About Authors:
Amol A. Dambal
Department of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Govt. College of pharmacy, Kathora naka,
Amravati-444604. (M.S.), INDIA.
ABSTRACT:
The Bark of Terminalia arjuna is considered as a Cardioprotective and hypolipidemic in folklore medicine. In present investigation, the detailed pharmacognostic study of Terminalia arjuna Bark is carried out to lay down the standards which could be useful in future experimental studies. The study includes macroscopy, microscopy, preliminary phytochemical screening and physicochemical evaluation.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1202
INTRODUCTION:
Terminalia arjuna is a large, evergreen tree, with a spreading crown and dropping branches. Its grown in most parts of India and has been used in Ayurvedic formulation since ancient times. Besides its wide range of medicinal uses, Terminalia arjuna is planted for shades and ornamental purposes. The powder of Arjuna is produced from the grinding and sieving of stem bark. It has following advantages like free of storage, Easy for intake for all ages of life, suitable form for Medicine can be prepared. Terminalia’s active constituents include tannins, cardenolide, triterpenoid saponins (arjunic acid, arjunolic acid, arjungenin, arjun glycosides), flavonoids (arjunone, arjunolone,luteolin), gallic acid, ellagic acid, oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs), phytosterols, calcium, magnesium, zinc, and copper.1,2.Improvement of cardiac muscle function and subsequent improved pumping activity of the heart seems to be the primary benefit of Terminalia. It is thought the saponin glycosides might be responsible for the inotropic effect of Terminalia, while the flavonoids and OPCs provide free radical antioxidant activity and vascular strengthening.3 A dose-dependent decrease in heart rate and blood pressure was noted in dogs given Terminalia intravenously.4 Recently, two new cardenolide cardiac glycosides were isolated from the root and seed of Terminalia.5,6The main action of these cardenolides is to increase the force of cardiac contraction by means of a rise in both intracellular sodium and calcium.
In literature details of morphology, Phytoconstituents, medicinal properties & uses of Terminalia arjuna is very sparce therefore, in present study Pharmacognostic standards of the bark of Terminalia arjuna studied. These standards are of almost importance not only finding out genuity, but also in detection of adulterants in marketed drugs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Terminalia arjuna was obtained from local area of amravati. The sample was authenticated for its botanical identity by Botanist (Dr. P.Y.Bhogavkar VMV College of amravati) & voucher specimen deposited in herbarium of the institute. After collection the fresh bark of the plant was dried, soak in water for few days. Dried bark was made into powder. An exhaustive Pharmacognosy was carried out using standard methodology.
MACROSCOPIC STUDY
Size : 7.9 - 11.5 -15.5cm in length. 3.8 - 4.5 - 5.7cm in breadth.
Shape : Elliptical
Margin : Entire
Venation : Parallel
Apex : Acute to acuminate
Base : Sub sessile to cuneate
Surface : Leathery to coriacious
Texture : Firm, flexible, slightly succulent
Colour : Dark green adaxially, light green abaxially
Taste : Bitter
Odour : Characteristic
Table .1 PHYSICOCHEMICAL EVALUATIONS:
|
Extractive value |
Percentage |
|
Ethanol |
25.0% |
|
Aqueous |
20.0% |
|
Pet ether |
1.4% |
|
Loss on drying |
5.12% |
|
Ash |
< 5% w/w |
|
Heavy Metal Lead |
< 10 ppm |
|
Acid insoluble ash |
< 3% w/w |
|
Test for pathogen |
Nil |
MICROSCOPY:
cork consists of a few layers of tangentially running & radially elongated cells, phellogen, 2-4 celled thick, phelloderm narrow, consisting of 4-6 rows of tangentially elongated & radially arranged cells. Phloem, very broad, traversed by uniseriate medullary rays running straight & parallel, occasionally becoming slightly curved near the rosette crystals; groups of phloem fibers, lignified, thin walled, tangentially arranged, associated with idioblasts containing clusters & rosettes of calcium oxalate. Some parenchymatous cells of cortex & secondary phloem contain reddish brown pigment & some cells contain starch grains.
