About Authors:
Nishtha Tiwari
Department of pharmacy,
b.u Bhopal (m.p.), India
Nishthatiwari.18@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
The oral route of drug administration is the most important method for administering drugs for systemic effects. Except in certain cases the parenteral route is not routinely used for self administration, e.g. insulin. The topical route of administration has only recently been employed to deliver drugs to the body for systemic effects. The parenteral route of administration is important in treating medical emergencies in which the subject is comatose or cannot swallow. Nevertheless it is probable that at least 90% of all drugs used to provide systemic effects are administered by the oral route.
An Fast dissolving tablet, orally disintegrating tablet or orodispersible tablet (ODT) is a drug dosage form available for a limited amount of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. ODTs differ from traditional tablets in that they are designed to be dissolved on the tongue rather than swallowed whole. The ODT serves as an alternative dosage form for patients who experience dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) or for where compliance is a known issue and therefore an easier dosage form to take ensures that medication is taken. Common among all age groups, dysphagia is observed in about 35% of the general population, as well as up to 60% of the elderly institutionalized population and 18-22% of all patients in long-term care facilities During the last decade, ODTs have become available in a variety of therapeutic markets, both OTC and by prescription. An additional reason to use an ODTs is the convenience of a tablet that can be taken without water.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1632
INTRODUCTION
The oral route of drug administration is the most common route for systemic effect of drug. Solid dosage forms are most popular because ease of administration, accurate dosage, self medication, pain avoidance and most importantly patient compliance. The most commonly used solid dosage forms are tablets and capsules; one of the drawback for some patients, difficulty to swallow. Drinking water plays important role for swallowing of oral dosage forms.often times people experience inconvenience in swallowing conventional dosage forms such as water whereas water is not available in case of motion sickness( kenetosis) and sudden episodes of coughing during common cough and cold,allergic condition and bronchitis.
Recent developments in technology have presented viable dosage alternatives for patients who may have difficulty swallowing tablets or liquids. Traditional tablets and capsules administered with an 8-oz. glass of water may be inconvenient or impractical for some patients. However, some patients, particularly pediatric and geriatric patients, have difficulty swallowing or chewing solid dosage forms. Many pediatric and geriatric patients are unwilling to take these solid preparations due to fear of choking. For example, a very elderly patient may not be able to swallow a daily dose of antidepressant.
Orodispersible tablets are uncoated tablets intended to be placed in the mouth where they disperse rapidly before being swallowed.According to European Pharmacopoeia adopted the term "Orodispersible Tablet" as a tablet that to be placed in oral cavity where it disperses rapidly before swallowing. Orodispersible tablets dispers rapidly within 3 min.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF ORODISPERSIBLE TABLETS
absorption and many have similar absorption and bioavailability to standard oral dosage forms with the primary route remaining GI absorption. However, a fast disintegration time and a small tablet weight can enhance absorption in the buccal area. The first ODTs disintegrated through effervescence rather than dissolution, and were designed to make taking vitamins more pleasant for children This method was adapted to pharmaceutical use with the invention of microparticles containing a drug, which would be released upon Tablets designed to dissolve on the buccal (cheek) mucous membrane were a precursor to the ODT. This dosage form was intended for drugs that yield low bioavailability through the digestive tract but are inconvenient to administer parenterally, such as steroids and some narcotic analgesics Absorption through the cheek allows the drug to bypass the digestive tract for rapid systemic distribution. Not all ODTs have buccal effervescence of the tablet and swallowed by the patient Dissolution became more effective than effervescence through improved manufacturing processes and ingredients (such as the addition of mannitol to increase binding and decrease dissolution time. Catalent Pharma Solutions (formerly Scherer DDS) in the U.K., Cima Labs in the U.S. and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in Japan led the development of ODTs. The first ODT form of a drug to get approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was a Zydis ODT formation of Claritin (loratadine) in December 1996. It was followed by a Zydis ODT formulation of Klonopin (clonazepam) in December 1997, and a Zydis ODT formulation of Maxalt (rizatriptan) in June 1998. The regulatory condition for meeting the definition of an orally disintegrating tablet is USP method 701 for Disintegration. FDA guidance issued in Dec 2008 is that ODT drugs should disintegrate in less than 30 seconds. This practice is under review by the FDA as the fast disintegration time of ODTs makes the Disintegration test too rigorous for some of the ODT formulations that are commercially in the market.Difficulty in swallowing (Dysphagia) is a common problem in all age groups, especially the elderly and pediatrics, because of physiological changes associated with these age groups. It is common to see those afflicted carrying a small device with them, which is used for crushing tablets, enabling easy ingestion. Other categories that experience problems using conventional oral dosage forms include are the mentally ill, uncooperative and nauseated patients, those with conditions of motion sickness, sudden episodes of allergic attack and coughing. Sometimes, it may be difficult to swallow conventional products due to unavailability of water. These problems led to the development of a novel type of solid oral dosage form called mouth-dissolving tablets, which disintegrate and dissolve rapidly in saliva without the need of the water. They are also known as fast dissolving tablets, melt-in-mouth tablets, rapimelts, porous tablets, oro-dispersible, quick dissolving or rapidly disintegrating tablets.
