 ABOUT AUTHOR
ABOUT AUTHOR
Ms. Sapna
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Himalayan Institute of Pharmacy and Research Rajawala, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
*bhandarisapna747@gmail.com
ABSTRACT: The present investigation deals with development of orally disintegrating tablets of Rizatriptan Benzoate to produce the intended benefits. Orally disintegrating tablets of Rizatriptan Benzoate were prepared by wet granulation method to provide faster relief from pain to migraine sufferers. Formulation research is oriented towards safety, efficacy and quick onset of action of existing drug molecule through novel concept of drug delivery. About four formulations for the present study were carried out full factorial design. Kyron 314 was used as super disintegrants, while microcrystalline cellulose and mannitol was used as diluents. Starch was used as binder. The prepared batches of tablets were evaluated for weight variation, hardness, friability, wetting time, drug content and in-vitro dissolution studies. The optimized formulation dispersed in within 15 seconds. It also showed a higher water absorption ratio and 99.67% of drug is released within a minute.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2548
INTRODUCTION: Oral Disintegrating Tablets (ODT) is solid unit dosage forms, which disintegrate rapidly in the mouth without chewing and in absence of water. ODTs are widely used for pediatric, geriatric and physically weak patients due to their ease of administration. The first ODTs disintegrated through effervescence rather than dissolution, and were designed to make taking vitamins more interesting for children. Dissolution became more effective than effervescence through better manufacturing processes. Tablets designed to dissolve on the buccal mucous membrane were a precursor to the orally disintegrating tablets. This dosage form was intended for drugs that yield low bioavailability through the digestive tract but are difficult to administer parenterally, such as steroids and narcotic analgesics. Absorption through the cheek allows the drug to bypass the digestive tract for instant systemic distribution.
Advantages of ODTs:
1. Increased bioavailability due to pregastric absorption.
2. Improved safety due to low risk of choking or suffocation during oral administration.
3. They are easy to consume and as such are convenient for such patients as "the elderly, stroke victims, and bedridden patients, patients affected by renal failure, and patients who deny swallowing, such as pediatric, geriatric, and psychiatric patients".
Disadvantages Of ODTs:
1. Cost-effective production process.Expensive packaging of oral film.
2. Lack of physical resistance in standard blister packs.
Technologies used to prepare:
1. Direct compression: Easiest way to manufacture tablets Low manufacturing cost, conventional equipment’s and limiting no. of processing steps. It is essential to choose a suitable and an optimum concentration of disintegrates to ensure quick disintegration and dissolution. Superdisintegrants are the rooky substances which are more effective at lower concentration with greater disintegrating efficiency and mechanical strength.
2. Sublimation: The slow dissolution of the compressed tablet containing even highly soluble ingredients is due to the low porosity of the tablets. The volatile materials were then removed via sublimation, which produces porous structures. Additionally, several solvents (e.g. Cyclohexane benzene) can be also used as pore forming agents.
3. Tablet moulding: In this method, tablets are prepared by using water soluble ingredients so that the tablet dissolves completely and rapidly. The powder blend is moistened with a water– alcoholic solvent and is molded into tablet under pressure lower than that used in conventional tablet compression. The solvent is then removed by air drying.
4. Freeze drying/ Lyophilization: A process in which water is sublimated from the product after freezing Lyophilization is a pharmaceutical technology which Allows drying of heat sensitive drugs and biological at low temperature under conditions that allow removal of water by sublimation. Lyophilization results in preparation, which is highly porous with a very high specific surface area.
5. Mass extrusion: In this method active blend is softened using the solvent mixture of water-soluble polyethylene glycol and methanol and then subsequent expulsion of softened mass through the extruder or syringe is made to get a cylinder of the product into even segments using heated blade to form tablet. The dried cylinder can also be used to coat granules for bitter drugs.
6. Spray drying: In this technique, gelatin can be used as a supporting agent and as a matrix, mannitol as a bulking agent and sodium starch glycolate or crosscarmellose or crospovidone are used as superdisintegrants. Tablets manufactured from the spray-dried powder have been reported to disintegrate in less than 20 seconds in aqueous medium.
VALIDATION:
Validation is a process of establishing documentary evidence demonstrating that a procedure, process, or activity carried out in production or testing maintains the accurate level of compliance at all stages. In Pharma Industry it is very important apart from final testing and compliance of product with standard that the process adapted to produce itself must assure that process will consistently produce the expected results.
