{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
ABOUT AUTHORS
D.Visagaperumal*, Justin Ebuka Ezekwem, Hemaprasad Munji, Vineeth Chandy
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry,
T. John College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
*vishak_dr@yahoo.co.in
ABSTRACT
The review article is focused on studies of Isatin-based Schciff Bases and their biological and pharmacological activities. Isatin-based Schiff base are generally synthesized by condensation of the keto group of Isatin with different aromatic primary amines carrying imine or azomethine (–C=N–) functional group. Isatin Schciff Base possesses numerous biological properties like antitumor, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antiviral, anti HIV, antioxidant, CNS depressant activities
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2585
|
PharmaTutor (Print-ISSN: 2394 - 6679; e-ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 6, Issue 5 Received On: 02/04/2018; Accepted On: 04/04/2018; Published On: 01/05/2018 How to cite this article: Visagaperumal D, Ezekwem JE, Munji H, Chandy V; Isatin Schiff Base -An Overview; PharmaTutor; 2018; 6(5); 38-47; http://dx.doi.org/10.29161/PT.v6.i5.2018.38 |
INTRODUCTION
Isatin or 1H-indole-2, 3-dione (1) is an indole derivative. The compound was first obtained by Erdman and Laurent in 1841 (Otto Linne Erdmann, 1840) . Isatin is an important class of heterocyclic compounds. Recently, heterocyclic compounds analogues and their derivatives have attracted strong interest in medicinal chemistry due to their biological and pharmacological properties. (Manju P et. al., 2011). The small and simple isatin nucleus possesses numerous biological properties like antimicrobial (Singh UK et. al., 2010), anti HIV (Pandeya SN et. al., 1999), antitubercular (Ozlen G et. al., 2008), antitumor (Hoyun L et. al., 2009), anti-inflammatory (Gummadi SB et. al., 2010), antioxidant (Prakash CR et. al., 2011), antiviral (Shibinskya MO et. al., 2010), anticonvulsant (Prince PS et. al., 2009) and CNS depressant activities (Zapata-Sudo G et. al., 1986).
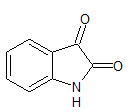
1
In nature, isatin is found in plants of the genus Isatis12, in Calanthe discolor (Yoshikawa M et. al., 1998), in Couroupita guianensis Aubl (Bergman J et. al., 1985), has also been found as a component of the secretion from the parotid gland of Bufo frogs (Wei L et. al., 1982) and in humans as it is a metabolic derivative of adrenaline (Ischia M et. al., 1988), ( Palumbo A et. al., 1989). Substituted isatins are also found in plants, for example the melosatin alkaloids (methox phenylpentyl isatins) obtained from the Caribbean tumorigenic plant Melochia tomentosa (Kapadia GJ et. al., 1980), ( Kapadia GJ et. al., 1977) as well as from fungi: 6-(3’-methylbuten-2’-yl)isatin was isolated from Streptomyces albus (Grafe U and Radics L, 1986) and 5-(3’-methylbuten-2’-yl)isatin from Chaetomium globosum (Breinholt J et. al., 1996). Isatin is one of the most promising new classes of heterocyclic molecules having many interesting activity profiles and well-tolerated in human (Yan Y et. al., 1992), (Joaquim FM et. al., 2001)
Synthesis of Isatin
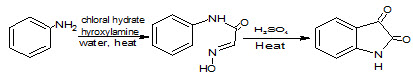
2
It may be prepared from cyclizing the condensation product of chloral hydrate, aniline and hydroxylamine in sulfuric acid (Marvel CS and Hiers GS, 1925), (Sandmeyer T, 1919). This reaction is called the Sandmeyer isonitrosoacetanilide isatin synthesis (2) and discovered by Traugott Sandmeyer in 1919. The method applies well to anilines with electron withdrawing substituents, such as fluoroaniline (Alam M et. al., 1989)
Schiff Bases
