 About Authors:
About Authors:
Kapil Sharma1*, Subhash Gupta 2, Yogesh Sharma1
1 Yaresun Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.Jaipur - 302006, Rajasthan, India.
2 Oasis test house ltd.jaipur-302006,
Rajasthan, India.
METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND ITS VALIDATION FOR ESTIMATION OF TORSEMIDE IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY RP-HPLC AND UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRY AND COMPARISON OF TWO DEVELOPED METHODS BY USING t-TEST
ABSTRACT
One HPLC and one UV spectrophotometric method have been developed for the determination of torsemide (TRS) in tablet dosage form. The first method is based on determinetion of TRS in tablet dosage form by RP- HPLC method. Chromatgraphy was carried out on a nucleosil C-18,250 x 4.6 mm column using a mixture of phosphate buffer and methanol (50:50 v/v) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.3 ml/min. Run time was 15 min. Detection was done at 288 nm and retention time of the drug was 7.05 min. This method produced linear responses in the concentration range 60-140 µg/ml of torsemide. The accuracy of the method was assessed by recovery studies and was found to be 99.90± 0.41 for torsemide. The second method is based on the estimation of torsemide in tablet dosage form by UV spectrophotometry using 50% v/v methanol in distilled water. Beer’s law obeyed over the concentration range 2-26 µg/ml at 288 nm with apparent molar absorptivity of 1.26 x 104. Both developed methods were found to be applicable for routine analysis of drug in tablet dosage form. The result of the analysis were validated statistically.The results were compared obtained from UV spectrophotometry and HPLC.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1158
INTRODUCTION
Torsemide is chemically 3-isopropyl carbamyl sulfonamide-4-(31-methyl phenyl) amino pyridine and used as diuretic. It inhibits Na+, K+-Cl- symport across the thick ascending limb of loop of Henley1. It is official in USP2. Literature survey revealed that one GC-MS3 and three HPLC4-6 methods have been reported for estimation of torsmide. Hence the objective of work is to develop RP-HPLC and spectrophotometric method for estimation of torsemide (TR) in tablet dosage form with good accuracy,simplicity,precision and economy. The results of analysis using the spectrophotometric and RP-HPLC method for quantitative determination was found to be satisfactory such that the developed method can be used for routine analysis of drug from tablet dosage form.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Instrument, reagents and chemicals
A shimadzu HPLC containing LC-10AT pump, variable wavelength programmable UV/Vis detector SPD-10AVP was used for the analysis. The method was carried out on a Nucleosil C-18 (250 x 4.6 MM) column as stationary phase and phosphate buffer with methanol (50:50 v/v) as mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.3 ml/min. A rheodyne injector with a 20 µl loop was used for the injection of samples. A dual-beam shimadzu UV/Vis spectrophotometer 1601 was used. Gift sample of TRS was procured from Micro labs ltd,bangalore. Tablets of 10 mg strength of TRS were procured from local pharmacy of two brand (Retorlix-10 and Torsinex).
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
HPLC METHOD
Preparation of mobile phase
Monobasic potassium phosphate was weighed (2.7 gm) and dissolved in 1000 ml HPLC grade water. pH of solution was adjusted with orthophosphoric acid and triethylamine to 3.5 ± 0.1 . This solution was mixed with methanol in the ratio of 50:50 .
Preparation of stock solution of torsemide
Torsemide was weighed (100 mg) accurately and transferred to 100 ml volumetric flask. About 90 ml of HPLC grade methanol was added and sonicated to dissolve. The volume was made up to the mark with HPLC grade methanol. The final dilution contained about 1000μg/ml of torsemide.