Process Validation:
Process validation for solid oral dosage form in the pharmaceutical industry is required by the current good manufacturing practices for finished pharmaceutical products. According to FDA’s guidelines process validation defined as follows:“Process validation is establishing documented evidence which provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its pre – determined specification and quality characteristics.”
Benefits of Process validation:
1. Compliance with government regulation.
2. Harmonization of global GMP’s.
3. Internationally accepted quality is attained.
4. Decreased risk of process variables.
5. Built in quality & hence the small size sample in production batches.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
AIM &OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY:
Aim: The study deals with the formulation of orally disintegrating tablets of new generation Rizatriptan benzoate that is used for the treatment of Migraine& to get the predetermined specification & optimized results.
Objective of the study: - Literature Survey.
-To evaluate the Preformulation studies.
-To characterize interaction between the drug & the excipients used.
-To formulate oral disintegrating tablets for new generation drug of anti – migraine.
-To develop a stable & robust manufacturing process for Rizatriptan benzoate ODT.
-To prepare an optimized formulation & meeting its predetermined specification.
-To develop tablets for commercial purpose with successful process validation.
DRUG PROFILE:
Chemical Properties:
Name of drug: Rizatriptan Benzoate
Category: Rizatriptan benzoate is a triptan drug used for the treatment of migraine headaches. It is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine1 receptor subtype agonist.
Chemical structure:

- IUPAC Name:
N, N-dimethyl-5-(1H-1, 2, 4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-indole-3ethanamine monobenzoate.
- Empirical formula: Rizatriptan: C15H19N5
- Rizatriptan benzoate: C22H25N5O2
- Appearance: White or almost white crystalline powder.
Physicochemical Properties:
* Molecular weight: 269.4 (Free base)
* Solubility: Soluble in water at about 42 mg/ml (expressed as free base) at 25°C.
* Mechanism of action: The therapeutic activity of Rizatriptan in migraine can most likely be attributed to agonist effects at 5-HT1B/1D receptors on the extra cerebral, intracranial blood vessels that become dilated during a migraine attack and on nerve terminals in the trigeminal system. Activation of these receptors results in cranial vessel constriction, inhibition of neuropeptide release and reduced transmission in trigeminal pain pathways.
* Indications: Rizatriptan is FDA-approved to treat acute migraine attacks with or without aura. It does not prevent future migraine attacks and is also used off-label to treat cluster headaches.
* Pharmacokinetic data: Bioavailability = 45%
Protein binding = 14%
Metabolism = by monoamine oxidase Biological half-life = 2–3 hours
Excretion = 82% urine; 12% faeces
* Dosage Form/Strength: Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) 5, 10 mg tablets.
* Proposed Dosage: Adolescents patients, 12 to 17 years: <40 kg, 5 mg single dose; ≥40 kg, 10 mg single dose.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
Materials:
Table 1.List of materials used in formulation
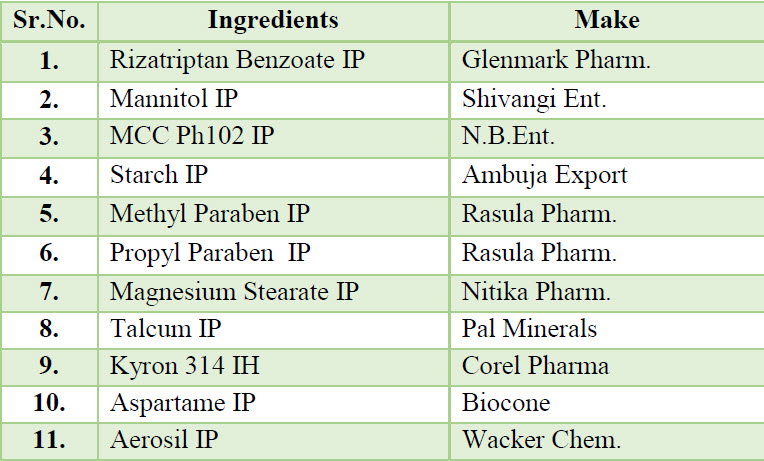
Table 2. List of equipment’s used during manufacturing process
