{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
 ABOUT AUTHORS
ABOUT AUTHORS
*K. Vinod1, B, Dr. N. Surendra Reddy1,Dr. K. Chandra Sekhar2, Dr. D. Ranganayakulu1
1Department of Pharmacy Practice,
Sri Padmavathi School of Pharmacy,
Tiruchanoor, Tirupati, India.
2 Department of General Medicine,
Sri Venkateswara Medical College,
Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India .
*drvinodkatiboina@gmail.com
ABSTRACT:
A 25 years married man was admitted on to emergency acute medical care unit. He had fallen ill after an afternoon meal from 4 days ago which consisted of rice and 3 tubers identified as gloriosa superb. About 3hrs after the ingestion, he developed abdominal pain, vomiting (15-20 episodes), and watery diarrhoea 15-20 episodes. He developed bleeding gums, yellowish discoloration, hematemesis 30-50 ml, 24episodes, haematuria, decreased urine output along with continued diarrhoea and vomiting. He was treated with iv fluids crystalloids and colloids titrated, 1 fresh frozen plasma (FFP), 1fresh platelet transfusion, inj. vit K, supportive treatment with close monitoring of vitals. Therapy as planned for ventilator support, however had ever had bleeding per rectum and hematemesis with aspiration, even with best available resuscitative efforts he succumbed to his illness and declared clinically dead after 36hrs of admission, his cause of death was given as multiorgan dysfunction see to gloriosa superb. Though poisoning with gloriosasuperba is rare it is mostly fatal and requires aggressive and prompt treatment is mandatory from saving the patient from death.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2515
|
PharmaTutor (Print-ISSN: 2394 - 6679; e-ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 5, Issue 8 Received On: 30/04/2017; Accepted On: 06/05/2017; Published On: 01/08/2017 How to cite this article: Singh B, Jalwal P, Ruhil VK, Minocha N;Appearing in B.Pharmacy Examination (Sessional/ Semester End/ Year End Final Examination): An Art or Science?; PharmaTutor; 2017; 5(8);12-14 |
INTRODUCTION:
Gloriosa superb is a climbing hedge plant growing all over India mostly in southern part, also known by name glory lily, flame lily, pulasapadupappugadda, gharbainatin in Sanskrit meaning which cause abortion.
A medicinal plant cultivated for colchicines used for various ailments like Joint pains.Colie, antifertility, abortifacient, leprosy, anthelminthic, gonorrhoea to name to afew.

Zimbabwe has declared gloriosa as national flower and tamilnadu as state flower. Fresh tubers are more poisonous contains 6mg of colchicines per 10grams of tuber,also have other alkaloids gloriosine and resins.
Primary actions of gloriosa are:
1. Blocks mitosis at metaphase in dividing cells especially GI tract,bone marrow.
2. Reduction of neutrophils migration,phagocytosis,adhesion and chemo taxi
3. Negative inotropic effects,decreased calcium myofilaments sensitivity decreased sarcoplasmic reticular on cardiac muscle.
4. Neurotoxicity by decreased function axonal transport and vesicle release
Clinical features can be divided into
|
Stage 1 0-24 hrs |
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdomina lpain, anorexia, periphera lleucocytosis, electrolyte imbalance |
|---|---|
|
Stage 2 24hrs-7d |
Pancytopenia, coagulopathy, cardiotoxicity, ARDS, sepsis, Rhabdomyolysis, myopathy-proximal muscle weakness, neuropathy-ascending paralysis, bone marrow hypoplasis, mental state changes. |
|
Stage 3 7d |
Reversible alopecia, reversible azoospermia, peripheral neuropathy, skin changes |
Treatment includes
Gastic lavage with activated charcoal,large volume of crystalloids and colloids, FFP,platelet ,blood transfusions,inotropic support for cardiogenics and circulatory shock,treatment of electrolyte imbalance,GM-CSF for pancytopenia,mechanical ventilation for ADRS with O2 inhalation, antibiotics for sepsis,dialysis for renal failure.since alopecia and azoospermis are reversible wait and watch therapy is used.reports of colchicines specific fab are published but availablility,success rate are to be measured.
Case report:
A 25 years married man was admitted on to emergency acute medical care unit of S.V.R.R.G.H,Tirupati,Andra Pradesh. He had fallen ill after an afternoon meal from 4 days ago which consisted of rice and 3tubers identified as gloriosa superb. The colchicine content of the fresh tubers was 0.3%. Total amount consumed was of 300gm of tuber with colchicines 180 mg.
About 3hrs after the ingestion, he developed abdominal pain, vomiting (15-20 episodes), and waterydiarrhoea 15-20 episodes. He was treated at a local hospital for 4 days and referred to our hospital. He developed bleeding gums, yellowish discoloration, hematemesis 30-50 ml,24episodes, haematuria,decreased urine output along with continued diarrhoea and vomiting.
