About Authors: Deepti Maithani *, Vikas Jain
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shobhit University, Meerut
Reference ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1084
Introduction
From the ancient time it has been the endeavor of the physician and the apothecary to provide patients with the best possible forms of medicine, for recovery from disease faster and completely within minimum adverse effects. Paul Ehrlich in1902 initiated the era of targeted delivery,who proposed drug delivery to be as magic bullet. An ideal drug delivery system is that fulfils the objective of spatial placement and temporal delivery resulting maximized therapeutic effect and least toxicity. With the progress in time and growth of science and technology, the dosage forms have evolved from simple mixtures and pills, to highly sophisticated technology intensive systems, which are known as novel drug delivery systems (NDDS). (1) A different approaches have materialized into various forms of NDDS such as microemulsions, multiple emulsions, liposomes, niosomes, micospheres, pharmacosomes, virosomes, dendrimers, etc.. Most often the problems associated with these delivery systems are their stability and predictability in biological systems which reduce their clinical potential, although each one is associated with its own strong points. Nanotechnology is a rapidly expanding field today. According to the National Nanotechnology Initiative (U.S) nanotechnology is broadly defined as the understanding and control of matter at dimensions of roughly 1 to100 nanometers, where unique phenomena enable novel applications. (2) . Most often the problems associated with these delivery systems are their stability and predictability in biological systems which reduce their clinical potential, although each one is associated with its own strong points.
Nanoemulsion emerged as a boon of nanotechnology in the form of a novel drug delivery system(NDDS). Nanoemulsions Nanosized or submicron emulsions can be defined as systems of at least two nearly immiscible fluids dispersed one into another in the form of droplets with diameter significantly below one micrometer in nano range.

Nanoemulsion and Microemulsion (Shah et al.)
CLASSIFICATION OF OIL-IN-WATER NANOSIZED EMULSIONS. Mainly divided into two type oil in water o/w and w/o type based on dispersion media .
Based on the emulsifier combinations used in the formation of submicron emulsion droplets, the o/w nanosized emulsions can be classified into three types
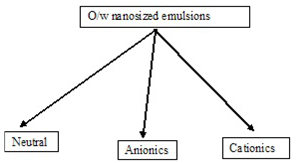
A typical example of the aqueous soluble emulsifiers are nonionic surfactants (e.g.Tween 20) which are preferred because they are usually less irritant than their ionic counter parts
Formulation consideration of Nanoemulsion: Nanoemulsion composition mainly consist of oil phase, aqueous phase, emulsifiers (surfactant and cosurfactant ), antioxidant etc.
a.Oil is the main component of nanoemulsion,the final oil concentration for ocular use is now widely accepted to be at or below 5% taking into account that the emulsion must be kept in a low-viscosity range of between 2 and 3 centipoises, which also is the optimal viscosity for ocular preparations (3). However, for all other medical uses, the amount of oil may be varied but generally is within 5-20% w/w. Sometimes, a mixture of oils may be employed to facilitate drug solubilization in the oil phase.Medium chain triglycerides (MCT) are preferred over Long chain fatty acid natural oils .Oils used in nanoemulsion must be FDA approved GRAS certified .Commonly used oils in NE s preparation are IPM(Isopropyl Myristrate ),Triacetin(Glycryl triacetate) ,Sefsol 218(Propylene glycol mono ethyl ether ) etc these are preferred over conventional high density oils like castor oil,coconut oil,sesame oil etc.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
b.Emulsifiers (4-5): Most of the known synthetic and efficient emulsifirs are toxic upon parentral administration because of haemolysis .The emulsifiers most frequently used in parentral formulation are phospholipids (generally from egg yolk sources ),block copolymers of polyoxyethylene –polyoxypropylene (poloxamer ) and to a lesser extent ,acetylated monoglycerides ,other emulsifiers such as fatty acid esters of sorbitans(various types of Spans ;ICI Americas) and polyoxyethylene sorbitans (various types of Tweens ;ICI UK), are already approved by various pharmacopeias for parentral administration and can therefore be considered for emulsion formulation design .Unlikely microemulsion and macroemulsion system that require a high surfactant concentration 20% and higher the nanosized emulsion can be prepared by using relatively lower surfactant concentration.Non ionic surfactants are preferred over ionic surfactant because of comparatively low toxicity profile.