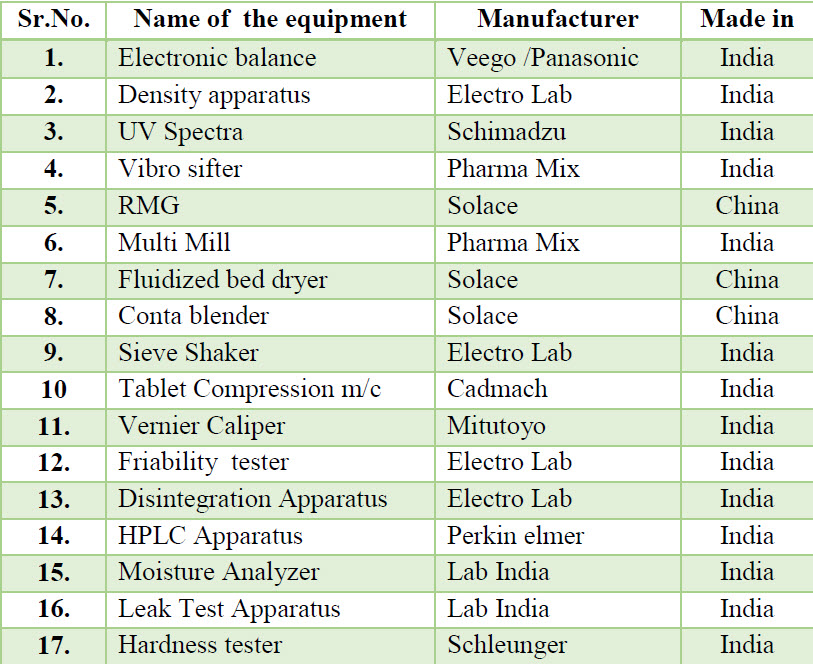
METHODS:
Preformulation Studies: Preformulation Studies are the first step in the rational development of dosage form of a drug substance. The objective of the Preformulation studies are to develop a portfolio of information about the drug substances, so that this information useful to develop formulation. Preformulation can be defined as investigation of physical and chemical properties of drug substance alone and when combined with excipients.
a. Melting point test
b. Solubility studies
c. Flow properties of API
d. Compatibility studies
a. Melting Point Test: Procedure: Reduce the substance to a very fine powder and, dry it at a temperature considerably below its melting temperature or at a pressure of 1.5 to 2.5 kPa over self- indicating silica gel for 24 hours. Introduce into a capillary glass tube, a sufficient quantity of the dry powder to form a compact column 4 to 6 mm high. Heat the bath until the temperature is about 10° below the expected melting temperature. Remove the thermometer and quickly attach the capillary tube to the thermometer by wetting both with a drop of the liquid of the bath or otherwise and adjust its height so that the closed end of the capillary is near the middle of the thermometer bulb. Replace the thermometer and continue the heating, with constant stirring, sufficiently to cause the temperature to rise at a rate of about 10° per minute. Continue the heating and note the temperature at which the column of the sample collapses definitely against the side of the tube at any point, when melting may be considered to have begun and note also the temperature at which the sample becomes.
b. Solubility Studies: A semi quantitative determination of solubility can be made by adding a solute in small incremental amounts of fixed volume of solvents whose pH ranging from 1.2 to 7.4 including distilled water.
c. Flow Properties of API: Flow property of Rizatriptan Benzoate (API) was performed by certain parameters as Angle of repose, Bulk Density, Tapped Density, Housner’s ratio & Compressibility Index .Hence during dosage form developed excipients be incorporated to improve flow properties.
d. Compatibility Studies: The compatibility of drug and formulation components is important prerequisite before formulation. It is therefore necessary to confirm that the drug does not react with the polymers and excipients under experimental conditions and affect the shelf life of product or any other unwanted effects on the formulation. Drug–Excipients compatibility study of Rizatriptan Benzoate with different categories of excipients was carried out. The study was carried out at different conditions of temperature and humidity like 40°C/75%RH, 2–8°C, room temperature & found their physical appearance, impurity level and water content after 2 week, 4 weeks and compare with initial value. The result shows impurity level with some drug and excipients combination increases and also slight changes in appearance, all were compatible with Rizatriptan benzoate. Excipients were considered compatible only if the total impurities do not exceed 2–times the impurities of initial. Compatibility studies were checked carefully for the best Excipients selection. One gram of each sample was filled in 10 ml clear glass vial and non-leachable, impermeable closure was fitted to the vials. After mentioned storage time samples were analyzed as per schedule.