On examination he was conscious,restless, dehydrated with toxic took,pulse rate 108, moderate volume in sinus rhythm, B.P 100/70 mmofHg,R.R of 18/m,general examination showed pallor, icterus,mild pedal oedema, bleeding gums, non palpablepurpura, echymotic patches on both upperlimbs, subconjuctival hemorrhage. Lungs showed fine inspiratory crepitations, tachycardia. Abdominal examination revealed diffuse tenderness, mild distension, hepatomegaly with respiratory seizures examination, 3cms below ICM, soft .tender with sluggish bowel sounds.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Investigations revealed
|
Hb |
8.4 gms |
|
Dc |
74N,21L,05E |
|
BT |
3.40 |
|
Platelets |
26000 |
|
PT/INR |
1.4 |
|
Bilurubin |
1.0 |
|
Direct |
0.3 |
|
SGOT |
235 |
|
SGPT |
230 |
|
ALP |
64 |
|
Proteins |
6.4 |
|
Alb |
2.7 |
|
Urea |
32 |
|
Creatinine |
0.9 |
|
Na |
124 |
|
K |
4.8 |
|
Cl |
99.8 |
|
Urec acid |
4.7 |
|
Usg abdomen |
Minimal free fluid include sac distended loops s/o particalobsrtuction |
|
ECG |
ST elevation V1-6,T interval 2,3,av F f/o myocarditis |
|
C/X RAY |
Prominent broncho vascular marking No pulmonary edema |
|
Urine microscopy |
Plenty of RBC/hpf |
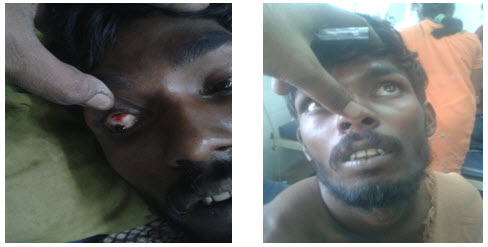
He was treated with iv fluids crystalloids and colloids titrated,1 fresh frozen plasma (FFP),1fresh platelet transfusion,inj.vit k, supportive treatment with close monitoring of vitals.next day he developed heavy about of hemetemisis 200ml fresh blood,anuria past 12 hours,vitals showed PR 124/min,B.P 80/60mmof Hg,tachypnoea, spo2 of 74% with 6lts of O2,was put on inotrope support nor adrenaline and dopamine titrated to his vitals.1FFP was transfused along with 1packet of blood. Investigations showed following
|
platelets |
20000c/cumm |
|
bilurubin |
2.0mg |
|
indirect |
1.2 |
|
creatinine |
1.4mgs |
Therapy as planned for ventilator support, however had ever had bleeding per rectum and hematemesis with aspiration, even with best available resuscitative efforts he succumbed to his illness and declared clinically dead after 36hrs of admission, his cause of death was given as multiorgan dysfunction see to gloriosa superb.
Conclusion: Though poisoning with gloriosa superb is rare it is mostly fatal and require aggressive and prompt treatment is mandatory from saving the patient from death
REFERENCES:
1. Bunyapraphatsara and van Valkenburg, (1999)
2. ,Bagavan A, Kamaraj C, Elango G, AbduzZahir A, Abdul RA (2009). Adulticidal and larvicidal efficacy of some medicinal plant extracts against tick, fluke and mosquitoes. Vet. Parasitol., 166: 286-292
3. Bhargava N (1983). Ethnobotanical studies of the tribes of Andamanand Nicobar Islands, India. I. Onge. Econ. Bot., 37(1): 110-119.
4. Bunyapraphatsara N, Van VJLCH (1999). Gloriosa superba L. In: de Padua LS, Bunyapraphatsara N, Lemmens RHMJ (eds). Plant Resources of South-East Asia No. 12(1) Medicinal and poisonous plants 1. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, Netherlands. pp. 289-292.
5. Burkill HM (1995). The useful plants of West Tropical Africa. Volume 3. Families J-L. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, United Kingdom.
6. Chopda MZ, Mahajan RT (2009). Wound healing plants of JalgaonDistrict of Maharashtra State, India. Ethnobot. Leafl., 13: 1-32.
7. Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC (1956). Glossary of Indian medicinal plants. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Dehli
8. Dounias E (2006). Gloriosa superba L. http://database.prota.org/search.htm. (accessed 15 June 2010).
9. Ghani A (1998). Medicinal plants of Bangladesh: Chemical constituents and uses. Dhaka, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh
10. Jain A, Katewa SS, Chaudhary BL, Praveen G (2004). Folk herbal medicines used in birth control and sexual diseases by tribals of southern Rajasthan, India. J. Ethnopharmacol., 90(1): 171-177
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