Schiff bases are the compounds carrying imine or azomethine (–C=N–) functional group. These are the condensation products of primary amines with carbonyl compounds and were first reported by Hugo Schiff (Schiff H, 1864), (Dhar DN and Taploo CL, 1982), (Sathe BS et. al., 2011) Schiff bases form an important class of the most widely used organic compounds and has a wide variety of applications in many fields including analytical, biological, and inorganic chemistry. Schiff bases have gained importance in medicinal and pharmaceutical fields due to a broad spectrum of biological activities like anti-inflammatory (Sondhi SM et. al., 2006), (Pandey A et. al., 2011), (Chandramouli C et. al., 2012), (Singh N et. al., 2006), analgesic (Chinnasamy RP et. al., 2010), (Mounika K et. al., 2010) antimicrobial (Venkatesh P, 2011) (Chaubey AK and Pandeya SN, 2012), anticonvulsant (Aboul-Fadl T et. al., 2003), antitubercular (Miri R et. al., 2013), anticancer (Ali SMM et. al., 2012), ( Wei D et. al., 2006), antioxidant (Avaji PG et. al., 2009), anthelmintic (Venugopala KN and Jayashree BS, 2003) and so forth. The nitrogen atom of azomethine may be involved in the formation of a hydrogen bond with the active centers of cell constituents and interferes in normal cell processes (Vashi K and Naik HB, 2004), (Li S et. al., 1996 ). Apart from biological activities, Schiff bases are also used as catalysts, intermediates in organic synthesis, dyes, pigments, polymer stabilizers and corrosion inhibitors (Chohan ZH et. al., 1997). Studies enlightened that metal complexes show greater biological activity than free organic compounds (Ershad S et. al., 2009). Augmentation of biological activity was reported by implementation of transition metals into Schiff bases (Tisato F et. al., 1994). Schiff bases played an influencing role in development of co-ordination chemistry and were involved as key point in the development of inorganic biochemistry and optical materials (Jarrahpour A et. al., 2007.) Schiff bases have been utilized as synthons in the preparation of a number of industrial and biologically active compounds like formazans, 4-thiazolidinines, benzoxazines, and so forth, via ring closure, cycloaddition and replacement reactions (Bhattacharya A et. al., 2003). Eg. Isatin Schiff base (3)
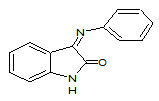
3
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES
Antimicrobial Activities:
U. K. Singh et. al., reported the synthesis of Schiff’s and N-Mannich bases of isatin and its derivatives with 4-amino-N-carbamimidoyl benzene sulfonamide (4) and was tested for antibacterial activity by MIC method on strains: S. aureus, B. pumulis, B. subtilis, E. coli, S. abony, K. pneumoniae. All compounds exhibited very significant and better antibacterial activity (Singh UK et. al., 2010).
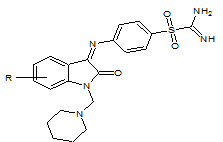
R = H, NO2, Cl, Br, CH3
4
Chhajed S.S et. al., reported the synthesis of schiff and mannich bases of isatin and its derivatives with quinoline (5). Investigation of antimicrobial activity of the compounds was made by the agar dilution method on strains: B. substilis, S. aureus, S. faecalis, E. Coli, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans A. niger. And the compounds are significantly active against bacteria and fungi (Chhajed SS and Padwal MS, 2010).
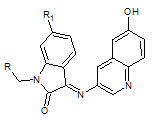
5
Aliasghar Jarrahpour et. al., reported the synthesis of some novel bis-schiff bases of isatin and their derivatives. These newly synthesized bis-schiff bases (6) were also tested for their antibacterial and antifungal activities by MIC method on strains: S. cerevisiae, S. aureus, C. albicans, E. coli (Aliasghar J et. al., 2007).
6
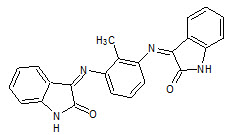
Ramachandran et. al., reported the synthesis of schiff and mannich bases of isatin derivatives (7) and was tested for antimicrobial activity by Cup-plate method on strains: like Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsilla aerogenes, Candida albicans. Most of the compounds shown greater antibacterial and antifungal activities when compared with the standard drugs (Ramachandran S, 2011).
7
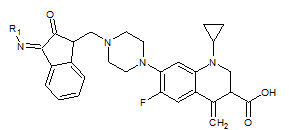
Seshaiah Krishnan Sridhar et. al., reported the synthesis of synthesis of hydrazones, schiff and mannich bases of isatin derivatives (8). The compounds were screened for antibacterial activity on strains: Bacillus subtillus, Staphylococcus aureous, E.coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of the active compounds were determined. 1- Diphenyl amino-methyl-3-(4-bromo phenylimino)-1, 3-dihydro-indol-3-one and 3-(4-bromo phenylimino)-5-nitro-1, 3-dihydroindol- 3-one were found to be the most active compounds of the series (Seshaiah KS et. al., 2001).
