sometimes used as part of a treatment for psoriasis flare-ups. However, these mutations were found in patients who had been prescribed psoralens along with those who hadn’t, suggesting that it could have come from environmental exposure.