Non ionic surfactants selection is done on the basis of HLB value .HLB is scale given by Griffin in order to classify Non Ionic Surfactants .For o/w emulsion non ionic surfactant having HLB range 8-16
c.Additives: Additives are needed to adjust the emulsion to physiological pH and tonicity.Glycerol is usually recommended as an isotonic agent and can be found in almost every parentral emulsion.Ph is usually adjusted with an aqueous solution of NaoH or HCl depending on the value that should be reached .The Ph of the emulsion is generally adjusted to 7-8 to allow physiological compatibility and maintain emulsion physical integrity by minimizing fatty acid ester hydrolysis of MCT LCT and phospholipids .Furthermore emulsion stabilizers are often needed to protect emulsion from oxidation or phase separation .To prevent from oxidation antioxidants or reducing agents such as Tocopherols ,dferoxamine mesylate and ascorbic acid .To prevent phase separation stabilizing agent capable of localizing in the interfacial film should be added .Such molecules are amphipathic and are poor surfactants but can stabilize the film by enhancing molecular interactions and increasing electrostatic surface charge of droplets .A well known stabilizer is oleic acid or its sodium salt(6) Cholic acid ,Deoxy cholic acid and their respective salts also have been shown to markedly impove drug incorporated emulsion solubility.
Preparation methods of nanoemulsion:
1.Phase inversion method: In this method fine dispersion is obtained by chemical energy resulting of phase transition taking place through emulsification path .The adequate phase transition are produced by varying the composition at constant temperature or by varying the temperature at constant composition,phase inversion temperature (PIT) method was introduced by Shinoda et al., based on the changes of solubility of polyoxyethylene – type surfactant with temperature .This surfactant becomes lipophillic with increase in temperature due to dehydration of polymer chain .But at low temperature ,the surfactant monolayer has a large positive spontaneous curvature forming oils-swollen micellar solution phase.(7)
2.Sonication method: Sonication method is another best way to prepare nanoemulsion .In this method droplet size of conventional emulsion or even microemulsion are reduced with the help of sonication mechanism .This method is not suitable for large batches of nanoemulsion can be prepared by this method(8)
3.High Pressure homogenization: This method is performed by applying a high pressure over the system having oil phase ,aqueous phase and surfactant or cosurfactant. The pressure is applied with the help of special equipment known as homogenizer .There are some problems associated with homogenizer such as poor productivity,component deterioration due to difficult mass production and generation of much heat,With this method only oil in water (o/w) liquid nanoemulsion of less than 20% oil phase can be prepared and cream nanoemulsion of high viscosity or hardness with a mean droplet diameter lower than 200 nm can not be prepared(9)
Drug incorporation techniques:
There are four different approaches (10) to incorporate lipophilic drugs or heat labile
molecules into the oil phase or at the o/w
interface of the nanosized emulsions:
(A) extemporaneous drug addition,
(B) de novo emulsion preparation,
(C) an interfacial incorporation approach, which includes the recently developed SolEmul® technology,
(A)Extemporaneous drug addition: incorporation of the drug into preformed emulsion (Addition of Amphotericin B directly into the preformed 20% emulsion (11)
(B)De novo emulsion preparation: In principle, the lipophilic drug molecules (thermostable) should however be incorporated by a de novo process as described earlier. Thus,the drug is initially solubilized or dispersed together with an emulsifier in suitable single-oil or oil mixture by means of heating. The waterphase containing the osmotic agent with or without an additional emulsifier is also heated and mixed with the oil phase by means of highspeed mixers. Further homogenization takes place to obtain the needed small droplet size range of the emulsion.
(C) Interfacial incorporation approach: Since many drugs of commercial interest generally have a solubility that is too low in FDA approved oils, Lance et al (12) proposed a method to incorporate such drugs into the interfacial o/w layer of the emulsion droplets. This can be achieved by initially dissolving the drug along with the phospholipid (emulsifier) in an organic solvent, instead of in the oil. Following the solvent evaporation, the obtained phospholipids/drug co-mixture is used in the de novo production of the emulsions (13). However, this approach suffers from possible drug nanocrystal formation and from the use of organic solvent during the emulsion preparation process. To overcome such drawbacks, a novel SolEmul® technology was developed in which an additional high speed homogenization step is included to mix the drug with emulsion. The drug particles are micronized to the nanosize range prior to incorporation into the emulsion. By this technique, adequate amounts of lipophilic drugs can be substantially incorporated into the lipophilic core or intercalated between the selected emulsifier molecular films at the o/w interface of the emulsions. The drugs reported to have been incorporated by this novel approach are amphotericin B, carbamazepine and itraconazole(14-15)
Advantages of nanoemulsion over simple emulsion and reasons for its acceptance:(42-43)
1.Nanoemulsion never shows creaming and sedimentation kinds of problems due to its very small droplet size.