8
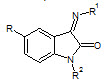
Sanjay Bari et. al., reported the synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new isatin derivatives (9) antimicrobial activity of compounds with 5-bromo substitution showed the most favorable antimicrobial activity (Sanjay B et. al., 2006).
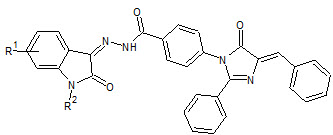
9
G. Sammaiah et. al., reported the synthesis of 2-aminobezoic acid (2-oxo-1, 2-dihydro-indol-3- ylidene)-hydrazides, as indole hydrazides have shown proven to be good antimicrobial agents. Some new series of indole hydrazides synthesized (10) few 2-amino benzoic acid (2-oxo-1, 2-dihydro-indol-3-ylidene)-hydrazides which showed good antimicrobial activity (Sammaiah G et. al., 2011).
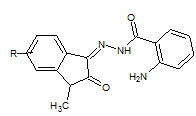
10
Antitubercular Activities
Sangamesh A. Patil et. al., reported the synthesis, biological evaluation Co (II), Ni (II),and Mn (II) metal complexes of novel isatin schiff base ligand (11) the complexes show activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv (Sangamesh AP, et. al., 2011)
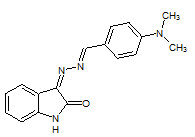
11
Sandeep K. Gupta et. al., reported the synthesis some thiobenzimidazolyl derivatives (12). Most of them reported good antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Sandeep KG and Shyam SP, 2011)
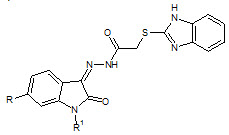
12
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Anticancer activities
Hoyun Lee et. al., reported the hybrid pharmacophore design and synthesis of isatin benzothiazole analogs (13). All examined compounds were quite effective on all the cancer cell lines examined. The compounds 4-bromo-1-diethylaminomethyl-1H-indole-2,3-dione and 4-chloro-1-dimethylaminomethyl-3-(6-methyl-benzothiazol-2-ylimino)-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one emerged as the most active compounds of this series (Hoyun L et. al., 2009).
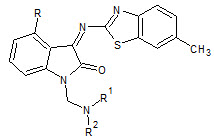
13
Abadi et. al., reported the synthesis of 3-substituted-2-oxoindoles (14). Compounds were tested for potential antiangiogenic properties, and also tested for in vitro antitumor properties against MCF7 (breast), NCI-H460 (lung) and SF268 (CNS) cancer cell lines (Ashraf H Abadi et. al., 2006).
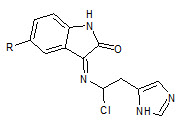
14
Sarangapani Manda et. al., reported the synthesis of certain 3-{4-(5-mercapto-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole- 2- yl)phenylimino}indolin-2-one derivatives. All derivatives 15 were screened for anticancer activity against HeLa cancer cell lines using MTT assay (Sarangapani M et. al., 2011).
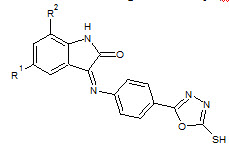
15
N. H Eshba et. al., had synthesized 5-(2-oxo-3-indolinyl) thiazolidine-2,4-dione having positions 1 and 3 of the isatin and thiazolidine rings, respectively, substituted by various Mannich bases 16 and screen for anticancer activity (Eshbha NH and Salama HM, 1985).
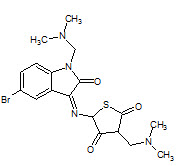
16
Anti-Inflammatory activity
Gummadi Sridhar Babu et. al., reported the synthesis, characterization and evaluation of Novel N-(1H benzimidazol- 2-yl)-2-isatinylidene-hydrazinecarboxamide (17). Anti-inflammatory data revealed that the compounds possess significant activity which is on a par with the standard ligand (Gummadi SB et. al., 2010).
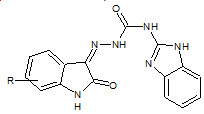
17
B. Durga Prasad et. al., reported the synthesis, characterization of isatin derivatives (18). All the synthesized isatin derivatives have been investigated for their anti-inflammatory activity (Durga PB et. al., 2012).