Preparation of Standard solution of torsemide
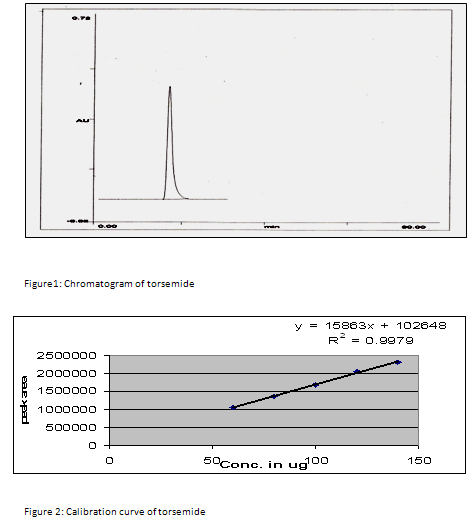
Standard solution of containing 100 µg/ml was prepared by dissolving 5 ml TRS stock solution in 50 ml mobile phase. Standard solution was injected into the HPLC system. The chromatogram was shown in figure 1.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Linearity and accuracy
Linearity and accuracy in the concentration range of 60-140 µg/ml were examined employing intraday and interday studies for the determination of TRS. The results for intraday and interday experiments with a good correlation were obtained and evaluated statistically as demonstrated in table 1 and 2. Calibration curve is shown in figure 2.
Table 1: Result of Recovery study of Torsemide (HPLC Method)
|
S.No. |
Drug |
Conc. before spiking (mg/ml) |
Reference Std. added (mg/ml) |
Conc. after spiking (mg/ml) |
% Recovery |
Mean % Recovery |
|
1 |
Torsemide |
20 |
40 |
59.68 |
99.46 |
99.90 ± 0.41 |
|
20 |
60 |
79.98 |
99.97 |
|||
|
20 |
80 |
100.28 |
100.28 |
Table 2: Summary of Validation Parameters (HPLC Method)
|
PARAMETER |
OBSERVATION |
|
Specificity |
No interference was found w.r.t. excipients |
|
Linearity (Correlation coefficient r2) |
0.9978 |
|
Accuracy (% Recovery) |
99.90% |
|
Precision RSD |
|
|
Repeatability (n= 6) |
0.540 |
|
Intra-day (n=3) |
0.348 |
|
Inter-day (three days) |
0.116 |
|
Robustness Overall RSD |
|
|
Change in pH |
|
|
· pH 3.3 |
0.98 |
|
· pH 3.7 |
0.81 |
|
Change in temperature |
|
|
· Temp 25 0C |
0.31 |
|
· Temp 35 0C |
0.26 |
|
Change in flow rate |
|
|
· 1.2ml/min |
0.77 |
|
· 1.4ml/min |
0.10 |
System Suitability Parameter
System suitability testing is an integral part of many analytical procedures. The tests are based on the concept that the equipment, electronics, analytical operations and samples to be analyzed constitute an integral system that can be evaluated as such.Results are shown in table 3.
Table 3: Results of System Suitability Parameter (HPLC Method)
|
S.No. |
Parameter |
Limit |
Result |
|
1 |
Resolution |
Rs >2 |
3.7(with internal standard frusemide) |
|
2 |
Injection precision |
RSD <1% for n³5 |
RSD=0.540% n=6 |
|
3 |
Tailing factor |
T £2 |
1.3 |
|
4 |
Theoretical plate |
N >2000 |
2303 |
|
5 |
Retention time |
|
7.05 |
Application of proposed procedure for the determination of Torsemide in tablet dosage form
Twenty tablets were taken, and accurately weighed. The tablets were crushed to a fine powder. The powder sample equivalent to 10 mg of torsemide was transferred to a 100 ml volumetric flask and about 80 ml of mobile phase was added and sonicated to dissolve. The volume was made up to the mark with mobile phase. The solution was filtered through a membrane filt
er (0.22mm) and sonicated to degas. 10 ml of this solution was diluted to 100 ml with mobile phase. The solution prepared was injected in five times into the HPLC system and the observations were recorded. A duplicate injection of the standard solution was also injected into the HPLC system and the chromatograms were recorded.
UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRY METHOD
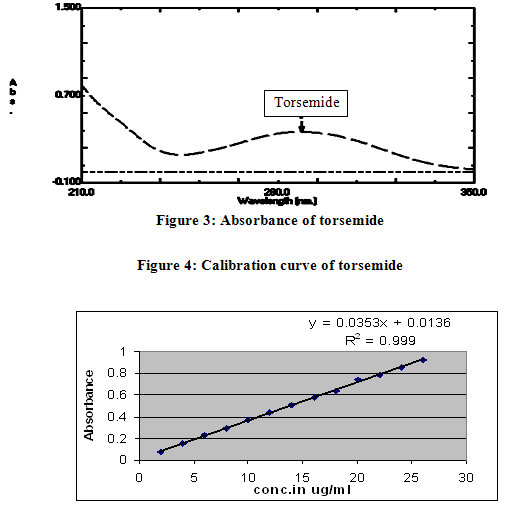
Preparation of Standard solution of torsemideStandard solution of containing 10 µg/ml was prepared by dissolving 1 ml torsemide stock solution in 100 ml 50 % v/v methanol in distilled water. Standard solution was analyzed by UV-spectrophotometer. Maximum absorbance for torsemide was found to be at 288 nm. The spectrum was shown in figure 3.
Linearity and accuracy
Linearity and accuracy in the concentration range of 1-26 µg/ml were examined employing intraday and interday studies for the determination of TRS. The results for intraday and interday experiments with a good correlation were obtained and evaluated statistically as demonstrated in table 4 and 5. Calibration curve is shown in figure 4.
Table 4: Result of Recovery study of Torsemide (UV-Spectrophotometric Method)
|
S.No. |
Drug |
Conc. before spiking (mg/ml) |
Reference Std. added (mg/ml) |
Conc. after spiking (mg/ml) |
percent Recovery |
Mean % Recovery ± SD |
|
|
1 |
Retorlix-10 |
8.096 |
4.064 |
12.184 |
100.59 |
100.15 ± 0.461 |
|
|
8.096 |
6.096 |
14.172 |
99.67 |
||||
|
8.096 |
8.128 |
16.232 |
100.18 |
||||
|
2 |
Torsinex |
7.87 |
4.064 |
11.97 |
100.88 |
100.26 ± 0.768 |
|
|
7.87 |
6.096 |
13.93 |
99.40 |
||||
|
7.87 |
8.128 |
16.12 |
101.50 |
||||
|
RSD |
RETORLIX-10 |
0.460 |
|
||||
|
TORSINEX |
0.766 |
|
|||||
Table 5: Summary of Validation Parameters (UV-Spectrophotometric Method)
|
PARAMETER |
OBSERVATION |
|
Torsemide |
|
|
Specificity |
No interference was found w.r.t. excipients |
|
Linearity (Correlation coefficient r2) |
0.999 |
|
Accuracy (% Recovery) |
100.15 (Retorlix-10) 100.26 (Torsinex) |
|
Precision RSD Repeatability (n= 6) Intra-day (n=3) Inter-day (days=3) |
0.242 1.314 1.070 |
Application of proposed procedure for the determination of Torsemide in tablet dosage formTwenty tablets were taken, and accurately weighed. The tablets were crushed to a fine powder. The powder sample equivalent to 10 mg of Torsemide was transferred to a 100 ml volumetric flask and about 80 ml of 50%v/v aqueous methanol was added and sonicated to dissolve. The volume was made up to the mark with 50%v/v aqueous methanol. This solution was filtered through whatman filter paper 42. This solution was diluted (10 ml) to 100 ml with 50%v/v aqueous methanol. The solutions were analyzed by UV-Spectrophotometer. The samples were analyzed in five times. 50 % v/v aqueous methanol was used as blank.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
One RP-HPLC method and one UV spectrophotometry method have been developed for the estimation of torsemide in tablet dosage form. Different chromatographic conditions were used to develop the HPLC method. Elution was carried out on Nucleosil C-18,250 x 4.6 mm with a mobile phase consisting of Methanol: phosphate buffer (50:50 v/v) at pH 3.5±0.1,the flow rate was 1.3 ml/min at 288 nm. The retention time for torsemide was found 7.05 minute. Run time was found to be 15 minutes. Solvent used was 50 % v/v methanol in distilled water in UV spectrophotometry method. Measurement was done at 288 nm. Beer’s law was obeyed in the concentration range 2-26 µg/ml .Both developed validated methods are simple, rapid, precise and accurate can be used for routine analysis for the estimation of torsemide in tablet dosage form. The comparison of both developed (RP-HPLC and UV/Vis spectrophotometer) method was shown in table 6,7 and 8. Comparison reveals that the RP-HPLC method is much linear, accurate and precise than the spectrophotometric method. But the spectrophotometric method has linearity, accuracy, and precision under acceptable range of limits. So both the methods can be used for industrial applications. In table 7 and 8 tcrit is greater than tstat indicating that there is nosignificant difference between the recoveries of TORSEMIDE by the two methods. Variable 1 is method by RP-HPLC and variable 2 is method by Spectrophotometer.
