About Authors:
Chandan bisht1*, Dr.Jagannath sahoo2, Dr.M.Irfan Khan3
1,2 Shri Ram Murti Smarak college of Eng. & Tech( department of pharmacy) Bareilly.
3 Deccan Healthcare pvt. Ltd. Pantnagar industrial area
*chandanbisht2011@gmail.com
Abstract:
Mouth dissolving tablets (MDT) are useful in patients, such as pediatric, geriatric, bedridden, or developmentally disabled, who may face difficulty in swallowing conventional tablets or capsules and liquid orals or syrup, leading to ineffective therapy, with persistent nausea, sudden episodes of allergic attack, or coughing for those who have an active life style. Over the past three decades, mouth dissolving tablets have gained considerable attention as a preferred alternative to conventional tablets and capsules due to better patient compliance The objective of this article is to review the development of MDTs, challenges in formulation, benefit, limitation ,new MDT technologies and evaluation methodologies.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1706
INTRODUCTION
1. Mouth Dissolving Tablet
Oral drug delivery has been known for decades as the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for the systemic delivery of drugs via various pharmaceutical products of different dosage forms. The reason that the oral route achieved such popularity may be in part attributed to its ease of administration.
All the pharmaceutical products formulated for systemic delivery via the oral route of administration, irrespective of the mode of delivery (immediate, sustained or controlled release) and the design of dosage forms (solid, dispersion or liquid) must be developed within the intrinsic characteristics of GI physiology. Therefore, a fundamental understanding of various disciplines, including GI physiology, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and formulation design are essential to achieve a systemic approach to the successful development of pharmaceutical dosages forms. The more sophisticated a delivery system, the greater is the complexity of these various disciplines involved in the design and optimization of the delivery system. In any case, the scientific framework required for the successful development of an oral drug delivery system consists of a basic understanding of the following three aspects.
* Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics characteristics of the drug.
* The anatomic and physiologic characteristics of the GIT.
* Physicochemical characteristics and the drug delivery mode of the dosage form to be designed1.
Oral routes of drug administration have wide acceptance up to 50-60% of total dosage forms. The most popular solid dosage forms are being tablets and capsules; one important drawback of this dosage forms for some patients, is the difficulty to swallow.
Solid dosage forms are popular because of
* accurate dosage
* self-medication
* ease of administration
* pain avoidance
* patient compliance.
Drinking water plays an important role in the swallowing of oral dosage forms. Often times people experience inconvenience in swallowing conventional dosage forms such as tablet when water is not available, in the case of the motion sickness (kinetosis) and sudden episodes of coughing during the common cold, allergic condition and bronchitis. For these reasons, tablets that can rapidly dissolve or disintegrate in the oral cavity have attracted a great deal of attention. Rapidly dissolving or disintegrating tablets are not only indicated for people who have swallowing difficulties, but also are ideal for active people2.
Mouth dissolving tablets are also called as fast dissolving tablets, melt-in mouth tablets, Orodispersible tablets, rapimelts, porous tablets, quick dissolving etc. Mouth dissolving tablets are those when put on tongue, disintegrate instantaneously releasing the drug which dissolves or disperses in the saliva .Faster the drug into solution, quicker the absorption and onset of clinical effect.

Fig no.1: Conceptual Diagram of MDT’s
Some drugs are absorbed from the mouth, pharynx and esophagus as the saliva passes down into the stomach. In such cases, bioavailability of drug is significantly greater than those observed from conventional tablets dosage form. The bioavailability of some drugs may be increased due to absorption of drug in oral cavity and also due to pregastric absorption of saliva containing dispersed drugs that pass down into the stomach. Moreover, the amount of drug that is subjected to first pass metabolism is reduced as compared to standard tablet. The advantage of mouth dissolving dosage forms are increasingly being recognized in both, industry and academics3.