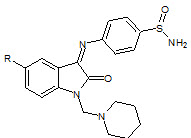
18
Panda et. al., reported the synthesis of some isatin nucleus (19). The synthesized compounds were screened for their analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents (Panda J, 2012).
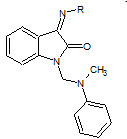
19
Perumal Panneerselvam et. al., reported the synthesis of some novel Schiff’s bases of 5- subsituted Isatin (20). These synthesized compounds were investigated for analgesic (Tail immersion method), anti-inflammatory (carrageenan- induced paw oedema method) activity (Perumal P et. al., 2010)
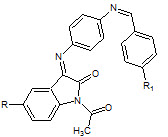
20
Maharaj Pogula et. al., reported the synthesis of new isatin derivatives (21). The synthesized derivatives were evaluated for in vivo anti-inflammatory activity. The compounds unsubstituted compounds 5-chloro, 5-fluoro, 6-bromo were found to have moderate potent activity (Maharaj P et. al., 2012)

21
Anti HIV Activity
Dharmarajan Sriram et. al., reported the synthesis of aminopyrimidinimino isatin analogues Compound 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7[[N-4-[3’-(4’-amino 5’trimethoxybenzylpyrimidin-2’-yl)imino-1’-isatinyl] methyl]N-1-piperazinyl]-3-quinoline carboxylic acid (22) emerged as the most potent broad-spectrum chemotherapeutic agent active against HIV, HCV (Dharmarajan S et. al., 2005)
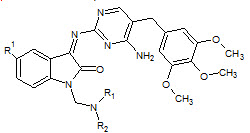
22
S. N. Pandey et. al., reported the synthesis of 1-[N, N-dimethylaminomethyl]isatin-3-[1'(6''-chlorobenzothiazol-2''-yl)] by reacting 3-[-1-(-6-chlorobenzothiazol-2-yl)thiosemicarbazone] and formalin with dimethylamine (23). The synthesized compounds were screened for anti-HIV activity at HIV-1(III B) in MT-4 cells (Pandeya SN et. al., 1999)
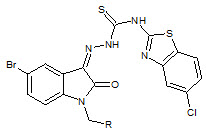
23
S. N. Pandey et. al., reported synthesized Schiff bases of isatin derivatives with sulfodoxine (24). All the compounds showed notable activity. The piperidino methyl compounds were found to be the most active ones in the series (Pandeya SN et. al., 1998).
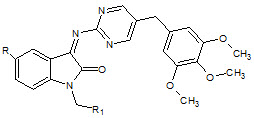
24
Y. Teiltz et. al., reported synthesis of N-methyl isatin-β-4',4'-diethylthiosemicarbazone (25) and shown inhibition of HIV by their action on reverse transcriptase, viral structural proteins (Teitz Y et. al., 1993).
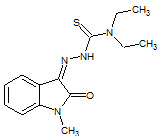
25
CNS depressant activity
Prince P Sharma et. al., reported the synthesis of some novel isatin schiff’s bases (26). These compounds were screened for anticonvulsant activity (Prince PS et. al., 2009).
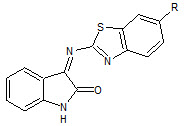
26
Sivakumar Smitha et. al., reported the synthesis of N-Acetyl/Methyl Isatin derivatives (27). The synthesized compounds were screened for their anticonvulsant and Sedative-Hypnotic activities. The synthesized compounds showed significant sedative-hypnotic activity (Sivakumar S et. al., 2008)
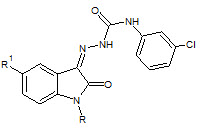
27
S N Pandey et. al., had synthesized isatin-3-hydrazone by isain, para bromo and phenoxy acetyl hydrazide with glacial acetic acid (28) which showed anticonvulsant activity (Pandeya SN et. al., 2002)
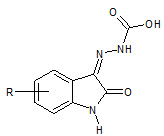
28
Krishan Nand Singh et. al., had been synthesized (3Z)-5-bromo-1-methyl-3-[(4- nitrophenyl)imino]-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one by reacting 5-substituted N-methyl/N-acetyl isatin and aromatic amine (29) with glacial acetic acid and has shown to possess good anticonvulsant activity (Singh KN et. al., 2004).