- Two vials (Drug + Excipients) in 40 oC/75 % RH along with the placebo.
- Two vials (Drug + Excipients) for initial analysis along with the placebo.
- This is for to analyze the compatibility between Rizatriptan Benzoate and Excipients proposed to incorporate into the formulation.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Procedure for Calibration Curve
Solvent Mixture
- Mobile phase A: A mixture of 90 volumes of buffer solution prepared by dissolving 2.6 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.0 g of dibutyl amine and 0.8 g of ortho-phosphoric acid in 1000 ml of water, adjusted to pH 6.5 with NAOH solution and 10 volumes of a mixture of 6 volumes of acetonitrile and 4 volumes of methanol.
- Mobile phase B: A mixture of 60 volumes of buffer solution and 40 volumes of a mixture of 6 volumes of acetonitrile and 4 volumes of methanol.
- Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance under examination in 50.0 ml of the solvent mixture. Dilute 5.0 ml of this solution to 50.0 ml with the solvent mixture.
- Reference solution: A 0.01 per cent w/v solution of Rizatriptan benzoate RS in the solvent mixture.
The calibration curve was constructed by plotting concentration on X- axis versus and peak areas on Y- axis and linear regression equation was calculated as shown .The calibration curve was found to be linear with correlation coefficient of 0.998.
Formulation aspects of ODTs:
Calculation of dose of Rizatriptan Benzoate
Oral dose of Rizatriptan is 5mg.
269.40mg Rizatriptan= 391.46mg of Rizatriptan benzoate
So,
5mg Rizatriptan= 5 x 391.46/269.40
= 7.265mg of Rizatriptan benzoate.
Table 3.Formulation for Rizatriptan Benzoate OD tablet

Method used for manufacturing of ODTs: Wet Granulation: All the ingredients are dispensed as per manufacturing formula & sifted all the material separately through # 40 mesh. Take purified water in SS tank disperse starch, Methyl Paraben& Propyl Paraben. Boil the mixture in jacketed steam kettle for lumps free good paste. Rizatriptan benzoate, diluents were loaded in RMG (Rapid mixture granulator) & run the RMG at slow speed for 15 minutes. Add the above paste at slow speed and run the chopper at high speed. Check the formation of good granules. Discharge the granules from RMG. Dry the granules in fluidized bed dryer for 45 to 50 minutes at set inlet temperature. Check LOD in IR Moisture balance. Sift the dried granules through # 24 SS sieve using sifter & pass the retention using multi mill 1.5 mm screen. All the granules should pass through the sieve. Above sifted material were loaded in Conta blender& blended it for 15 min. at 10 RPM Speed. Then add lubrication and run it for 5 minutes at 10 RPM.
Compression: The lubricated blend was compressed as per specification. Tablets were compressed at 27 station double rotator cadmach machine D tooling. In process check was done continuously during compression.
Evaluation of orally disintegrating tablets:
I. Evaluation of blend:
Evaluation parameter of tablets mentioned in the Pharmacopoeias need to be assessed, along with some special test. The quality of tablet, once formulated be rule, is generally dictated by the quantity of physiochemical properties of blends.
a. Angle of Repose
b. Hausner’s ratio
c. Bulk density
d. Tapped density
e. Carr’s compressibility index
a. Angle of Repose: It is described as the maximum possible angle possible among the surface piles of powder to the horizontal plane. The angle of repose was measured by means of conventional fixed funnel method. 100 gm of the drug powder was flown through funnel which was fixed to the stand at a fixed height (h). Then radius and the height of the powder bed were measured.

Where, h- Height in cm
r - Radius in cm
b. Hausner’s ratio: It is an indirect index of easy of powder flow and is measured from the bulk and tapped density of Rizatriptan sublingual powder formulation, it is expressed as
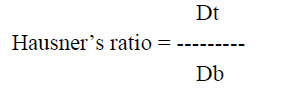
Where, Dt is powder tapped density
Db is powder bulk density.
c. Bulk density: This is defined as the ratio of mass of the total powder to the bulk volume of powder. It was determined by placing 100 gm of powder material into the measuring cylinder and noted the initial volume of the powder. This is called as a bulk volume. Through this bulk volume, bulk density was measured by using the following formula.