Since 1986 when the Zydis® lyophilized, fast-dissolving dosage forms were first introduced, a number of other fast-dissolving formulations were developed, and the technology is still improving. Using the concept of, Scherer has patented the Zydis technology.
The network is highly porous solid form, which allows rapid penetration of liquid and facilitates quick disintegration of the dosage unit. The freeze-drying approach produces the fastest dissolving tablets, but the process is expensive, and the resulting tablets are mechanically weak. The other most widely used method to manufacture these tablets is via regular compression that can produce tablets with higher mechanical strengths. The disintegration or melting time of the compressed tablets is not as fast as the freeze-dried dosage forms, but the compressed tablets provide many advantages, such as high mechanical strength facilitating their handling and processing. The technology of the compressed tablets is also making major improvements, producing tablets that can melt within several seconds in the mouth.
DIFFICULTIES WITH EXISTING ORAL DOSAGE FORM
1. Patient may suffer from tremors therefore they have difficulty to take powder and liquids .In dysphagia physical obstacles and adherence to an esophagus may cause gastrointestinal ulceration. Liquid medicaments (suspension and emulsion) are packed in multidose container; therefore achievement of uniformity in the content of each dose may be difficult.
2. Buccal and sublingual formation may cause irritation to oral mucosa, so patients refused to use such medications.
3. Cost of products is main factor as parenteral formulations are most costly and discomfort. Swallowing of solid dosage form like tablet and capsules may zproduce difficulty for young adult of incomplete development of muscular and nervous system and elderly patients suffer from dysphagia. Cost of products is main factor as parenteral formulations are most costly and discomfort.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
DESIRED CRITERIA FOR ORODISPERSIBLE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
· It should not require water to swallow, but it should dissolve or disintegrate in the mouth in matter of seconds.
· It should be compatible with taste masking.
· It should be portable without fragility concern.
· It should have a pleasing mouth feel.
· It should leave minimal or no residue in the mouth after oral administration.
· Exhibit low sensitivity to environmental conditions as humidity and temperature.
· Allow the manufacture of tablet using conventional processing and packaging equipment at low cost.
ADVANTAGES OF ORODISPERSIBLE DOSAGE FORM
· Ease of administration for patients who are mentally ill, disabled and uncooperative
· Requires no water intake.
· Quick disintegration and dissolution of dosage form.
· Overcomes unacceptable taste of the drugs
· Can be designed to leave minimal or no residue in the mouth after administration and also to provide a pleasant mouth feel.
· Allows high drug loading.
· Faster onset of action
· Convenient - ideal dosage form when fast relief required, for example, pain relief, migraine, or allergy.
· Liquid medicaments (suspension and emulsion) are packed in multidose container; therefore achievement of uniformity in the content of each dose may be difficult.
Selection of drug candidates for ODTS:
Different types of charerterisitcs are considered for selection of appropriate drug candidates for development of orodispersible tablet
1.Good solubility in water and saliva.
2.Free from bitter taste.
3.Dose lower than 20mg.
4.Small to lower molecular weight.
5.Partially non ionized to oral cavity at ph (6.8).
6.Ability to permeate oral mucosal tissues.
7. Ability to diffuse and parttion into the epithelail of upper part of GIT.
Wide range of drugs can be considered as a suitable candidate for such type of dosage forms likeAntiulcer agents such as ranitidine, sulpiride. Antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory agents such as aspirin, ibuprofen, mefenamic acid, Bronchodilators such as salbutamol sulfate terbutaline sulfate, mabuterol hydrochloride, fenoterol hydrobromide, or methoxyphenamine hydrochloride Oral antibacterial and antifungal agents such as penicillin, ampicillin,. Antitussive, anti-asthmatic agents such as theophylline, aminophylline, Diuretics such as acetazolarmide, spironolactone, triamterene, fluorothiazide, Gout suppressants allopurinol, probenecid etc.
LIMITATION OF FAST DISINTEGRATING TABLET
1.Drugs which are having relatively lager doses are difficult to formulate in form of fast disintegrating tablet example like ciprofloxin.
2.The tablets usually have insufficient mechanical strength.Hence careful handaling is required.
3. The tablets may leave unpleasant taste or grittiness in the mouth if not formulated properly.
4. Patients who councurrently taking medicine like anticholenergics may not be the best candidates for fast disintegrating tablets and the patients suffers from sjogren’s syndrome or dryness of mouth due to decrases saliva production may not be good candidate for such type of formulation.
INGREDIENTS TO BE USED FOR FAST DISINTEGRATING TABLET
Important ingredients that are used in the formulation of fast-disintegrating tablets should allow quick release of the drug, resulting in faster dissolution.This includes both the active and inactive ingridents Excipients balance the properties of the actives in fast-disintegrating tablets. This demands a thorough understanding of the chemistry of these excipients to prevent interaction with the actives. Determining the cost of these ingredients is another issue that needs to be addressed by formulators. The role of excipients is important in the formulation of fast-melting tablets. These inactive food-grade ingredients, when incorporated in the formulation, impart the desired organoleptic properties and product efficacy. Excipients are general and can be used for a broad range of actives, except some actives that require masking agents.
