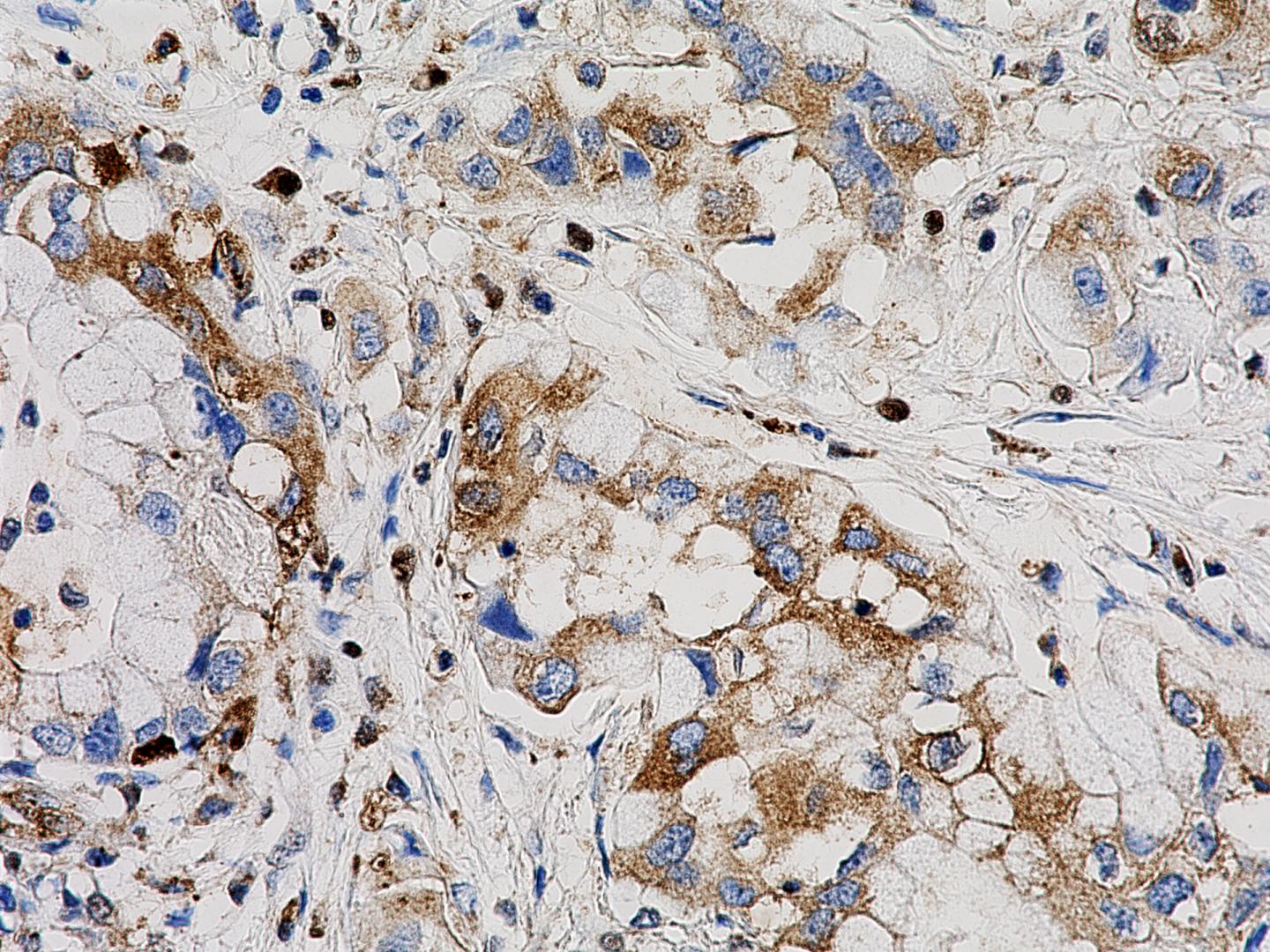
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), through its New Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative (NMITLI) program, has approved a project towards development of human monoclonal antibodies (hmAbs) that can neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in patients. This project on generation of neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies as a therapeutic strategy will be implemented by a multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary team.