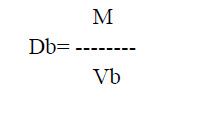
Where, M is powder mass
Vb is powder bulk volume
Db is bulk density.
d. Tapped density: It is defined as the ratio of the total powder mass to the tapped volume of powder. This was determined by tapping the 100 gm of the powder for 750 times and noted the volume using tap density tester USP (Tap density tester, Electro lab ETD-1020). The tapping is further continued till the differences between two successive volumes is <2% and is expressed in gm/ml, given by
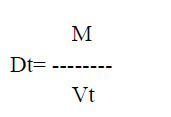
Where, M is powder mass
Vt is tapped volume of powder.
e. Carr’s index: It can be calculated form bulk and tapped density. Which shows powder flow properties and is expressed as
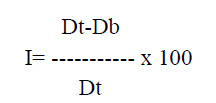
Where, Dt -tapped density of the powder
Db - bulk density of the powder.
II. Evaluation of tablets:
Evaluation parameter of all the formulated orally disintegrating tablets was subjected to the following quality control tests:
a. Weight variation
b. Hardness
c. Friability test
d. Disintegration time
e. Uniformity of dispersion
f. Water absorption ratio
Weight variation: The weight variation test is carried out in order to ensure uniformity in the weight of tablets in a batch. First the total weight of 20 tablets from formulation is determined& the average is calculated. The individual weight of the each tablet is also determined to find out the weight variation. IP specification for uniformity of weight is given as
Average weight of Tablet
1. 80 mg or less : ±10 % Deviation
2. More than 80 mg but less than 250 mg : ±7.5 % Deviation
3. 250 mg or more : ±5 % Deviation
Hardness: The hardness of tablet is an indication of its strength. Measuring the force required to break the tablet across tests it. The force is measured in kg and the hardness of about NLT 2 kg/cm2 is considered to be satisfactory for uncoated tablets. Hardness of 10 tablets is determined by Digital hardness tester.
Friability test: Friability is the loss of weight of tablet in the container due to removal of fine particles from the surface. Friabilator is employed for friability of tablets. Weight the 20 tablets and place in friabilator that will rotate at 25 rpm for 4 minutes. Dedust all the tablets and weight again. The percentage of friability can be calculated using the formula
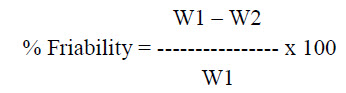
Where, W1 = Weight of tablet before test
W2 = Weight of tablet after test
d. Disintegration time: The disintegration apparatus contain six glass tube that are “3 long, open at the top, and held against 10” screen at the bottom end of the basket rack assembly. One tablet is placed in one tube and the basket rack is positioned in 1 liter beaker of distilled water at 37±2 oC, such that the tablets remain below the surface of the liquid on their upward movement and descend not closer than 2.5 cm from the bottom of the beaker.
e. Uniformity of dispersion: Keep the two tablets in 100 ml water and stir gently for 2 minutes. The dispersion is passed through 710 mm screen. The tablets will consider passing the test if no residue remained on the screen.
f. Water Absorption Ratio: A small piece of tissue paper folded twice is placed in a small Petri dish containing 6 ml of water. Put a tablet on the paper and the time required for complete wetting is measured. The wetted tablet is then reweighed. Water absorption ratio, is determine by using following formula
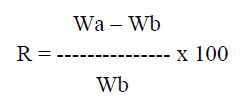
Where, Wa is the weight of tablet before water absorption
Wb is the weight of tablet after water absorption
VALIDATION: Prospective process validation was performed on consecutive three batches after success of tentative batch. A validation protocol was prepared & approved prior to validation batches. The three validation batches were labeled as (RIO 16001, RIO 16002&RIO 16003). The protocol has the sampling plan & acceptance criteria at different process variables. During the manufacturing, samples were collected as per the sampling plan & send for analysis.
Sampling plan for validation batches: Samples were collected as per sampling plan. The sampling procedure and sample size at each sampling location was carried out as per the protocol. a. Dry Mixing: Withdraw 5 gm sample at 6 different locations from RMG as shown below after 10, 12 and 15 minutes mixing.