Binders: The choice of a binder is critical in a fast- dissolving formulation for achieving the desired sensory and melting characteristics, and for the faster release of active ingredients. Binders keep the composition of these fast dissolving tablets together during the compression stage. The right selection of a binder or combination of binders is essential to maintain the integrity and stability of the tablet. The temperature of the excipients should be preferably around 30 to 350C for faster melting properties. Binders can either be liquid, semi solid, solid or mixtures of varying molecular weights such as polyethylene glycol.
Lubricants: Lubrications are used for to reduces the friction during compaction and ejection of tablets in present study magnesium stearte and talc were used as lubricant.
Bulking agent: The material contributes functions of a diluent, filler and cost reducer. Bulking agents improve the textural characteristics that in turn enhance the disintegration in the mouth, besides; adding bulk also reduces the concentration of the active in the composition. The recommended bulking agents for this delivery system should be more sugar-based such as mannitol, polydextrose, lactate and starch hydrolysate for higher aqueous solubility and good sensory perception. Lactate in particular has high aqueous solubility and good sensory perception. Bulking agents are added in the range of 10 percent to about 90 percent by weight of the final composition.
Emulsifying agents: Emulsifying agents are important excipients for formulating fast-melting tablets, they aid in rapid disintegration and drug release without chewing, swallowing or drinking water. In addition, incorporating emulsifying agents is useful in stabilizing the immiscible blends and enhancing bioavailability. A wide range of emulsifiers is recommended for fast-tablet formulation, including alkyl sulfates, propylene glycol esters, lecithin, sucrose esters and others. These agents can be incorporated in the range of 0.05 percent to about 15 percent by weight of the final composition.
Flavours and sweetners: The addition of these ingredients assists in overcoming bitterness and undesirable tastes of some active ingredients. Formulators can choose from a wide range of sweeteners including sugar, dextrose and fructose, as well as non-nutritive sweeteners such as aspartame, sugar alcohols and sucralose. The addition of sweeteners contributes a pleasant taste as well as bulk to the composition.nowadays aspartame is most commonly used as an instense sweet sweetening agent in pharmaceutical prepration. Its appropriate sweetning power is 180-200 times that of sucrose. It does not posses bitter after taste.
Role of superdisintegrants: As day’s passes, demand for faster disintegrating formulation is increased. So, pharmacist needs to formulate disintegrants i.e. Superdisintegrants which are effective at low concentration and have greater disintegrating efficiency and they are more effective intragranularly. But have one drawback that it is hygroscopic therefore not used with moisture sensitive drugs.
And this superdisintegrants act by swelling and due to swelling pressure exerted in the outer direction or radial direction, it causes tablet to burst or the accelerated absorption of water leading to an enormous increase in the volume of granules to promote disintegration.
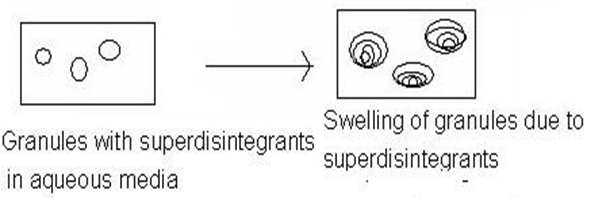
Figure1.1: Mechanism of superdisintegrants by swelling
Mechanism of action of superdisintegrants: The tablet breaks to primary particles by one or more of the mechanisms listed below
I. By swelling
II. By capillary action
III. Because of heat of wetting
IV. Due to disintegrating particle/particle repulsive forces
V. Due to deformation
VI. Due to release of gases
BY SWELLING:
Tablets with high porosity show poor disintegration due to lack of adequate swelling force. On the other hand, sufficient swelling force is exerted in the tablet with low porosity. It is worthwhile to note that if the packing fraction is very high, fluid is unable to penetrate in the tablet and disintegration is again slows down.
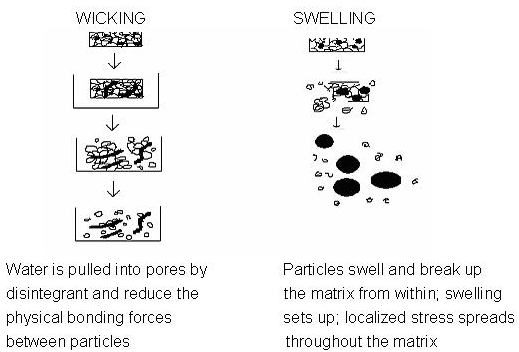
Figure 1.2: Disintegration of Tablet by Wicking and Swelling
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
BY CAPILLARY ACTION
Disintegration by capillary action is always the first step. When we put the tablet into suitable aqueous medium, the medium penetrates into the tablet and replaces the air adsorbed on the particles, which weakens the intermolecular bond and breaks the tablet into fine particles. Water uptake by tablet depends upon hydrophilicity of the drug /excipient and on tableting conditions. For these types of disintegrants maintenance of porous structure and low interfacial tension towards aqueous fluid is necessary which helps in disintegration by creating a hydrophilic network around the drug particles.