2.Small droplet size prevent coalescence of droplets .In the coalescence process small droplets come together and form large droplets .
3.Dispersibility of nanoemulsion is very high compared to microemulsion because small droplet size prevent the flocculation of droplets and this process makes the system dispersed without separation .
4.Nanoemulsion formulation provides a rapid penetration of active ingredients through skin due to large surface of droplets .Even sometime it is found that nanoemulsion penetrate easily through rough skin This property of nanoemulsion minimizes the additional utilization of penetration enhancer which is responsible for incompatibility of formulation.
5.Nanoemulsion formulation required low amount of surfactant compared to micro or macroemulsion.For example 20-25% surfactant is rezuired for the preparation of microemulsion but 5-10% is sufficient in case of nanoemulsion .
6.Nanoemulsion has a transparent and fluidiry property which improve patient compliance and safe for administration due to absence of any thickening agent and colloidal particles .
7.It is also rported that nanoemulsion may be used for the target delivery of active ingredient especially in cancer therapy.
8.Nanoemulsion formulation may become stable alternative for liposomes and vesicle type of delivery systems.
9.Nanoemulsion formulation can be administered by various routes of body. There are various reported methods which support the administration of nanoemulsion formulation through parentral, oral, topical, nasal and ocular route
10.These formulations may be used to increase the bioavailability of poor water soluble drug by developing oil in water type of nanoemulsion.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
Limitation:(42-43)
1.The manufacturing of nanoemulsion formulation is an expensive process because size reduction of droplets is very difficult as it required a special kind of insteument and process methods.For example ;homogenization,ultrasonicator and microfluidiser are expensive instruments.
2.Ostwald ripening is the instability problem associated with nanoemulsion,this is due to high rate of curvature of small droplet show greater solubility as compared to large drop with a low radius of curvature ,
3Less availability and comparatively high cost of oils ,surfactant and cosurfactant required for manufacturing of nanoemulsion.
Characterisation of nanoemulsion:
Following parameters must be analyzed at the time of preparation of nanoemulsion(36)
1.Particle size Analysis :Formulated nanoemulsion should be analyzed for their hydrodynamic particle size and particle size distribution .Generally in case of nanoemulsion dynamic light scattering (DLS) principle based Photon Correlation Spectroscopy ,Zetasizer is used for measurement of average particle size and further particle size distribution(16)
3.Droplet Surface Charge : The electrical charge on emulsion droplet is measured by use of either a Zetasizer (Malvern Instruments,England) or moving boundary electrophoresis technique ,which has been shown to yield accurate electrophoretic mobility data.It should be greater than -30 Mv to yield stable nanoemulsion(17)
4.Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM):This method is used to observe the morphology of nanoemulsion.
5.Viscosity is measured to ensure the better delivery of formulation according to route of delivery and appliction for example in ocular formulation viscosity should not be more than 2-3 centipoise.(10).
6.Drug entrapment efficiency:To measure the exetent of drug entrapped in the desired phase,for example lipophillic drug entrapped in oil phase ,and hydrophilic drug entrapped in aqueous phase,calculated by formula: DE=Initial amount of drug –free drug / Initial drug ×100 (18)
7.Invitro release study: To estimate the invivo drug release pattern using Dialysis Sac Diffusion Technique (19).A given volume of drug loaded nanoemulsion should be placed in the dialysis sac which should be hermetically sealed and dropped into an appropriate sink solution.The entire system should be kept at 37?C with continuous magnetic stirring .Sample should be withdrawn from sink solution at predetermined time and analysed for drug content.