Table 6: Comparison of the two developed methods
|
PARAMETER |
RP-HPLC OBSERVATION |
UV- SPECTROSCOPIC OBSERVATION |
||
|
Linearity (Correlation coeff.) |
0.9979 |
0.999 |
||
|
Accuracy (Percent recovery) |
99.90 Retorlix-10 |
99.89Torsinex |
100.15Retorlix-10 |
100.26 Torsinex |
|
Precision RSD Repeatability (n= 6) Intra-day (n=3) Inter-day (days=3) |
0.540 0.348 0.116 |
0.242 1.314 1.070 |
||
Table 7: T-test applied for Torsemide by two methods for recovery(Retorlix-10)
|
Parameters |
Variable 1 |
Variable 2 |
|
Mean |
99.90 |
100.15 |
|
Variance |
0.17 |
0.21 |
|
Observations |
3.00 |
3.00 |
|
Pooled Variance |
0.19 |
|
|
Hypothesized Mean Difference |
0.00 |
|
|
Df |
4.00 |
|
|
t Stat |
0.69 |
|
|
P(T<=t) one-tail |
0.266 |
|
|
t Critical one-tail |
2.13 |
|
|
P(T<=t) two-tail |
0.533 |
|
|
t Critical two-tail |
2.78 |
Table 8: T-test applied for Torsemide by two methods for recovery (Torsinex)
|
Parameters |
Variable 1 |
Variable 2 |
|
Mean |
99.89 |
100.26 |
|
Variance |
0.16 |
0.59 |
|
Observations |
3.00 |
3.00 |
|
Pooled Variance |
0.19 |
|
|
Hypothesized Mean Difference |
0.00 |
|
|
Df |
4.00 |
|
|
t Stat |
0.49 |
|
|
P(T<=t) one-tail |
0.217 |
|
|
t Critical one-tail |
2.13 |
|
|
P(T<=t) two-tail |
0.434 |
|
|
t Critical two-tail |
2.78 |
REFERENCES
1. Tripathi, K.D.Essential Medical Pharmacology, 5th ed., Jaypee Brothers, New Delhi,2004;P.525.
2. United states pharmacopoeia, 28th ed, Washington, Published by the board of trustees, 2005:Vol-II: 1953.
3. Barroso MB, Meiring HD, jong A.de, Alonso RM, Jimenez RM. Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of the loop diuretic torsemide in human urine. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 1997;690:105-13.
4. Engelhardt S, Meineke I, Brockmoller J. Improved solid- phase extraction and HPLC measurement of torsemide and its important metabolites. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed life Sci 2006;831:31-5
5. March C, Farthing D, Well B, Besenfelder E, Karnes HT. Solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatographiy of torsemide and metabolites from plasma and urine. J Pharm Sci 1990; 79:453-7.
6. Barroso MB, Alonso RM, Jimenez RM. Simultaneous determination of torsemide and its major metabolite M5 in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr Sci 2001; 39; 491-6.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









