{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
ABOUT AUTHOR
Bharath kumar Dasari, Shyamsunder Anchuri, Manishkumar T, Saikiran velpula, Nagaraju Vallepu, Pranitha Adepu
Department of pharmacy practice
Balaji institute of pharmaceutical sciences, Narsampet, Warangal, Telangana
ABSTRACT.
Chronic kidney disease also called chronic renal failure is most commonly seen in the patients of hypertension and diabetes
Case Report
A female patient of age 60 yrs was admitted in a multispecialty hospital located in Warangal ,with the complaints of SOB, confusion, fever Since 3dys ,she had a past medical history of HTN.
Discussion :
Patient’s data was collected in a profile form and the details were saved confidentially .the patient was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease with HTN and the treatment was given.
Conclusion :
the patient was given a complete course and was given counselling for chronic kidney disease and the problem got resolved , hereby it shows the need of pharmacist in the area of patient care and quality treatment in the present scenario to expect quality of life.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2640
|
PharmaTutor (Print-ISSN: 2394 - 6679; e-ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 7, Issue 01 Received On: 13/11/2018; Accepted On: 27/12/2018; Published On: 01/01/2019 How to cite this article: Dasari, B. kumar, T, M., gaju, R. kumar, velpula, S., Vallepu, N. and Adepu, P. 2019. A case report on Chronic Kidney Disease and Role of Clinical Pharmacist. PharmaTutor. 7, 1 (Jan. 2019), 59-62. DOI:https://doi.org/10.29161/PT.v7.i1.2019.59 |
INTRODUCTION
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) or chronic renal failure { CRF} is a condition in which there is a reduction in rate of kidney function for over a period of months or years. In beginning there will be no symptoms. Later, edema, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, or confusion may arise. Complications may include heart disease, HTN, bone disease, or anaemia. If there is no perfect therapeutic regimen it may lead to total renal system damage. CKD is very common and is mainly associated with ageing. The older you get, the more likely you are to have some degree of kidney disease. It is estimated that about one in five men and one in four women between the ages of 65 and 74 has some degree of CKD.
CKD is mostly associated with the effects caused by other chronic diseases, (hypertension) and diabetes mellitus type 2
Its seen commonly in population of India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Pakistan) and black people than the other population. higher rates of diabetes in south Asian people and high blood pressure in African or Caribbean people are the main reasons for this condition.
Case Report
A female patient of age 60 yrs was admitted into a multispecialty hospital with the chief complaints of SOB, confusion, fever Since 3dys ,she had a past medical history of HTN . the clinical and laboratory findings of the patient were found to be
• Temp-100 F
• BP- 190/40mmHg
• pulse-85/min
• WBC- 15000cu/mm
• Urea - 149 mg%
Clinical symptoms
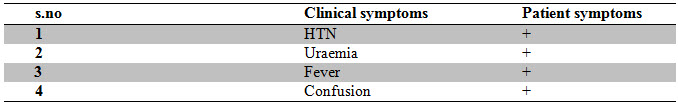
Classification of chronic kidney disease
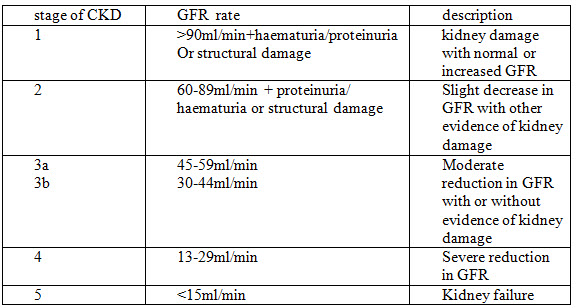
Discussion :
Patient’s data was collected in a profile form and the details were saved confidentially .the patient was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease with HTN and the treatment was started with
DRUGS:
Ranitidine 1amp -IV -TID
Piperacillin /tazobactam 4.5g - IV - BID
Furosemide - 50mg -IV -TID
Ondansetron - 4g- IV -BD
Insulin glargine 15mg P/O -BD
Cyanocobalamin - 1amp IV -OD
Nitrofurantoin - 100mg P/O –BD
Present scenario in this case reveals that The patient had HTN which is not in control because of illiteracy and medication adherence to anti hypertensives , which lead to the present condition of the patient . then treatment initiated and patient counselling regarding life style modifications, drugs and their side effects with regular follow up.
Patient counselling :
Diet
A healthy diet is important for preventing chronic kidney disease (CKD). It will lower the amount of cholesterol in your blood and keep your blood pressure at a healthy level. Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables (five portions a day) and whole grains.
Limit the amount of salt in your diet to no more than 6g (0.2oz) a day. Too much salt will increase your blood pressure. One teaspoonful of salt is equal to about 6g.