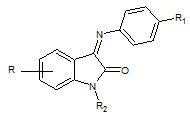
29
Antiviral activity
Sriram et. al., reported the synthesis of a novel series of lamivudine prodrugs involving N4- substitution with isatin derivatives (30). The synthesized compounds showed in-vitro antiretroviral activities and one compound was found to be equipotent to lamivudine with EC50 OF 0.0742 ± 0.04 μM (Sriram D et. al., 2005).
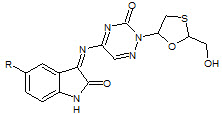
30
Antioxidant activity
C.R. Prakash et. al., reported the synthesis of some novel isatin derivatives and analogs (31). These compounds were screened for antioxidant activity. In this method, the compound 3-(4-(4-dimethylaminobenzylideneamino) phenylimino) indoline-2-one showed highest antioxidant activity (Prakash CR et. al., 2011).
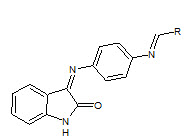
31
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
CONCLUSION
The literature reveals that isatin derivatives has diverse biological activity and the various synthetic routes brought an interest to the chemists, pharmacologists and researchers. Due to their wide range of applications, these compounds received a great deal of attention. In conclusion, a wide variety of biological activity of isatin shiff base has been described.
REFERENCES
1. Aboul-Fadl T., Mohammed F. A., and Hassan E. A. Synthesis, antitubercular activity and pharmacokinetic studies of some Schiff bases derived from 1- alkylisatin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003; 26; 778–784.
2. Alam M., Younas M., Zafar M.A., Naeem. Scientific study and development meat barian a tradesnal food product Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1989; 32; 246.
3. Ali S. M. M., Abul Kalam Azad M., Jesmin M. et al., In vivo anticancer activity of Vanillin semicarbazone, Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012; 2; 438–442.
4. Aliasghar J., Dariush K., Erik D.C., Chanaz S. Jean Michel Brunel Synthesis, Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antiviral Activity Evaluation of Some New bis-Schiff Bases of Isatin and Their Derivatives. Molecules. 2007; 12; 1720-1730.
5. Ashraf H. Abadi , Sahar M. Abou-Seri, Doaa Abdel-Rahman E. Christian Klein Olivier Lozach, Laurent Meijer. The synthesis of 3-substituted-2-oxoindoles and their evaluation as kinase inhibitors, anticancer and antiangiogenic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006; 41; 294-305.
6. Avaji P. G., Vinod Kumar C. H., Patil S. A., Shivananda K. N., and Nagaraju C. Synthesis, spectral characterization, in-vitro microbiological evaluation and cytotoxic activities of novel macrocyclic bis hydrazone, Euro. J. Med. Chem. 2009; 44; 3552–3559.
7. Bergman J., Lindstrom J.O., Tilstam U. The structure and properties of some indolic constituents in Couroupita guianensis aubl. Tetrahedron. 1985; 41; 2879–2881.
8. Bhattacharya A., Purohit V. C., and Rinaldi F. Environmentally friendly solvent-free processes: novel dual catalyst system in Henry reaction, Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2003; 7; 254–258.
9. Breinholt J., Demuth H., Heide M., Jensen G.W., Moeller I.L., Nielsen R.I., Olsen C.E., Rosendahl C.N. Prenisatin (5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl) indole-2, 3-dione): an antifungal isatin derivative from Chaetomium globosum. Acta Chem. Scand. 1996; 50; 443.
10. Chandramouli C., Shivanand M. R., Nayanbhai T. B., Bheemachari B., and Udupi R. H. Synthesis and biological screening of certain new triazole schiff bases and their derivatives bearing substituted benzothiazole moiety, J. . Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012; 4; 1151-1159.
11. Chaubey A. K. and Pandeya S. N. Synthesis & anticonvulsant activity (Chemo Shock) of Schiff and Mannich bases of Isatin derivatives with 2-Amino pyridine (mechanism of action), Int. J. PharmTech. Res. 2012; 4; 590–598.
12. Chhajed S.S., Padwal M.S. Antimicrobial Evaluation of Some novel Schiff and Mannich bases of Isatin and its derivatives with quinoline. Int. J. ChemTech. Res. 2010; 2; 209-213.
13. Chinnasamy R. P., Sundararajan R., and Govindaraj S. Synthesis, characterization, and analgesic activity of novel schiff base of isatin derivatives, J. Adv. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2010; 3; 342–347.