Mouth dissolving drug delivery systems (MDDDS) are a new generation of formulations which combine the advantages of both liquid and conventional tablet formulations and at the same time, offer added advantages over both traditional dosage forms. They provide the convenience of a tablet formulation and also allow the ease of swallowing provided by a liquid formulation. MDDDS offer the luxury of much more accurate dosing than the primary alternative, oral liquids. This segment of formulation is especially designed for dysphagic, geriatric, pediatric, bed-ridden, travelling and psychotic patients who are unable to swallow or refuse to swallow conventional oral formulations. They do not require water for administration, thus are good alternative for travelers and for bed ridden patients. They simply vanish when placed in the mouth, so cannot be hidden in mouth by psychotic patients. These products not only increase the patient’s compliance but also fetch large revenues to manufacturers due to line extension of the existing formulation. In the recent past, several new advanced technologies have been introduced for the formulation of mouth dissolving tablets (MDTs) with very interesting features, like extremely low disintegration time, exceptional taste masking ability, pleasant mouth feel and sugar free tablets for diabetic patients. The technologies utilized for fabrication of MDDDS include lyophilization, moulding, direct compression, cotton candy process, spray drying, sublimation, mass extrusion, nanonization and quick dissolve film formation. These techniques are based on the principles of increasing porosity and/or addition of superdisintegrants and water soluble excipients in the tablets. The formulations prepared from these techniques differ from each other on the basis of the factors like mechanical strength of final product, drug and dosage form stability, mouth feel, taste, rate of dissolution of the formulation in saliva, rate of absorption from saliva and overall drug bioavailability5.
Although, numerous technologies had been developed for the fabrication of these unique dosage forms in last two decades, but so far, no standardized technique has been designed or mentioned in pharmacopoeias for their evaluation except in European Pharmacopoeia (EP), which defines Orodispersible tablets as “uncoated tablets intended to be placed in the mouth where they disperse rapidly before being swallowed”. EP also specifies that the Orodispersible tablets should disintegrate within 3 minutes when subjected to conventional disintegration test used for tablets and capsules. Orally Disintegrating (OD) tablet technology has been approved by United state Pharmacopoeia (USP), Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). USFDA defined OD tablet as ” A solid dosage form containing medicinal substance , which disintegrate rapidly ,usually within a matter of seconds , when placed upon the tongue”6.
Despite various terminologies used, Mouth dissolving tablets are here to offer unique form of dug delivery with advantages over the conventional oral solid dosage forms.
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
1.1. Criteria for Mouthdissolving Drug Delivery System7
The tablets should
* Not require water to swallow, but it should dissolve or disintegrate in the mouth in matter of seconds.
* Be compatible with taste masking.
* Be portable without fragility concern.
* Have a pleasant mouth feel.
* Leave minimum or no residue in the mouth after oral administration.
* Exhibit low sensitive to environmental condition like temperature and humidity
* Allow the manufacture of the tablet using conventional processing and packaging equipments, at low cost.
1.2. Salient Feature of MouthDissolving Drug Delivery System 7
* Ease of Administration to the patient who cannot swallow, such as the elderly, stroke victims, bedridden patients and patient who refuse to swallow such as pediatric, geriatric & psychiatric patients.
* No need of water to swallow the dosage form, which is highly convenient feature for patients who are traveling and do not have immediate access to water.
* Rapid dissolution and absorption of the drug, which will produce quick onset of action.
* Some drugs are absorbed from the mouth, pharynx and esophagus as the saliva passes down into the stomach. In such cases bioavailability of drug is increased.
* Pregastric absorption can result in improved bioavailability and as a result of reduced dosage; improve clinical performance through a reduction of unwanted effects.
* Good mouth feel property helps to change the perception of medication as bitter pill particularly in pediatric patient.
* The risk of chocking or suffocation during oral administration of conventional formulation due to physical obstruction is avoided, thus providing improved safety.