Avoid eating foods that are high in saturated fat because this will increase your cholesterol level.
Foods that are high in saturated fat include:
• meat pies
• sausages and fatty cuts of meat
• butter
• ghee (a type of butter often used in Indian cooking)
• lard
• cream
• hard cheese
• cakes and biscuits
• foods that contain coconut oil or palm oil
Eating some foods that are high in unsaturated fat can help decrease your cholesterol level. Foods that are high in unsaturated fat include:
• oily fish
• avocados
• nuts and seeds
• sunflower oil
• rapeseed oil
• olive oil
Alcohol
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol will cause your blood pressure to rise, as well as raising the cholesterol levels in your blood. Therefore, sticking to the recommended alcohol consumption limits is the best way to reduce your risk of developing high blood pressure (hypertension) and CKD.
The recommended limits for alcohol are:
• 21 standard drinks of alcohol a week for men
• 14 standard drinks of alcohol a week for women
A standard drink of alcohol is equal to about half a pint of normal strength beer, a small glass of wine or a pub measure of spirits. For more information,
Exercise
Regular exercise should help lower your blood pressure and reduce your risk of developing CKD.
At least 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) of moderate-intensity aerobic activity (i.e. cycling or fast walking) every week, is recommended.
Avoid nephrotoxins eg; NSAIDS etc
CONCLUSION : the patient was given a complete course and was given counselling for chronic kidney disease and the problem got resolved , hereby it shows the need of pharmacist in the area of patient care and quality treatment in the present scenario to expect quality of life.
Comprehensive listing of clinical pharmacy activities performed in CKD and ESRD patients
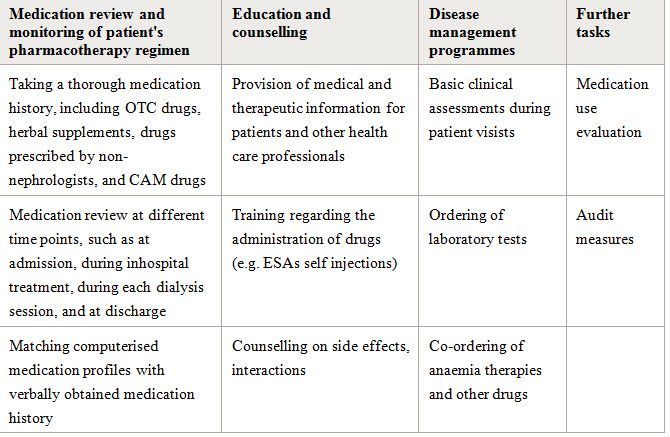
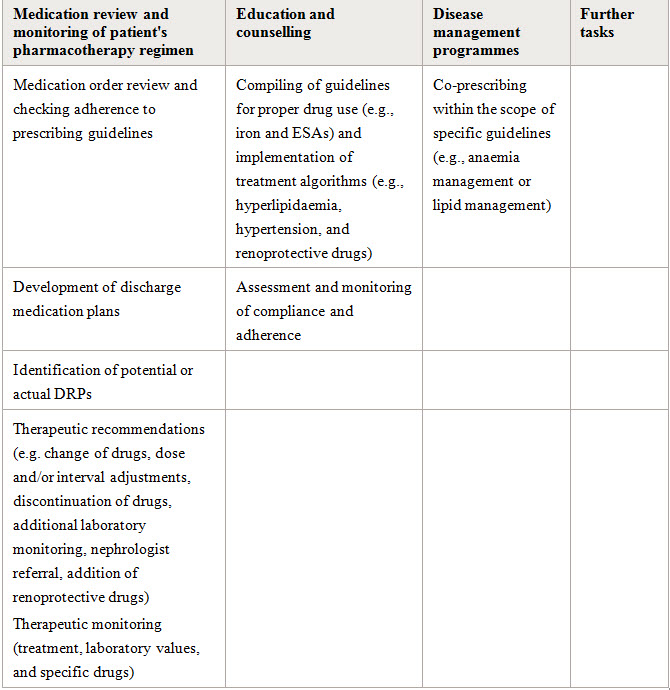
Abbrevations used
CAM: complementary and alternative medicines
CKD: chronic kidney disease
DRP: drug-related problem
ESA: erythropoiesis stimulating agent
ESRD: end-stage renal disease
HTN: Hypertension
REFERENCES
1. Gunar Stemer and Lemmens-Gruber R. (2011); Clinical pharmacy activities in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease patients: a systematic literature review; BMC Nephrology; 12; 35
2. Roger Walker, and Cate Whittlesea (2012); Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 5th Edition; Churchill Livingstone; London.
3. https://www.hse.ie/eng/health/az/c/chronic-kidney-disease
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









