ISOTOPE EFFECTS
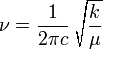
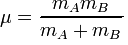
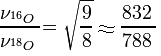
TWO DIMENSIONAL IR SPECTROSCOPY (2DIR)
Two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy is a nonlinear infrared spectroscopy technique that has the ability to correlate vibrational modes in condensed-phase systems.
This technique provides information beyond linear infrared spectra, by spreading the vibrational information along multiple axes, yielding a frequency correlation spectrum.
Experiments of two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy have only become possible with the development of ultra fast lasers and the ability to generate femtosecond infrared pulses.









