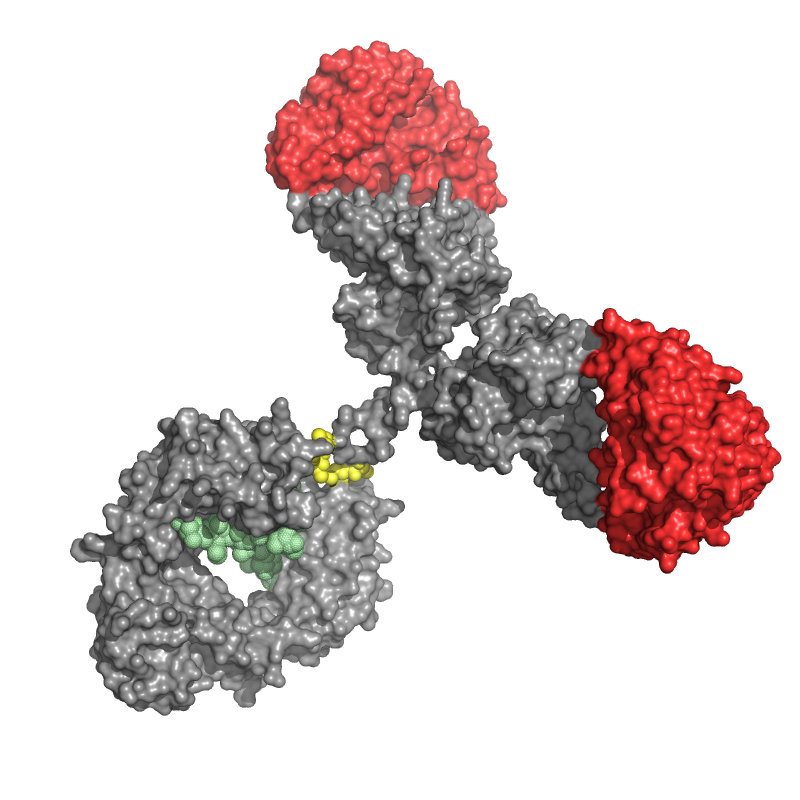
In red the part that binds to the virus, in grey the “tail” of the antibody (named Fc) that binds the receptors of the antibodies present on the different types of cells, and in yellow the LALA mutation that blocks the binding of the antibody to such receptors.
A team of researchers from the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB, USI Università della Svizzera italiana) and the Swiss biotech company Humabs BioMed SA has identified novel therapeutic monoclonal antibody candidates isolated from Zika-infected patients and new strategies for Zika virus diagnostics. An article published today in the renowned scientific journal Science describes for the first time an in-depth analysis of the human antibody and T cell immune response to the Zika virus infection with important implications for differential diagnostics and for the development of vaccines and new treatments.