Applications of Nanoemulsion:
1.Use of nanoemulsion in cosmetics: NEs have recently beome increasingly important as potential vehicles for the controlled delivery of cosmetics and for optimized dispersion of active ingredient in particular akin layers.Due to their lipophillic interior .NEs are more suitable for the transport of liophillic compounds than liposomes .similar to liposomes ,they support the skin penetration of active ingredients and thus increase their concentration in skin,Another advantage is the small size droplets with its high surface area allowing effective transport.NEs are acceptable in cosmetics because there are no inherent creaming ,sedimentation ,flocculation,or coalescence that are observed with microemulsion.The incorporation of potentially irritating surfactant can often be by using high energy equipment during manufacturing(20)
2.Antimicrobial nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial NEs are oil-in-water droplets that range from 200 -600 nm.They are composed of oil and water and are stabilized by surfactants and alcohol.The NE has a broad –spectrum activity against bacteria (e.g. E.coli ,Salmonella,S.aureus ),enveloped viruses (e.g.HIV ,Herpes Simplex),fungi (e.g Candida ,Dermatophytes ) and Spores (e.g .anthrax).The NE particles are thermodynamically driven to fuse with lipid containing organisms. This fusion is enhanced by the electrostatic attraction between cationic charge of emulsion and anionic charge on the pathogen .When enough nanoparticles fuse with Pathogens they release part of energy trapped within emulsion .Both the active ingredient and energy released destabilize the pathogen lipid membrane resulting in cell lysis and death .In the case of spores ,additional germination enhancers are incorporated into emulsion.Once initiation of germination takes place ,the germinating spores become become susceptible to the antimicrobial action of NE .A unique aspect of the NE is their selective toxicity to microbes at concentrations that are non irritating to skin or mucous membrane .The safety margin of NE is due to low level of surfactant in each droplet,yet when acting in concert ,these droplets have sufficient energy and surfactant to destabilize the targeted microbes without damaging healthy cells .As a result ,the NE can achieve a level of topical antimicrobial activity that has only been previously achieved by systemic antibiotics (21)
3.Prophylactic in bioterrorism attack: Based on their antimicrobial activity ,research has begun of NEs as a prophylactic medication ,a human protective treatment ,to protect people exposed to bio attack pathogens such as anthrax and ebola .A broad spectrum NE was tested on surfaces by the US army (Rest Ops ) in December 1999 for decontamination of anthrax spore surrogates .It was tested again by Rest Ops in March 2001 as a chemical decontamination agent .All test wer successful. The technology has been tested on gangrene and Clostridium botulism spores and even can be used on contaminated wounds to salvage limbs.The NE technology can be formulated into a cream,foam ,liquid or spray to decontaminate a variety of materials marketed as NANOSTAT (Nanobio Corp)(22)
3.Nanoemulsion a mucosal vaccines: NE are being used to deliver either recombinant proteins or inactivated organism to mucosal surface to produce an immune response.The first application an influenza vaccine and an HIV vaccine can proceed to clinical trial(19) .The NE cause proteins applied to mucosal surface to be adjuvanted and it facilitates uptake by antigen presenting cells .This results a significant systemic and mucosal immune response that involve the production of specific Ig G and Ig A antibody as well as cellular immunity .Initial work in influenza has demonstrated that animals can be protected against influenza after just a single mucosal exposure to the virus mixed with emulsion .Research has also demonstrated that animals exposed to recombinant gp120 in NE on their nasal mucosa develop significant responses to HIV ,thus providing a basis to examine the use of this material as HIV vaccine .Additional reseeach is ongoing to complete the proof of concept in animal trial for other vaccines including Hepatitis B and Anthrax.(23)
4.Nanoemulsion as nontoxic disinfectant cleaner (24-25): A breakthrough nontoxic disinfectant cleaner for use in commercial market that include health care ,hospitality ,travel ,food processing and military applications has been developed by Enviro Systems,Inc.that kills tuberculosis and a wide spectrum of viruses ,bacteria and fungi in 5-10 minutes without any hazards posed by other categories of disinfectants.The product needs no warning labels.It does not irritate eyes and can be absorbed through skin,inhaled or swallowed without harmful effects.The disinfectant formulation is made up of nanospheres of oil droplets less than micrometer that are suspended in water to create NE requiring only miniscule amount of active ingredient .The nanosphere carry surface charges that efficiently penetrate the surface charges on microbes membranes-much like breaking through an electric fence.PCMX (Parachlorometaxylenol) marketed as a Eco Tru (Enviro Systems,Inc)