14. Chohan Z. H., Praveen M., and Ghaffar A. Structural and biological behaviour of Co(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) metal complexes of some amino acid derived Schiff-bases, Metal-Based Drugs 1997; 4; 267–272.
15. Dhar D. N. and Taploo C. L. Schiff bases and their application. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1982; 41; 501-506.
16. Dharmarajan S., Tanushree R.B., Perumal Y. Aminopyrimidinimino isatin analogues: Design of novel nonnucleosideMHIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors with broadspectrum chemotherapeutic properties. J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2005; 8; 565-577.
17. Durga P.B., Vasanthi R., Kanth B.C., Prabhakar D., Mohan R. Synthesis, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of isatin derivatives. Int. J. Bio. Pharm. Res. 2012; 3; 182- 187.
18. Ershad S., Sagathforoush, Karim-Nezhad G., and Kangari S. Electrochemical behavior of N2SO Schiff-base Co(II) complexes in non-aqueous media at the surface of solid electrodes, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009; 4; 846–854.
19. Eshbha N.H, Salama H.M. 5-(2-Oxo-3-indolinylidene) thiazolidine-2, 4-dione-1, 3-diMannich base derivatives: Synthesis and evaluation for antileukemic activity, Pharmazie. 1985; 40; 320–322.
20. Grafe U., Radics L. Isolation and structure elucidation of 6-(3'- methylbuten-2'-yl)isatin, an unusual metabolite from Streptomyces albus. J. Antibiotics. 1986; 39; 162– 163.
21. Gummadi S.B., Nanam R., Puttireddy S.M., Bethi S., Umasankar K., Jupally V.R. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of novel N-(1Hbenzimidazol-2-yl)-2-Isatinylidene hydrazine carboxamide derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. Der. Pharma. Chemica. 2010; 2; 196-204.
22. Guo Y., Chen F. TLC-UV-spectrophotometric and TLC scanning determination of isatin in leaf of Isatis. Zhongcaoyao. 1986;17; 8-11.
23. Hoyun L., Solomon V.R., Changkun H. Hybrid pharmacophore design and synthesis of isatin– Chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009; 17; 7585-7592.
24. Ischia M., Palum M.A., Prota G. Adrenalin oxidation revisited. New products beyond the adrenochrome stage. Tetrahedron. 1988;44; 6441-6446.
25. Jarrahpour A., Khalili D., De Clercq E., Salmi C., and Brunel J. M. Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activity evaluation of some new bis-Schiff bases of isatin and their derivatives, Molecules. 2007; 12; 1720–1730.
26. Jnyanaranjan P. Synthesis of some Antibacterial, Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory agents containing isatin nucleus. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012; 4; 2304-2313.
27. Joaquim F.M., Da Silva, Simon J. Garden, Angelo C. Pinto. The Chemistry of Isatin. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001; 12; 273-324.
28. Kapadia G.J., Shukla B.K., Chowdhury S.P., Basak H.M., Falesm E.A. Phenylpel isatins: a novel class of alkaloids from Melochia tomentosa. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Comm. 1977; 15; 535–536.
29. Kapadia G.J., Shukla Y.N., Basak S.P., Sokoloski E.A., Fales H.M. The melo- satins a novel class of alkaloids from Melochia tomentosa. Tetrahedron. 1980; 36; 2441–2447.
30. Li S., Chen S., Lei S., Ma H., Yu R., and Liu D. Investigation on some Schiff bases as HCl corrosion inhibitors for copper, Corrosion Sci. 1999; 41; 1273–1287.
31. Maharaj P., Blessi P.K., Uresh R., Shobaran B., Sammaiah G. Synthesis and characterization of new isatin derivatives for anti-inflammatory activity. Int. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2012; 4; 248-251.
32. Manju P., Neeraj K., Sharma P., Jha K.K. Synthetic and biological multiplicity of isatin: A Review. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2011; 2; 35-44.
33. Marvel C.S., Hiers G. S. Organic Syntheses Coll. 1941;Vol. 1: p.327 & 1925;Vol. 5; p.71.
34. Miri R., Razzaghi-asl N., and Mohammadi M. K., QM study and conformational analysis of an isatin Schiff base as a potential cytotoxic agent, J. Mol. Model. 2013; 19; 727–735.