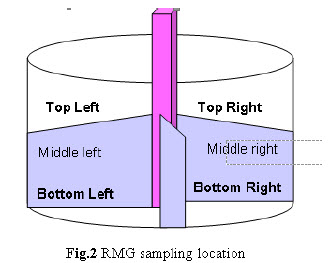
Drying: Perform drying in FBD dry the wet mass at ambient temperature for 15 min. Rack the mass of the bowl. Then dry at 60°C - 70°C inlet temperature for 45-50 min. with intermediate raking till LOD of granules obtain 1.5-2.0 % w/w. After drying collect 5 gm sample by sampling thief at 5 different locations from the FBD bowl as per given below.
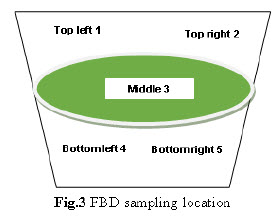
Blending: The blending was performed in Conta blender. The sample from each location was collected using sampling rod. Sample was drawn from 10 position of the Conta blender as shown in fig.3. Triplicate samples were collected from each location at both pre lubricated & lubricated stages & tested for content uniformity.
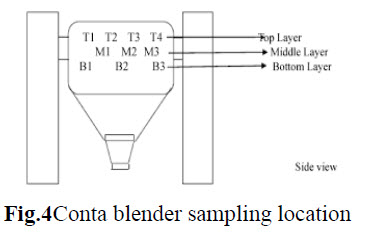
d. Compression: Tablets were compressed using 27 station double rotator compression machine with punches of given dimension to get tablets of specified specification. The effect of vibration during compression on blend uniformity was evaluated with hopper study. The hopper was filled completely & the compression machine was run at target speed for compression. The tablets were collected when the powder level in the hopper was full, approx. middle of the hopper & when it was nearing end of the hopper the tablets were evaluated for uniformity of weight.
- Machine speed study
- Hopper study
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
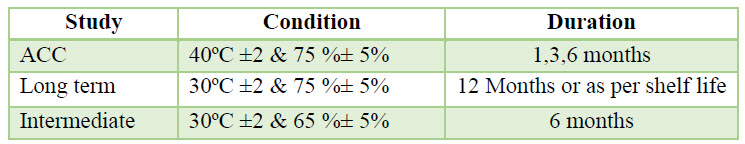
Packing & Stability: The finished product tested for finished product release & some specified sample of each batch was loaded in stability as per stability protocol. The sample was charged for stability, the long term stability was performed at temp. (30ºC±2 & 75%±5) & accelerated study was performed at (40ºC ±2 & 75 %± 5). The sample was analyzed at initial 1, 3, 6 months interval as:
Table 4. Stability Study Condition
RESULTS & DISCUSSION:
The following section briefly describes the experimental work &results of the various test performed during formulation, evaluation & Validation of the Rizatriptan benzoate ODTablets.
Preformulation Study:
a. Melting point test
b. Solubility studies
c. Flow properties of API
d. Compatibility studies
a. Melting Point Test: The M.P. of the drug was found to be in the range 178-180oC which matches with the reported value (178-180oC).
b. Solubility studies: Soluble in methanol & in water, sparingly soluble in Dimethyl sulphoxide and in dimethyl formamide, slightly soluble in ethanol (95 %) and in dichloromethane.
Table 5. ph Dependent Solubility
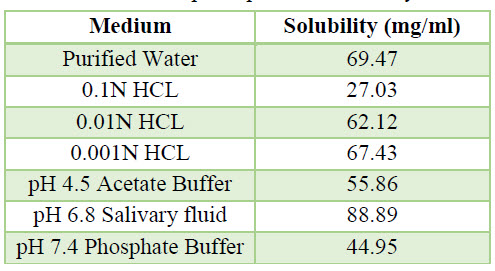
c. Flow Properties Of API: It can be explain by table which is given below
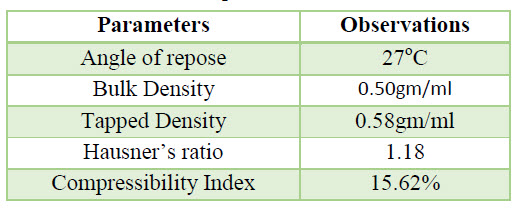
Table 6. Flow Properties observation of API
Compatibility studies: Drug – excipients compatibility: Drug–Excipients compatibility study of Rizatriptan Benzoate with different categories of excipients was carried out. The study was carried out at different conditions of temperature and humidity like 40°C/75%RH, 2–8°C, room temperature & found their physical appearance, impurity level and water content after 2 week, 4 weeks and compare with initial value. The result shows impurity level with some drug and excipients combination increases and also slight changes in appearance, all were compatible with Rizatriptan benzoate. Excipients were considered compatible only if the total impurities do not exceed 2–times the impurities of initial.