DUE TO DISINTEGRATING PARTICLE/PARTICLE REPULSIVE FORCES
Another mechanism of disintegration attempts to explain the swelling of tablet made with ‘non-swellable’ disintegrants. Guyot-Hermann has proposed a particle repulsion theory based on the observation that nonswelling particle also cause disintegration of tablets. The electric repulsive forces between particles are the mechanism of disintegration and water is required for it. Researchers found that repulsion is secondary to wicking.
DUE TO DEFORMATION.
Hess had proved that during tablet compression, disintegranted particles get deformed and these deformed particles get into their normal structure when they come in contact with aqueous media or water. Occasionally, the swelling capacity of starch was improved when granules were extensively deformed during compression. This increase in size of the deformed particles produces a break up of the tablet. This may be a mechanism of starch and has only recently begun to be studied.
DUE TO RELEASE OF GASES
Carbon dioxide released within tablets on wetting due to interaction between bicarbonate and carbonate with citric acid or tartaric acid. The tablet disintegrates due to generation of pressure within the tablet. This effervescent mixture is used when pharmacist needs to formulate very rapidly dissolving tablets or fast disintegrating tablet. As these disintegrants are highly sensitive to small changes in humidity level and temperature, strict control of environment is required during manufacturing of the tablets. The effervescent blend is either added immediately prior to compression or can be added in to two separate fraction of formulation.
BY ENZYMATIC REACTION
Here, enzymes presents in the body act as disintegrants. These enzymes destroy the binding action of binder and helps in disintegration
MARKETTED FORM OF FAST DISINTEGRAING TABLETS
Table 1.1
|
Product: |
Manufactured By/For: |
Active ingredient: |
Category: |
Indication: |
Intended Age: |
|
Abilify Discmelt |
Otsuka America/ |
aripiprazole |
Atypical antipsychotics |
Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder, adjunct therapy for Major Depressive Disorder |
13 years+ for Schizophrenia, 10 years+ for Bipolar disorder, adults for MDD |
|
Alavert Quick Dissolving Tablets |
Wyeth |
Loratadine |
Anti-histamines |
Allergy |
6 years+ |
|
Allegra ODT |
Sanofi Aventis |
Fexofenadine |
Anti-histamines |
Allergic rhinitis, Urticaria |
6–11 years |
|
Aricept ODT |
Eisai Co. |
Donepezil |
Acetyl |
Alzheimer's disease |
adults |
|
Benadryl FastMelt |
Pfizer |
Diphenhydramine |
Anti-histamines |
Allergy |
6 years+ |
||||||
|
Calpol Fast Melts |
McNeil Healthcare UK |
Paracetamol |
Analgesics |
Pain |
6 years+ |
||||||
|
Clarinex RediTabs |
Schering-Plough |
Desloratadine |
Anti-histamines |
Allergy |
6 years+ |
||||||
|
Claritin RediTabs |
Schering-Plough |
Loratadine |
Anti-histamines |
Allergy |
6 years+ |
||||||
|
Clonazepam ODT |
Par Pharmaceutical |
Clonazepam |
Benzodiazepines |
Anxiety, Panic Disorder, Seizure Disorders |
6 years+ |
||||||
CONVENTIONAL TECHNIQUES USED IN THE PREPARATION OF ODT
LYOPHILIZATION
Lyophilization is a pharmaceutical manufacturing technology, which allows drying of heat sensitive drugs and biologicals at low temperatures under conditions that allow removal of water by sublimation. Lyophilization results in preparations, which are highly porous, with a very high spherical surface area, which dissolve rapidly and show improved absorption and bioavailability. The freeze-drying process consists of three phases.
1. Freezing to bring the material below its eutectic zone.
2. Sublimation drying or primary drying to reduce moisture to around 4%w/w of dry product.
3. Desorption or secondary drying to reduce bound moisture to the required final value.
Tablets prepared by lyophilization are fragile and posses low mechanical strength, which make them difficult to handle and they also exhibit poor stability on storage under stressed conditions. Blank et al used a mixture of mannitol and one natural gum (e.g.; acacia guar or xanthan gum) as a carrier material, in formulation of lyophilized fast-dissolving tablets and found good stability in blister pack even when stored at high humidity conditions. Water penetrates through pores of network, resulting in rapid disintegration and / or dissolution of the dosage form.
SUBLIMATION
In this method highly porous and rapidly dissolving tablets, which includes the addition of a sublime salt to the tabletting components, compressing the blend and removing the salt by the process of sublimation. The active ingredient, a diluent(e.g.: lactose and trehalose), a sublime salt (e.g.: ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium acetate), a binder and other excipients are blended and tablets are prepared. Then volatile salt is removed by sublimation, by exposing the tablets to reduced atmospheric pressure for a time sufficient to completely remove the salt.