35. Mounika K., Anupama B., Pragathi J., and Gyanakumari C. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of a Schiff base derived from 3-ethoxy salicylaldehyde and 2-amino benzoic acid and its transition metal complexes, J. Sci. Res. 2010; 2; 513–524.
36. Otto Linne Erdmann. Untersuchungen uber den Indigo. Journal fur Praktische Chemie (1840);19 (1); 321-362.
37. Ozlen G., Nilgun K., Aydın S. Synthesis and antituberculosis activity of 5- methyl/trifluoromethoxy-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-thiosemicarbazone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008; 16; 8976-8987.
38. Palumbo A., Ischia M.D., Misuraca Prota G. A new look at the rearrangement of adrenochrome under biomimetic conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989; 990; 297–302.
39. Pandey A., Dewangan D., Verma S., Mishra A., and. Dubey R. D. Synthesis of schiff bases of 2-amino-5-aryl-1,3,4-thiadiazole and its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial and antitubercular activity, Int. J. ChemTech. Res. 2011; 3; 178-184.
40. Pandeya S.N., Senthil R., Stables J.P. Synthesis of isatin semicarbazones as novel anticonvulsants – role of hydrogen bonding. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2002; 5; 266–271.
41. Pandeya S.N., Sriram D., Nath G., Clercq E.D. Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti HIV activity of Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin with N-6-chlorobenzthiazol-2-ylthiosemicarbazide. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999; 61; 358-361.
42. Pandeya S.N., Yogeeswari P., Sriram D. Nath G. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of NMannich bases of 3-_N'-sulphadoximino- isatin and its methyl derivative. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1998; 137; 321–324.
43. Perumal P., Ravi S.R., Kumarasamy M.N, Ramesh K. Synthesis, analgesic, antiinflammatory and antimicrobial activities of some novel Schiff’s bases of 5-subsituted Isatin. Der. Pharm. Chem. 2010; 2; 28-37.
44. Prakash C.R., Raja S., Saravanan G., Dinesh K.P., Panneer S. Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant activities of some novel isatin derivatives and analogs. Asian. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2011; 1; 140-143.
45. Prince P.S., Pandeya S.N., Roy R.K., Anurag Verma K., Gupta S. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of some novel isatin schiff’s bases. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2009; 1; 758-763.
46. Ramachandran S. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of some novel Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin derivatives. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Chem. 2011; 1; 289-294.
47. Sammaiah G., Brahmeshwari G.M., Sarangapani. Synthesis and biological activity of 2- aminobezoic acid (2-oxo-1, 2 dihydro-indol-3-ylidene)-hydrazides, J. Adv. Pharm. Sci 2011; 476-52.
48. Sandeep K.G., Shyam S.P. Synthesis and evaluation of antitubercular activity of some thiobenzimidazolyl derivatives. Der. Pharm. Chem. 2011; 3; 274-279.
49. Sandmeyer T. Helv uber Isonitrosoacetanilide und deren Kondensation zu Isatinen. Chimica. Acta. 1919;2 (1) ; 234–242.
50. Sangamesh A.P., Manjunatha M., Udaykumar V.K., Prema S.B. Synthesis, spectral characterization and biological evaluation Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Mn(II) metal complexes of novel Isatin schiff base ligand. Der. Pharm. Chem. 2011; 3; 97-108.
51. Sanjay B., Ankur P., Gokul T., Jitendra P., Manda S. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Isatin Derivatives. Ira J Pharm Res 2006; 4; 249-254.
52. Sarangapani M., Rajyalakshmi G., Rama N.R. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of certain 3-{4-(5-mercapto-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-2- yl) phenylimino} indolin-2-one derivatives. Sau. Pharm. J. 2011; 19; 153–158.
53. Sathe B. S., Jaychandran E., Jagtap V. A., and Sreenivasa G. M. Synthesis characterization and anti-inflammatory evaluation of new fluorobenzothiazole schiff ’s bases, Int. J. Pharm. Res. Develop. 2011; 3; 164-169.
54. Schiff H. Mittheilungen aus dem Universitatslaboratorium in Pisa: eine neue reihe organischer Basen. Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 1864; 131; 118-119.
55. Seshaiah K.S., Muniyandy S., Atmakuru R. Synthesis and antibacterial screening of hydrazones, Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 36; 2001; 615–625.
56. Shibinskya M.O., Lyakhov S.A., Mazepa A.V., Andronati S.A. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, antiviral activity and interferon inducing ability of 6-(2-aminomethyl)-6H-indolo [2, 3-b] quinoxalines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010; 45; 1237-1243.