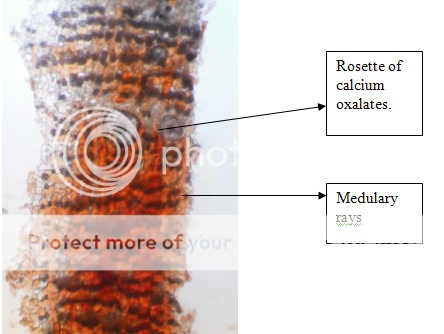
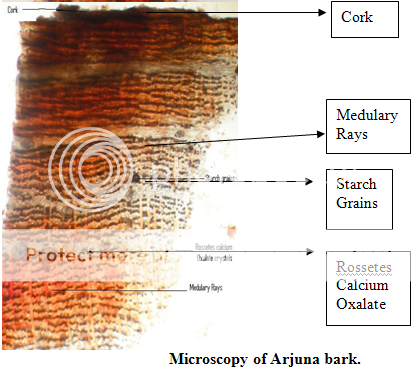
POWDER MICROSCOPY: In the powder microscopy of arjuna bark shows the uniseriate medullary rays running straight & parallel, occasionally becoming slightly curved , some cells contain starch grains.

TABLE. 2. PRELIMINARY PHYTO-CHEMICAL SCREENING.
|
Sr. no. |
Chemical Tests |
Ethanol extracts |
Aqueous extracts |
|
1 |
Alkaloids |
+ |
+ |
|
2 |
Carbohydrates |
+ |
+ |
|
3 |
Phytosteroids |
+ |
- |
|
4 |
Fixed oils & fats |
- |
- |
|
5 |
Saponins |
+ |
+ |
|
6 |
Phenolic compounds tannins |
+ |
+ |
|
7 |
Proteins & amino acids |
+ |
+ |
|
8 |
Gums & mucilages |
- |
- |
|
9 |
Volatiles oils |
- |
- |
|
10 |
Flavanoids |
+ |
+ |
(+ = present, - = absent)
TLC FOR ETHANOLIC TERMINALIA ARJUNA EXTRACTS:
To take 10ul spot on silica gel G coated plate run in mobile phase (Toluene: ethyl acetate: formic acid.) 07:03:0.5 proportion.
|
Sr No. |
Mobile phase |
Spots |
Rf values |
|
1 |
Toluene: ethyl acetate: formic acid. (07 : 03 : 0.5 ) |
1 2 3 4 |
0.81 0.10 0.20 0.39 |
References:
1) Kapoor LD. Handbook of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants. Boca Raton, FL. CRC Press; 1990:319-320.
2) Bone K. Clinical Applications of Ayurvedic and Chinese Herbs. Warwick, Queensland, Australia. Phyto-therapy Press; 1996:131-133.
3) Shridhar Dwivedi, Terminalia arjuna A useful drug for cardiovascular disorders Preventive Cardiology Group, University College of Medical Sciences, University of Delhi, Delhi110095,India.
4) The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India, part-I, vol. II 1st edn. New Delhi: government of India, ministry of health & family welfare, dept. of Indian systems of medicines & homeopathy 1999, p. 17-18.
5) Himant Singh, standardizations of Arjuna arishta
6) Formulation by TLC method, international journal of pharmaceutical science review & research, vol-2, issue 1 may-june 2010; article 007 p.25-28.
7) Quality standards of Indian medicinal plants, India council of medicinal research New Delhi, 2005vol-2 p.198
8) SSSBiotic.com, Nutraceuticals, Herbal extracts from India.
9) Dwivedi S, Jauhari R. Benefcial effects of Terminalia arjuna in coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J 1997;49:507-510.
10) Chopra R.N, Chopra I C, & Handa K L,Indigenous Drugs of India, edited by L D Kapur (Academic publishers India ),1994, 421.
11) Anonymous, 1999. Terminalia arjuna. Alternative Medicine Review
12) Shah, C.S., Bhavsar, G.C., 1956. Pharmacognosy of the bark of Terminalia tomentosaW&Aand comparison with Terminalia arjunaW&Abark. IndianJournal of Pharmacology 18, 81–84.
13) cidpusa.org/health_benefits_of_terminalia_ar.htm
14) Wallis, T.E., Practical Pharmacognosy, J. & A.Churchill Ltd., London, (Vth Ed.), (1984).
15) Damodaran S. kumar and Yenamandra S. prabhakar,on the ethnomedical significance of the ai3jun tree, terminala arjuna (roxb.) wight & arnot, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 20 (1987) 173-190
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