Tablet prepared by fast dissolving, highly porous compressed tablets by sublimation technique. Mannitol is incorporated as diluent and camphor as sublime material. Tablets prepared by this method dissolve rapidly and possess sufficient hardness. Water can also be used as pore forming material for preparation of highly porous fast dissolving tablets. A mixture of active ingredient and a carbohydrate (e.g: sucrose, glucose, xylitol or mannitol) was wetted with suitable amount of water and compressed into tablets. The water is evaporated, producing highly porous tablets with good mechanical strength.
SPRAY DRYING
Spray drying is a process by which highly porous, fine powders can be produced. spray drying technique for preparing fast dissolving tablets. The composition contained a bulking agent (e.g.: mannitol and lactose), a disintegrant (e.g.: sodium starch glycolate and croscarmellose sodium), an acidic ingredients (citric acid), and /or alkaline ingredients (e.g.; sodium bicarbonate) which when compressed into tablets showed fast disintegration and enhanced dissolution. The fast dissolving tablets prepared from spray drying technique disintegrated within 20seconds.
MASS-EXTRUSION
This technology involves softening the active blend using the solvent mixture of water-soluble polyethylene glycol, using methanol and expulsion of softened mass through the extruder or syringe to get a cylinder of the product into even segments using heated blade to form tablets. The dried cylinder can also be used to coat granules of bitter tasting drugs and thereby masking their bitter taste.
TABLET MOULDING
In this method, the delivery system is prepared in the form of tablets using water-soluble additives, to allow the tablets to dissolve rapidly and completely in mouth. All ingredientsof the formulation are passed through fine mesh, dry blended, wetted with a hydro-alcoholic solvent and then compressed into tablets using low compression forces. The solvent present inside the tablets is removed by air-drying. The so formed moulded tablets contain a porous structure, which enhances dissolution. The moulded tablets prepared by above method possess low mechanical strength, to improve the mechanical strength, a binding agent like sucrose, polyvinyl polypyrrolidone, and cellulose polymers like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose may be added to the solvent system.
Masaki prepared intrabucally fast-disintegrating tablets using agar solution as binder and moulding the preparation into a blister pack. In this process, a suspension containing an active ingredient, agar and soluble sugars like lactose and/or mannitol is prepared and filled into the blister packing well, solidifying the preparation into a jelly form at room temperature, and dried at 30o C under a pressure of 700 to 760 mm Hg. The moulded tablets obtained by this method would have adequate strength with hardness greater than 2.0 kg/cm2.
In other process, the drug containing micro particles are combined with aneffervescent disintegrating agent, which on dissolution forms a tasteless drug suspension in the mouth. Although prompt release is preferred, the protective material utilized in the micro particle should not dissolve instantaneously in water or saliva. That is, the micro particle should resist dissolution and release for a period of time, typically a few seconds or so, sufficient to permit the patient to swallow the released microcapsules, the tablet disintegrates. A combination of polymers (cellulose and syntheticcellulose derivatives, Eudragit. RL30) along with release promoters like soluble sugar (mannitol and magnesium oxide) serves the purpose. The size of micro particles may preferably be between 150 to 500 µ (100 meshes to 35 meshes). The micro particles are then blended with effervescent disintegrant and other adjuvant like binder, diluent, lubricant, color and flavor, and granulated by compaction, extrusion or globulation, and compressed into tablets.
Fast-disintegrating tablets prepared by vacuum drying process are reportedby Van Scoik. In this method, a frozen mixture containing a gum (e.g. Guar, tragacanth, carrageenan or xanthan gum), carbohydrates (mannitol, dextrose, maltose, sucrose or corn syrup), and a solvent was vacuum dried in a tablet shaped mould, which resulted in tablets with enhanced structural integrity than traditional moulded tablets.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
DIRECT COMPRESSION
It is the easiest way to manufacture tablets. Conventional equipment, commonly available excipients and a limited number of processing steps are involved in direct compression. Also high doses can be accommodated and final weight of tablet can easily exceed that of other production methods. This technique can now be applied to fast dissolving tablets because of the availability of improved tablet excipients, especially tablet disintegrants and sugar-based excipients.In this method, tablets are compressed directly from the mixture of the drug and excipients without anycan be directly compressed into tablets of acceptable quality. A type of disintegrant and its proportion are of prime importance. The other factors to be considered are particle size distribution, contact angle, pore size distribution, tablet hardness and water absorption capacity. All these factors determine the disintegration. The disintegrant addition technology is cost preliminary treatment. The mixture to be compressed must have adequate flow properties and cohere under pressure thus making pretreatment as wet granulation unnecessary. Few drugs effective and easy to implement at industrial level
TASTE MASKING
Taste masking is an essential requirement for fast dissolving tablets for commercial success. Taste masking ingredients can be achieved by various techniques; Drugs with unacceptable bitter taste can be microencapsulated into PH sensitive acrylic polymers. Cefuroxime axetile is microencapsulated in various types of acrylic polymers (e.g eudragit E eudragit L-55 and eudragit RL) by solvent evaporation and solvent extraction techniques. These polymer microspheres showed efficient taste masking and complete dissolution in a short period. Fine granules of drug and disintegrant (e.g. low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose) when coated with a water insoluble polymer (e.g. ethyl cellulose) masked the bitter taste of sparfloxacin. The addition of low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose as disintegrant to the drug in cores resulted in increased dissolution rate and bioavailability of sparfloxacin compared to its conventional tablets. A novel micro encapsulation process combined with wet spherical agglomeration techniques was also developed by using a modified phase separation method to mask the bitter taste of the drugs. The spherical agglomerates containing enoxacin and other additives including disintegrants were produced in acetone-n-hexane-ammonia water or acetone-n-hexane-distilled water system by wet spherical agglomeration, applying the phenomena of flocculation of particles in liquid. The agglomerates obtained could be microencapsulated with eudragit RS by phase separation technique. The resulting microcapsules were free from bitter taste and were found bioequivalent to the commercial enoxacin tablets.