5.Nanoemulsion in cell culture technology: Cell cultures are used for invitro assays or to produce biological compounds ,such as antibodies or recombinant proteins.To optimize cell growth the culture media can be supplemented with a number of defined molecules or with blood serum.Up to now it has been very difficult to supplement the media with oil soluble substances that are available to cell and only small amount of these lipophillic substances could be absorbed by the cells,NEs are new method for delivery of oil soluble substances to mammalian cell cultures.The delivery system is based on NE which is stabilized by phospholipids.These NE are transparent can be easily passed through .1µ filter for sterilization .NE droplets are easily taken up by cells.The advantages of using NEs in cell culture technology are better uptake of oil soluble supplements in cell culture ,improve growth and vitality of cultured cells,and allowance of toxicity studies of oil soluble drugs in cell culture(26)
6.Nanoemulsion in cancer therapy and in targeted drug delivery: The effects of the formulation and particle composition of gadolinium(Gd) containing lipid NE (Gd –nano LE)on the Biodistribution of Gd after its intravenous (IV) injection inD1-179 melanoma bearing hamsters were evaluated for its application in cancer neutron –capture therapy .Biodistribution data revealed that Brij 700 and HCO-60 prolonged the retention of Gd in the blood and enhanced its accumaulation in tumors .Among the core components employed ,soyabean yielded the highest Gd concentration in the bood and tumor and lowest in the liver and spleen .When each Gd –nano LE was was iv injected once or twice at a 24 hr interval,the Gd concentration in the tumour correlated well with the total dose and it reached maximum of a189µg/g wet tumor .This maximum Gd level was greater than the limit required for significantly suppressing tumor growth in neutron capture therapy .(27)In order to achieve penetration of Paclitaxel (PCL) into deeper skin layers while minimizing the systemic escape ,a (NE) was formulated and its invivo pharmacokinetic performance was evaluated .Further same formulation was explored for peroral bioavailability enhancement of PCL.Upon dermal application ,the drug was predominantly localized in deeper skin layers ,with minimum systemic escape .(28) The advantages of formulating various lipophillic anticancer drugs in submicron o/w emulsion are obvious .The oil phase of the emulsion systems can act as solubiizer for the lipophillic compound
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
7.Nanoemulsion in treatment of various other disease conditions: Pharmos’(US-based company has developed the nanoemulsion topical diclofenac cream as potential treatment for osteoarthritis (OA)pain .OA is painful condition affecting more thamn 30 million people in USA and is the most frequent cause of physical disability among adults ,mainly elderly .Topical diclofenac is also being considerd as treatment of soft tissue injury ,sprain and strain.It is estimated that 20% of OA patients don’t receive treatment mainly due to gastrointestinal side effects of oral NSAIDs and cardiovascular risk of COX -2 inhibitors .A topical NSAID offering adequate pain relief targeted to site of injury with an improved safety profile .Pharmos’ NE technology consist of an efficient solvent free topical vehicle based and drug entrapment in stable submicron particles of oil in water emulsions with a mean droplets size between 100 and 200nm that are uniformly dispersed in aqueous phase.One of the unique characteristics of NE technology is relatively high percentage of total particle volume occupied by the internal hydrophobic oil core of the droplets .This provide high solubilization capacity for lipohillic compound compared to other lipoidal vehicles such as liposomes.Viscosity imparting agents are used for nanoemulsion thickening to produce creams with desired semisolid consistencyfor application to skin.The skin penetrative propoeries of solvent free NE delivery technology and its low irritancy make it novel topical nanovehicle a promising candidate for effective transcutaneous delivery of lipophillic drugs.Co Q10 (CoQ10) also known as ubiquinone,is used for energy production within cells and act as antioxidant .Since CoQ10 is highly lipohllic ,the topical and oral bioavailbility is very low.Latest technical development reveal that encapsulation of CoQ10 in NEs result in significantly enhanced bioavailability.The application of CoQ10 has been further improved by the development of novel .CoQ10 double NE containing tocopherol and CoQ10 in individual nanodroplet,In addition ,the CoQ10 concentration in these NE could be increased by the development of supersaturated CoQ10 NE(29) Preclinical data using the carrageenan induced paw edema animal model showed enhanced anti-inflammatory activity with NSAID encapsulated in NE creams compared to conventional commercial formulations.A pharmacokinetic study using NE creams containing radiolabelled diclofenac and ketoprofen was performed to assess drug penetration through skin and to determine local tissue (muscle and joints) and plasma level of drugs following topical administration .Compared to oral administration ,NE-diclofenac and NE-ketoprofen showe 4-6 fold less drug in plasma,60-80 fold more drug in muscle tissue and about 9 fold more drug in joints.