57. Singh K.N., Verma M., Pandaye S.N. Synthesis of 3Z)-5-bromo-1-methyl-3-[(4- nitrophenyl) I mino]-1, 3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one by reacting 5-substituted N-methyl/Nacetyl isatin and aromatic amine with glacial acetic acid. Acta. Pharm. 2004; 54; 49-56.
58. Singh U.K., Pandeya S.N., Singh A., Srivastava B.K., Pandey M. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of schiff’s and N-mannich bases of isatin and its derivatives with 4-amino-carbamimidoyl benzene sulfonamide. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug. Res. 2010; 2; 151-154.
59. Singh U.K., Pandeya S.N., Singh A., Srivastava B.K., Pandey M. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of schiff’s and N-mannich bases of isatin and its derivatives with 4-amino-ncarbamimidoyl benzene sulfonamide. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug. Res. 2010; 2; 151-154.
60. Sivakumar S., Surendra N. P., James P.S., Suthakar. Anticonvulsant and Sedative-Hypnotic Activities of N-Acetyl Methyl Isatin Derivatives. Scientia. Pharmaceutica. 2008; 76; 621– 636.
61. Sondhi S. M., Singh N., Kumar A., Lozach O., and Meijer L. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and kinase (CDK-1, CDK-5 and GSK-3) inhibition activity evaluation of benzimidazole/benzoxazole derivatives and some Schiff ’s bases, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006; 14; 3758-3765.
62. Sondhi S. M., Singh N., Kumar A., Lozach O., and Meijer L. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and kinase (CDK-1, CDK-5 and GSK-3) inhibition activity evaluation of benzimidazole/benzoxazole derivatives and some Schiff ’s bases, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006; 14; 3758-3765.
63. Sriram D., Yogeeswari P., Gopal G. Synthesis, anti HIV and antitubercular activity of lamivudine prodrugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005; 40; 1373-137.
64. Teitz Y., Ladizensky E., Barko N., Burstein E. Selective repression of V-alb encoded protein by N-methylisatin-beta-4',4'-diethyl thiosemicarbazone and N-allylisatin-beta- 4',4'-diallylthiosemicarbazone. Antimicrob. Agents. Chem Ther 1993; 37; 2483–2486.
65. Tisato F., Refosco F., and Bandoli G. Structural survey of technetium complexes, Coordination. Chem. Rev. 1994; 135-136; 325–397.
66. Vashi K. and Naik H. B. Synthesis of novel Schiff base and azetidinone derivatives and their antibacterial activity, Euro. J. Chem. 2004; 1; 272–276.
67. Venkatesh P. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of various schiff bases complexes of Zn(II) and Cu(II) ions, Asian. J. Pharm. Health. Sci. 2011; 1; 8–11.
68. Venugopala K. N. and Jayashree B. S. Synthesis of carboxamides of 2'-amino-4' -(6-bromo-3-coumarinyl) thiazole as analgesic and antiinflammatory agents, Indian. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2003;12; 307–310.
69. Wei D., Li N., Lu G., and Yao K. Synthesis, catalytic and biological activity of novel dinuclear copper complex with Schiff base, Science in China B 2006; 49; 225–229.
70. Wei L., Wang Q., Liu X. Application of thin-layer chromatography in quality control of Chinese medicinal preparations II. Qualitative analysis of some Chinese medicinal preparations of Chansu. Yaowu. Fenxi. Zazhi. 1982; 2; 288–291.
71. Yan Y., Li G., Wang F., Mao W. Huadong Huagong Xueyuan Xuebao. 1992; 18:192. (CA 118:127985k)
72. Yoshikawa M., Murakami T., Kishi A., Sakurama T., Mat-suda H., Nomura M., Kubo M. Novel indole S, O-bisdesmoside, calanthoside, the precursor glycoside of tryptanthrin, indirubin and isatin with increasing skin blood flow promoting effects from two Calanthe species (Orchidaceae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998; 46; 886–888.
73. Zapata-Sudo G., Luana B. Pontes., Daniele G., Thaiana C.F.M., Nubia M.R., Angelo C.P., Margarete M. Trachez, Roberto TS. Sedative–hypnotic profile of novel isatin ketals. Biochem. Behavior. 2007; 86; 678-685
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