A polymer carrier system developed by Lu et al was used to reduce the bitter taste of macrolides (e.g. erythromycin and clarithromycin) by complexation to carbopol. The ionic bonding of amine macrolide to the high molecular weight polyacrylic acid results in macrolide-carbopol complex with reduced bitter taste. These complexes are prepared by dissolving or dispersing the drug and polymer in water or hydro alcoholic mixtures. Further taste masking of the complex is achieved with polymer coatings [e.g., hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (hp-55)] despite which it exhibits good bioavailability.Formulation testing is to generate information useful to the formulator in developing stable and bio available dosage forms that can be man produced.
Characteristics of Fast-Dissolving Tablets:
ZYDIS (R.P. Scherer, Inc.)
Zydis, the best known of the fast-dissolving/disintegrating tablet preparations, was the first marketed new technology tablet. The tablet dissolves in the mouth within seconds after placement on the tongue. Thirteen products are currently available using Zydis technology. In the U.S., they include: Claritin Reditab, Dimetapp Quick Dissolve, Feldene Melt, Maxalt-MLT, Pepcid RPD, Zofran ODT and Zyprexa Zydis. On the worldwide market, other Zydis formulations are available for oxazepam, lorazepam, loperamide, and enalapril.
There are some disadvantages to the Zydis technology. The process of freeze-drying is a relatively expensive manufacturing process. As mentioned earlier, the Zydis formulation is very lightweight and fragile, and therefore should not be stored in backpacks or the bottom of purses. Finally, the Zydis formulation has poor stability at higher temperatures and humidities. It readily absorbs water, and is very sensitive to degradation at humidities greater than 65%. If there is any pinhole or minor damage to the package, the patient may find the lyophilized product has collapsed due to absorption of moisture. As with most other drugs, patients should be advised to avoid storing the Zydis technology in the medicine cabinet in the bathroom. Patients should use their Zydis formulation within six months of opening the laminated foil pouch and immediately after opening its individual blister packaging.
ORASOLV (Cima Labs, Inc.)
OraSolv was Cima's first fast-dissolving/disintegrating dosage form. The OraSolv technology, unlike Zydis, disperses in the saliva with the aid of almost imperceptible effervescence. The OraSolv technology is best described as a fast-disintegrating tablet; the tablet matrix dissolves in less than one minute, leaving coated drug powder. The taste-masking associated with the OraSolv formulation is two-fold. The unpleasant flavor of a drug is not merely counteracted by sweeteners or flavors; both coating the drug powder and effervescence are means of taste-masking in OraSolv. This technology is frequently used to develop over-the-counter formulations. The major disadvantage of the OraSolv formulations is its mechanical strength. The OraSolv tablet has the appearance of a traditional compressed tablet. However, the OraSolv tablets are only lightly compressed, yielding a weaker and more brittle tablet in comparison with conventional tablets. For that reason, Cima developed a special handling and packaging system for OraSolv. An advantage that goes along with the low degree of compaction of OraSolv is that the particle coating used for taste masking is not compromised by fracture during processing. Lyophilization and high degrees of compression, as utilized in OraSolv's primary competitors, may disrupt such a taste masking approach. The OraSolv technology is utilized in six marketed products: four Triaminic Softchew formulations, Tempra FirsTabs, and Remeron SolTab.
DURASOLV (Cima Labs, Inc.)
DuraSolv is Cima's second-generation fast-dissolving/disintegrating tablet formulation. Produced in a fashion similar to OraSolv, DuraSolv has much higher mechanical strength than its predecessor due to the use of higher compaction pressures during tableting. The DuraSolv product is thus produced in a faster and more cost-effective manner. DuraSolv is so durable that it can be packaged in either traditional blister packaging or vials.
The newest DuraSolv formulation, NuLev, is actually dispensed in a conventional stock bottle. Pharmacists are advised to take care when dispensing such DuraSolv formulations from stock bottles to ensure they are not exposed to high levels of moisture or humidity. Excess handling of tablets can introduce enough moisture to initiate dissolution of the tablet matrix. One disadvantage of DuraSolv is that the technology is not compatible with larger doses of active ingredients, because the formulation is subjected to such high pressures on compaction. Unlike OraSolv, the structural integrity of any taste masking may be compromised with high drug doses. The drug powder coating in DuraSolv may become fractured during compaction, exposing the bitter-tasting drug to a patient's taste buds. Therefore, the DuraSolv technology is best suited for formulations including relatively small doses of active compound.10 DuraSolv is currently available in two products: NuLev and Zomig ZMT.