Primaquine(PQ) is one of the most widely used antimalarial and is the only available drug till date to combat relapsing form of malaria especially in case of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale .Primaquin acts specifically on the pre-erythrocytic schizonts that are concentrated predominantly in the liver and cause relapse after multiplication.However application of PQ in higher doses is limited by severe tissue toxicity including haematological andGI related side effects that are needed to be minimized .Lipid NE has been widely explored for parentral delivery of drugs .Primaquine when incorporated into oral lipid NE having a particle size in range of 10-200 nm showed effective antimalarial activity against Plasmodium berghii infection in swiss albino mice at a 25% lower dose level as compared to conventional oral dose.Lipid NE of Primaquine exhibited improved oral bioavailability and was taken up preferentially by liver with drug concentration higher at least by 45% as compared to plain drug.(27)
7.Nanoemulsion formulations for improved oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs
NE formulations were developed to enhance oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs.Paclitaxel was selected as prototype hydrophobic drug .The oil in water (o/w)NEs were made with pine nut oil as internal oil phase ,egg lecithin as the primary emulsifier and water as the external phase .Stearylamine and deoxycholic acid were used to impart positive and negative charge to emulsions,respectively .The formulated NE had a particle size of 90-120 nm and zeta potential ranging from +34mV to -45 mV .Following oral administration ,a significantly higher concentration of paclitaxel was observed in the systemic circulation when administered in the NE relative to control aqueous solution.The results of this study suggest that NE are promising novel formulations that can enhance the oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs.(28)
Co Q10 (CoQ10) also known as ubiquinone,is used for energy production within cells and act as antioxidant .Since CoQ10 is highly lipophillic ,the topical and oral bioavailbility is very low.Latest technical development reveal that encapsulation of CoQ10 in NEs result in significantly enhanced bioavailability.The application of CoQ10 has been further improved by the development of novel .CoQ10 double NE containing tocopherol and CoQ10 in individual nanodroplet,In addition ,the CoQ10 concentration in these NE could be increased by the development of supersaturated CoQ10 NE(29)
8.Nanoemulsion as a vehicle for transdermal delivery
From in vitro and invivo data it was concluded that the developed NE has great potential for transdermal delivery of aceclofenac(30) The NEs of system containing Ketoprofen evidenced a higher degree of stability .Ketoprofen loaded NEs enhanced the invitro permeation rate through mouse skins as compared to control(31) The study was developed to evaluate the potential of NEs for increasing the soubilty and invitro transdermal delivery of carvedilol.The prepared NE were subjected to physical stability tests.Transdermal penetration of carvedilol through rat abdominal skin was determined with Keshary –Chien diffusion cell.Significant increase(p≤0.05) in the steady state flux (jss) and permeability coefficient (Kp) was observed in NE formulations as compared to control drug loaded neat components .The irritation study suggest that optimized NE was nonirritant transdermal delivery system(32)
Celecoxib ,a selective COX-2 inhibitor ,has been recommended orally for the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis.Long term oral admininistration of celecoxib produces serious gastrointestinal side effects .Skin permeation mechanism of celecoxib from NE was evaluated by FTIR spectral analysis,DSC thermogram ,activation energy measurement and histopathological examination.The optimized NE was subjected to pharmacokinetic (bioavailability) studies on Wistar male rats.Photomicrograph of a skin sample showed the disruption of lipid bilayers as distinct voids and empty spaces were visible in epidermal region.The absorption of celecoxib through transdermally applied NE and NE get resulted in3.30 and 2.97 fold increase in bioavailability as compared to oral capsule formulation.Results of skin permeation mechanism and pharmacokinetic studies indicated that the NEs can be successfully used as potential vehicles for enhancement of skin permeation and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs (33)
9.Self –nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems(SNEDDS) for oral deliveryof protein drugs:Formulation development ,in vitro transport study and in vivo oral absorption study(34-36) An experimental design was adopted to develop SNEDDS for noninvasive delivery of protein drugs.Fluoroscent –labelled beta –lactamase(FITC-BLM),a model protein was loaded into SNEDDS through solid dispersion technique .The experimental design provided 720 compositions of different oil,surfactant and co surfactant in different ratios ,of which 33 SNEDDs prototypes were obtained.A SNEDDS was developed to load FITC-BLM into oilphase that can spontaneously form O/W NE upon the addition of water .Fluorescently labeled BLM(FITC-BLM) a model protein ,formulated into 16 SNEDDS preparations through a solid dispersion technique were studied for transport across monolayer .All the SNEDDS NEs result in higher transport rate than free solution.SNEDDs significantly increased the transport of FITC –BLM across MDCK monolayer in vitro.SNEDDS may be a potential effective delivery system for non invasive protein drug delivery .The oral absorption of BLM in ratswhen delivered by such a SNEDD was investigated and showed significantly enhance in oral bioavailability of BLM,so the SNEDDS has a great potential for oral delivery.