Table 7. Compatibility Study

Observation: There is no any colour change observed in the API and excipients.
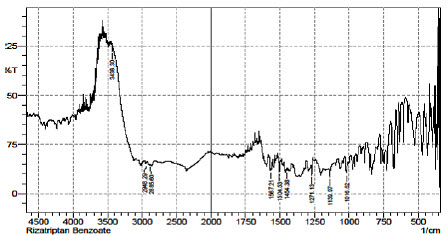
Fig.5 FTIR Spectrum of Rizatriptan Benzoate
Flow property of Rizatriptan Benzoate (API) was found to be fair. Hence during dosage form developed excipients are incorporated to improve flow properties.
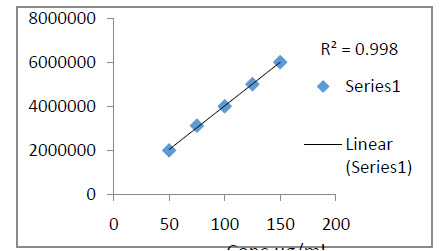
Fig.6 Calibration curve of Rizatriptan Benzoate
The calibration curve was found to be linear with correlation coefficient of 0.998.
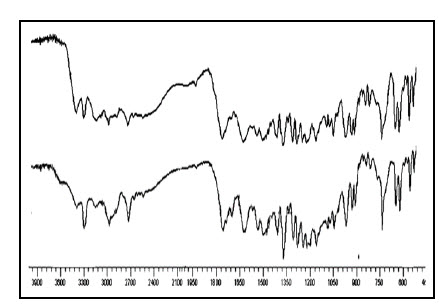
Fig.7 FTIR spectra of (a) Rizatriptan and (b) Physical mixture of OD formulation
Formulation & Evaluation:
Trail Batch: Trail Batch of Rizatriptan benzoate was prepared using standard manufacturing process for 2000 Tablets batch size, batch no: -T01, T02, T03, T04. The samples were collected& tested as per specification.
Exhibit Batch: After successful result of trail batch (T02), now we are taking a next step which is Exhibit Batch. Exhibit Batch of Rizatriptan benzoate was prepared using standard (Trail Batch No.–T02) manufacturing process for 100 kg batch size, batch no.-TBN 16001.
Validation Batches: After successful result of tentative batch, we should take three consecutive batches of validation. Batch size is same as tentative batch but their batch no. is VBN 16001, VBN 16002 and VBN 16003. Process is same as tentative batch but there parameter and result is some different.
Table 8. Micromeritics Result of Lubricated Blend
|
Test performed |
Specification |
Flow property results |
||||
|
T02 |
TBN 16001 |
VBN 16001 |
VBN 16002 |
VBN 16003 |
||
|
Loss on drying |
NMT 2.0 % |
1.68 |
1.64 |
1.61 |
1.68 |
1.71 |
|
Assay |
95.0- 105.0% |
99.78 |
99.78% |
99.7 |
99.78 |
99.69 |
|
Bulk density |
0.4 -0.6(g/ml) |
0.54 |
0.5 |
0.50 |
0.54 |
0.52 |
|
Tapped density |
0.3- 0.7(g/ml) |
0.60 |
0.6 |
0.56 |
0.60 |
0.59 |
|
Comp. Index |
16-20(%) |
18.7 |
18.5 |
18.32 |
18.7 |
18.10 |
|
Hausner’s ratio |
1.19-1.25 |
1.20 |
1.21 |
1.25 |
1.20 |
1.19 |
|
Angle of repose |
36-40 |
38 |
38 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
Table 9. Compression Data of Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
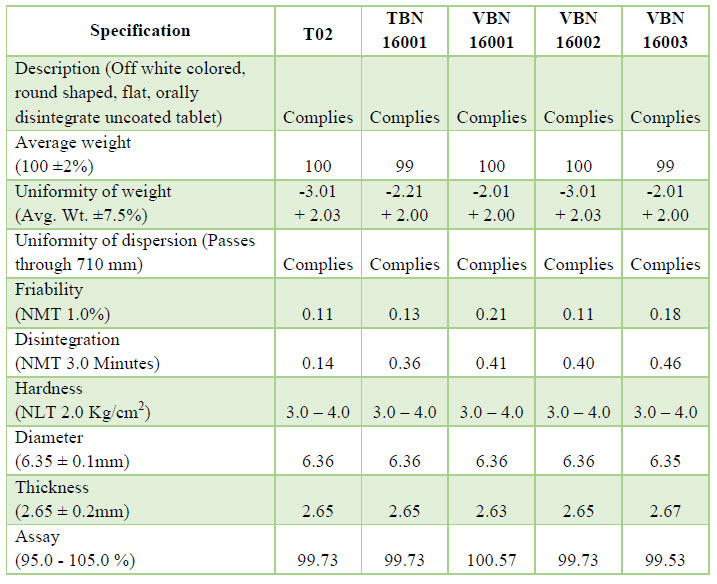
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
CONCLUSION: The goal of the present investigation was to identify the optimum combination of superdisintegrants for the development of orally disintegrating tablets of Rizatriptan benzoate.Rizatriptan Benzoate was prepared using wet granulation method on lab scale size and commercially. This study was carried out through a systemic plan; critical parameters were optimized to produce a stable & robust manufacturing process. Orally disintegrating tablet constitutes an innovative dosage form with great importance during the emergency cases whenever immediate onset of action is desired. The characterization of powdered blend of all the batches was done for determination of pre-compression parameter. The