WOWTAB (Yamanouchi Pharma Technologies, Inc.)
The WOWTAB fast-dissolving/disintegrating tablet formulation has been on the Japanese market for a number of years. It has just recently been introduced into the U.S. The WOWTAB technology utilizes sugar and sugar-like (e.g., mannitol) excipients. The two different types of saccharides are combined to obtain a tablet formulation with adequate hardness and fast dissolution rate. Due to its significant hardness, the WOWTAB formulation is a bit more stable to the environment than the Zydis or OraSolv. It is suitable for both conventional bottle and blister packaging. The taste masking technology utilized in the WOWTAB is proprietary, but claims to offer superior mouthfeel due to the patented SMOOTHMELT action.8
The WOWTAB product dissolves quickly in 15 seconds or less.8 The WOW in WOWTAB signifies the tablet is to be given With Out Water. Two WOWTAB formulations currently on the U.S. market are Benadryl Allergy & Sinus FASTMELT and Children's Benadryl Allergy & Cold FASTMELT.
FLASHDOSE (Fuisz Technologies, Ltd.)
Fuisz Technologies has three oral drug delivery systems that are related to fast dissolution. The first two generations of quick-dissolving tablets, Soft Chew and EZ Chew, require some chewing. However, these paved the way for Fuisz's most recent development, FlashDose. The FlashDose technology utilizes a unique spinning mechanism to produce a floss-like crystalline structure, much like cotton candy. This crystalline sugar can then incorporate the active drug and be compressed into a tablet. This procedure has been patented by Fuisz and is known as Shearform. The final product has a very high surface area for dissolution. It disperses and dissolves quickly once placed onto the tongue.
Interestingly, by changing the temperature and other conditions during production, the characteristics of the product can be altered greatly. Instead of a floss-like material, small spheres of saccharides can be produced to carry the drug. The process of making microspheres has been patented by Fuisz, and is known as CEFORM and serves as an alternative method of taste masking.
FLASHTAB (Prographarm Group)
The Flashtab technology is yet another fast-dissolving/disintegrating oral tablet formulation. It utilizes most of the same excipients as in conventional compressed tablets. A disintegrating agent and a swelling agent are used in combination with coated drug particles in this formulation to produce a tablet that disintegrates in the mouth in under one minute.
ORAQUICK (KV Pharmaceutical Co., Inc.)
The OraQuick fast-dissolving/disintegrating tablet formulation utilizes a patented taste masking technology. KV Pharmaceutical claims its microsphere technology, known as MicroMask, has superior mouthfeel over taste-masking alternatives. The taste masking process does not utilize solvents of any kind, and therefore leads to faster and more efficient production. Also, lower heat of production than alternative fast-dissolving/disinte-grating technologies makes OraQuick appropriate for heat-sensitive drugs. KV Pharmaceutical also claims that the matrix that surrounds and protects the drug powder in microencapsulated particles is more pliable, meaning tablets can be compressed to achieve significant mechanical strength without disrupting taste-masking. OraQuick claims quick dissolution in a matter of seconds, with good taste-masking. There are no products using the OraQuick technology currently on the market, but KV Pharmaceutical has products in development such as analgesics, scheduled drugs, cough and cold, psychotropics, and anti-infectives.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Table 1.2: Comparison of Fast-Dissolving/Disintegrating Technologies
|
ZYDIS (R.P. SCHERER, INC.) |
||
|
Novelty |
Handling/Storage |
Drug Release/Bioavailability |
|
First to market |
Do not push tablet through foil |
Dissolves in 2 to 10 seconds |
|
Freeze Dried |
Do not use dosage form from damaged package |
May allow for pre-gastric absorption leading to enhanced bioavailability |
|
|
Sensitive to degradation at humidities >65% |
|
|
ORASOLV (CIMA LABS, INC.) |
||
|
Novelty |
Handling/Storage |
Drug Release/Bioavailability |
|
Unique taste masking |
Packaged in patented foil packs |
Disintegrates in 5 to 45 seconds depending upon the size of the tablet |
|
Lightly compressed |
|
No significant change in drug bioavailability |
|
DURASOLV (CIMA LABS, INC.) |
||
|
Novelty |
Handling/Storage |
Drug Release/Bioavailability |
|
Similar to Orasolv, but with better mechanical strength |
Packaged in foil or bottles |
Disintegrates in 5 to 45 seconds depending upon the size of the tablet |
|
|
If packaged in bottles, avoid exposure to moisture or humidity |
No significant change in drug bioavailability |
|
WOWTAB (YAMANOUCHI PHARMA TECHNOLOGIES, INC.) |
||
|
Novelty |
Handling/Storage |
Drug Release/Bioavailability |
|
Compressed dosage form |
Package in bottles |
Disintegrates in 5 to 45 seconds depending upon the size of the tablet |
|
Compressed dosage form |
Package in bottles |
Disintegrates in 5 to 45 seconds depending upon the size of the tablet |
|
Proprietary taste masking |
Avoid exposure to moisture or humidity |
No significant change in drug bioavailability |
Table1.3: Some Patented Technologies for Fast Dissolving Tablets
|
Technology |
Company's Name |
Technology Base |
|
Durasolv, Orasolv |
CIMA Labs Inc. |
Molding |
|
Flash Tab |
Ethypharm |
Molding |
|
Wow Tab |
Yamanouchi pharma |
Molding |
|
Zydis |
R. P. Scherer, Inc. |
Freeze dried Wafers |
|
Flash Dose |
Fuisz Technology, Ltd. |
Cotton –candy Process |
|
Ziplets |
Eurand |
Molding |
|
Fast Melt |
Elan Corp. |
Molding |
References:
1. European Pharmacopoeia vol (1), 2004, 628
2. Indurwade N.H. et al., Novel Approach- fast dissolving tablets, Indian Drugs 39 (8) August 2002, 405-409.
3. Robin H. Bogner, R.Ph, Fast-Dissolving Tablets, U.S Pharmacist Japson Publication.
4. The theory and practice of Industrial Pharmacy, Leon Lachmann, Herbert A. Lieberman, Joseph L. Kanig. Pg. 293-303, Fourth edition.
5. pharmcast.com/Patents100/Yr2004/May2004/051104/6733781_FastDissolving051104.htm
6. Indurwade N.H. et al., Novel Approach- fast dissolving tablets, Indian Drugs 39 (8) August 2002, 405-409
7. Kaushik.D.Et et al., Mouth dissolving tablets: A Review, Indian drugs 41 (4) April 2004,187-193
8. Kaushik.D et al., Formulation and evaluation of olanzapine mouth dissolving tablets by effervescent formulation approach, Indian drugs 41(7) July 2004, 410- 412.
9. Reddy.L.H et al., Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of the literature, IJPS, July 2002
10. Sameer G .et al.. studied Effects of disintegration-promoting agent, lubricants and moisture treatment on optimized fast disintegrating tablets, 331-336.
11. Tripathi, K.D., Essential of medical pharmacology, 5th Ed., Jaypee Brothers medical Publisher, New Delhi, 2003, .135-144
12. 12.Giri, T.K. ,et al studied the A novel approach to optimize and formulate orodispersible tablet by using different techniques: A Review of the literature, IJPS, May 2010.
13. Sharad A. et al, studied the formulation and evaluation of orodispersible tablet by using different methods, A Review of the literature, IJPR,March 2009.
14. Zade P.S. et al, studied the effects of superdisintegrating agent by using,sodium starch glycolate,crosscarmellose sodium and crospovidone, A Review of the literature, IJPR,Oct-Dec 2011.
15. Schiermeier S, Schmidt PC, Fast dispersible ibuprofen Tablets, Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002 Apr;15(3):295-305
16. Fausett H, Gayser C, Dash AK. Evaluation of Quick Disintegrating Calcium Carbonate Tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2000; 1(3): article 20
17. Greogy.et.al, jaccard and leyder et al., Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery Systems: A Review, IJPS, July 2002, 331-336.
18. Nayak S.M. et al., Design and optimization of fast dissolving tablets for promethazine theoclate, Indian drugs 41(9) September 2004. 554-556.
19. Kuchekar b et al mouth dissolving tablets of salbutamol sulphate: a novel drug delivery system, Indian drugs, 41 (10), 2004,592,598
20. Shenoy .V et al., optimizing fast dissolving form of diclofenac sodium by rapidly disintegrating agents, IJPC march 2003, 197-201
21. Rishi R K, A review on fast dissolving tablets techniques, pharma Review, 2004:2:32.
22. Goodman, Gilman, Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics, Mc-Graw-Hill, 10th Ed., 645-657.
23. Adel M, Semreen M k, Qato M K, fast dissolving dosage forms-technique, Pharm Tech. 2005,68-75.
24. Quick dissolving tablets, biospace.com.27 May 2001.
25. Adel M, Semreen M k, Qato M K, fast dissolving dosage forms-technique, Pharm Tech. 2005,68-75.
26. Lachmann L., Liebermann H.A., Kiang J.L., The theory and practice of Industrial Pharmacy, 3rd Ed., Varghese Publishing House, Bombay, 1998, 430-440
27. wikipedia.com
28. Tablets: Formulation of tablets/Disintegration, pharmpedia.com, 2006.
29. Taudorf E, Bundgaard A, Fagerström PO, Weeke E, Weeke B42. et al., Prepared A sustained release preparation of terbutaline sulphate has been formulated (Bricanyl depot tablets). PMID: 7039400 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE.
30. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipient Third Edition, Edited by Arthur H. Kibbe; 102-103. . S. Corveleyn, J. P. Remon, US patent 6,010,719(2000).
31. Corveleyn, J. P. Remon, US patent 6,010,719(2000).
32. T. Makino, M. Yamado, J. I. Kikuta, “ Fast Dissolving Tablet” US patent 5,720,974(1998).
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