Solid self nanoemulsifying delivery systems as a platform technology for formulation of poorly soluble drugs .New drug discovery programs produce molecules with poor physicochemical properties making delivery of these molecules possible at right proportion into the body, a big challenge to the formulation scientist. The various options available to overcome the hurdle include solvent precipitation, micronisation/nanosization using high pressure homogenization jet milling, salt formation, use of microspheres, solid dispersions, cogrinding, complexation and many others. Self nanoemulsifying systems(SNES) form one of the most popular and commercially viable approaches for delivery of poorly soluble drugs exhibiting dissolution rate limited absorption,especially those belong to BCS (Biopharmaceutics Classification Systems II/IV.SNES are essentially an isotropic blend of oils,surfactants and or cosolvents that emulsify spontaneously to produce oil in water NE when introduced into aqueous phase under gentle agitation .Conventional SNES consist of liquid form filled in hard or soft gelatin capsules ,which are least preferred due to leaching and leakage phenomenon ,interaction with capsule shell components ,handling difficulties ,machinability and stability problems .Solidification of these liquid systems to yield solid self nanoemulsifying systems (SSNES) offer a possible solution to the mention complications,and that is why these systems have attracted wide attention (37)
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
Patented Nanoemulsions:
Some important patents related to NEs (38-40)
1.Patent name :Method of Preventing and Treating Microbial infections. Assignee:NanoBio Corporation (US) .US Patent numbers :6,506 ,803
2.Patent name :NE based on phosphoric acid esters and its uses in the cosmetics,dermatological,pharmaceutical and or ophthalmological fields .Assignee :L’Oreal (Paris,FR) US Patent number :6,274,150
3. Patent name :NE based on Ethylene oxide and propylene oxide block copolymers and its use in the cosmetics ,dermatological and or ophthalmological fields . Assignee :L’Oreal (Paris,FR) US Patent number :6,464,990
4.NE of 5-aminolevulinic acid (6,559,183).Assignee :ASAT AG Applied Science and Technology (Zug ,CH),PCT number :PCT/EP99/08711
5.NEs of poorly soluble pharmaceutical active ingredients and methods of making the same .Patent no:WO/2007/103294
6. Nanoemulsion of the oil water type, useful as an ophthalmic vehicle and process for the preparation there of : Assignee Laboratorios Cusi, S.A. (Barcelona, ES),Patent no 08/509746
Commercial Nanoemulsion (sub-micron emulsion) formulations(41)
|
Drug therapeutic |
Brand |
Manufacturer |
Indication |
|
Propofol |
Diprivan |
Astra Zaneca |
Anasthetic |
|
Dexamethasone |
Limethason |
Mitsubishi Pharmaceutical,Japan |
Steroid |
|
PalmitateAlprostadil |
Liple |
MitsubishiPharmaceutical,Japan |
Vasodilator platlet inhibitor |
|
Flurbiprofen axtil |
Ropion |
Kaken Pharmaceuticals,Japan |
NSAID |
|
Vitamin A,D, E and K |
Vitalipid |
Fresenius Kabi Europe |
Parentral nutrition |
Future Perspectives: Nanoemulsion since its emergence proved to be versatile and useful novel drug delivery system .Applicable for almost all routes of administration.Future perspectives of Nanoemulsion are very promising in different fields of therapeutics whether it is against development of vaccines or formulation against Cancer along with the its increasing application in development of cosmetics for hair or skin .Companies like Loreal are spending much on such innovative projects.
References
1. Vyas S.P,Khar R.K ,Basis of targeted drug delivery,Targeted &Controlled Drug delivery Novel Carrier Systems, cbs publishers,page no 39-41
2. Otilia M.Koo, Israel Rubinstein, MD Hayat Onyuksel,Role of nanotechnology in targeted drug delivery and imaging:a concise review, Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine (2005) 1 , 193– 212
(3) 46. Lee VHL, Robinson JR. Review: Topical ocular drug delivery: Recent developments and future challenges. J Ocul Pharmacol1986., 2:67-108,
4. Ljungberg S,Jeppson R, Acta Pharm . Suec .1970, 7,435 -440
5. Jeppsson R, Acta Pharm .Suec 1972,9,199-206
6. Levy M,Benita S, J Parenteral . Sci .Technol.1991,45,101-107
7. Shinoda K, Saito H,The effect of temperature on the phase equilbria and the the type of dispersion of the ternary system composed of water,Cyclohexane and nonionic surfactant ,J. Colloid Interface Sci,1968,(26):70-74
8. Walstra P,Emulsion stability ,P.Becher(Ed). Encyclopedia of emulsion technology ,Marcell Dekk,Newyork 1996,p.1-62
9. Floury J,Desrumaux A,Legrand J,Effect of high pressure homogenization on methylcellulose as food emulsifier,J. Food Engg, 2003;(58):227-238
10. Tamilvanan S, Benita S. The potential of lipid emulsion for ocular delivery of lipophilic drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 58:357-368, 2004.
11. Cohen T, Sauvageon-Martre H, Brossard D, D’Hermies F, Bardin C, Chast F, Chaumeil JC. Amphotericin B eye drops as a lipidic emulsion. Int J Pharm, 137:249-254, 1996.