values of pre-compression parameters like bulk density, tapped density, Hausner ratio, Compressibility index and angle of repose of all the batches were evaluated which were within prescribed limits and indicated a good flow property. The result for characterization of blend indicates good flow properties. After compression of powder blend, the tablets were evaluated for various post compression parameters i.e. friability, wetting time, hardness and disintegration time, weight variation and percentage drug content. Validation was performed of three batches & found the results of all the three batches within specification limits, & gives the specified results of Stability study performed at Acc. & Long term condition.
RFERENCES:
1. Vivek Dave, Renu Bala Yadav, Richa Ahuja, Atul:2017. Formulation and evaluation orally dispersible tablets of Chlorphenira-mine maleate by fusion method. Marmara Pharmaceutical journal, vol.21, pp. 67-77.
2. Bharath Kumar K*, Sreekanth Reddy CP; 2016. Formulation and evaluation of rizatriptan benzoate Oral dispersible tablets. International Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutics; Vol 6; pp. 23-33.
3. Mohana M. Nair* et al., 2016. Formulation and evaluation of mouth dissolving film of a poorly soluble anti-hypertensive drug. International journal of Pharmacy & Technology. Vol. 8; pp. 21635-21661.
4. Shahtalebi.M. A, Tabbakhian.M, & Koosha. S, 2015, Formulation and evaluation of orally disintegrating tablet of Ondansetron using natural superdisintegrant, Journal of HerbMed Pharmacology Vol.4 (3):pp. 102-109. 5. Bhatt P. &Patel.M., 2015, Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Film of Rizatriptan Benzoate, International Journal of MediPharm Research, Vol.01 (02): pp 58-77.
6. Ghosh B, Ray. S & Das M, 2015, Formulation, development and optimization of mouth dissolving tablets of Rizatriptan benzoate, Vol. 45(6): pp. 593–600.
7. Kushare A.A. 2015,Formulation and evaluation of Oral dispersible tablets of Rizatriptan Benzoate, World Journal Of Pharmaceutical Research, Volume 4, Issue 8:pp. 685-717.
8. Tabbakhian1M, Shahtalebi, M.A &Harandi. N.S., 2014, Formulation and evaluation of orally disintegrating tablet of Rizatriptan using natural super-disintegrants. Journal of HerbMed Pharmacology, vol. 3(1); pp. 21-29.
9. B Sree Giri et al., 2013.Formulation and Evaluation of Oro Dispersible Tablets of Rizatriptan Benzoate by Direct Compression Technique. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and chemical science,Vol.2(3); pp. 1558-1568.
10. Desu. R, Bonthagarala. B, Nama. S &Nagalakshmi.A., 2013, Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Films of Rizatriptan, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Bio- science, Vol.2 (3):pp. 298-305.
11. Sarita Jangra Bhyan et al; 2013. Formulation and evaluation of mouth dissolving tablets containing carvedilol solid dispersion. Scholars Research Library. Vol. 5(6); pp. 31-42.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