12. Lance MR, Washington C, Davis SS. Structure and toxicity of amphotericin B/triglyceride emulsion formulations. J Antimicrob Chemother, 36:119-128, 1995.
13. S.S. Davis, C. Washington, Drug emulsion, European Patent 0,296, 845 A1 (1988)
14. Buttle S, Schmidt RH, Müller RH. Production of amphotericin B emulsions based on SolEmuls te c h no lo g y , F ou r th World Me e t in g on P h a rm a c e u t i c s , B i o p h a rm a c e u t i c s a n d Pharmaceutical Technology, Florence, April 8-11, 2002, pp.1535-1536
15. Müller RH, Schmidt S. SolEmuls technology for i.v. emulsions of poorly soluble drugs: amphotericin B,Fourth World Meeting on Pharamceutics,Biopharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology, Florence, April 8-11, 2002, pp. 1451-1452
16.Groves M J, In Modern Methods of Particle Size Analysis ;Barth ,H G,Ed ; Wiley :Newyork 1984, pp 43-91
17.Hunter R, Zeta Potential in Colloid Science ; Academic Press :London ,1981 , pg 59-124
18. Sharmaa P, Srinivas G, Formulation and pharmacokinetics of lipid nanoparticles of a chemically sensitive nitrogen mustard derivative: Chlorambucil, International Journal of Pharmaceutics Volume 367, Issues 1-2, 9 February 2009, Pages 187-194
19.Levy M, Benita S, Int J Pharm ,1990 .66,29-37
20. Available from :http://www.happi.com/.
21. Available from :http://www.nanobio .com
22. Available from :http// www.use medicine .com/
23. Available from :http// www.echoedvoices .org/.
24. Available from :http://www.ewire.com/.
25. Available from :http://www.infectioncontroltoday.com/.
26. Available from ;http://www.mib-bio.com/
27.Ichikawa H,Watnabe T,Tokumitsu H,Fukumori Y,Formulation consideration of gadolinium lipid nanoemulsion for intravenous delivery to tumours in neutron capture therapy.Current Drug Delivery 2007;4:131-140
28. Khandavilli S,Panchagnula R,Nanoemulsions as versatile formulations for Paclitaxel delivery :Peroral and dermal delivery studies in rats,J Invest Dermatol 2007;127:154-62
29. Zulli F,Belser E,Preparation and properties of Coenzyme Q 10 Nanoemulsions,Cosmetic Science Technology ,Available from http://www.mib-bio.com
30. Shakeel F,Baboota S,Shafiq S,Nanoemulsions as vehicles for transdemal delivery of aceclofenac,AAPS PharmSci Tech 2007;8:E104 Available from:http://www.aapspharmscitech.org
31.Kim B,Won M,In vitro permeation studies of nanoemulsion containing ketoprofen as a model drug, Drug Delivery 2008;15:465-9
32. .Dixit N,Kohli K,Baboota S,Nanoemulsion system for transdermal delivery of poorly soluble cardiovascular drugs,J Pharm Sci Technol 2008;62;46-55
33.Shakeel F,Baboota S,Skin permeation mechanism and bioavailability enhancement of celecoxib from transdermally applied nanoemulsion,J Nanobiotechnol 2008;6:8
34. Rao SV,Shao J,Self nanoemulsifying drug delivery system(SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs 1.Formulation development .Int J Pharm 2008;362:2-9
35. .Rao SV,Agarwal P ,Shao J,Self nanoemulsifying drug delivery system(SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs 2.In vitro transport study .Int J Pharm 2008;362:10-5
36. Rao SV,Yajurvedi K,Shao J,Self nanoemulsifying drug delivery system(SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs 3,In vivo oral absorption study,Int J Pharm;362:16-9
37.Bansal T,Mustafa G,Solid self nanoemulsifying delivery systems as a platform technology for formulation of poorly soluble drugs.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 2008;25:63-116
38.Available from :http://www.patentstorm.us/.(last updated on 2007 Jul 29.)
39.Available from :http://www.wipo.org/.(last updated on 2007 July 30)
40. Available from :http://www.uspto.com/.(last updated on 2009 Jul 30)
41.Shah P,Balodia D, Shelat P,Nanoemulsion:A Pharmaceutical Review,Sys Rev Pharm ,2010,1(1),24
42. Sharma N, Bansal M et al., Nanoemulsion :A new concept of delivery system, Chronicles of Young Scientists, 2010 ;2:2-6
43.Tharwat F,Colloids in cosmetics and personal care,2003;(4):36-39
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org