* New business opportunity like product differentiation, product promotion, patent extensions and life cycle management.
1.3 Benifits of MouthDissolving Tablets 7:
* Administered without water, anywhere, any time.
* Suitability for geriatric and pediatric patients, who experience difficulties in swallowing and for the other groups that may experience problems using conventional oral dosage form, due to being mentally ill, the developmentally disableand the patients who are un-cooperative, or are on reduced liquid intake plans or are nauseated.
* Beneficial in cases such as motion sickness, sudden episodes of allergic attack orcoughing, where an ultra-rapid onset of action required.
* An increased bioavailability, particularly in cases of insoluble and hydrophobic drugs, due to rapid disintegration and dissolution of these tablets.
* Stability for longer duration of time, since the drug remains in solid dosage form till it is consumed. So, it combines advantage of solid dosage form in terms of stability and liquid dosage form in terms of bioavailability.
* Pregastric absorption can result in improved bioavailability, reduced dose and improved clinical performance by reducing side effects.
1.4. Limitations of Mouth Dissolving Tablets 8
* The tablets usually have insufficient mechanical strength. Hence, careful handling is required.
* The tablets may leave unpleasant taste and/or grittiness in mouth if not formulated properly.
1.5. Development challenges in Mouth Dissolvingdrug delivery systems 9
1.5.1. Palatability
As most drugs are unpalatable, orally disintegrating drug delivery systems usually contain the medicament in a taste-masked form. Delivery systems disintegrate or dissolve in patient’s oral cavity, thus releasing the active ingredients which come in contact with the taste buds; hence, taste-masking of the drugs becomes critical for patient compliance.
1.5.2. Mechanical strength
In order to allow ODTs to disintegrate in the oral cavity, they are made of either very porous and soft-molded matrices or compressed into tablets with very low compression force, which makes the tablets friable and/or brittle, difficult to handle and often requiring specialized peel-off blister packing that may add to the cost.
1.5.3. Hygroscopicity
Several orally disintegrating dosage forms are hygroscopic and cannot maintain physical integrity under normal conditions of temperature and humidity. Hence, they need protection from humidity which calls for specialized product packaging.
1.5.4. Amount of drug
The application of technologies used for ODTs is limited by the amount of drug that can be incorporated into each unit dose. For lyophilized dosage forms, the drug dose must be lower than 400 mg for insoluble drugs and less than 60 mg for soluble drugs. This parameter is particularly challenging when formulating a fast- dissolving oral films or wafers.
1.5.5. Aqueous solubility
Water soluble drugs pose various formulation challenges because they form eutectic mixtures, which result in freezing-point depression and the formation of a glassy solid that may collapse upon drying because of loss of supporting structureduring the sublimation process. Such collapse sometimes can be prevented by using various matrix-forming excipients such as mannitol than can induce crystallinity and hence, impart rigidity to the amorphous composite.
1.5.6. Size of tablet
The degree of ease when taking a tablet depends on its size. It has been reported that the easiest size of tablet to swallow is 7-8 mm while the easiest size to handle was one larger than 8 mm. Therefore, the tablet size that is both easy to take and easy to handle is difficult to achieve.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
2. Techniques of MDT Formulation
The fast-dissolving property of the MDTs is attributed to quick ingress of water into tablet matrix resulting in rapid disintegration. Hence, the basic approaches to develop MDTs include:
• Maximizing the porous structure of the tablet matrix.
• Incorporating the appropriate disintegrating agent/agents.
• Using highly water-soluble excipients in the formulation
2.1 Techniques for Preparing Fast dissolving Tablets 10
Many techniques have been reported for the formulation of Mouth dissolving tablets or Orodispersible tablets.
1. COMPACTION
a. Direct Compression by using Sugar Based Excipients
b. Wet/Dry Granulation using Superdisintegrants
2. Lyophilization
3. Phase transition process
4. Sublimation
5. Tablet Moulding
6. Mass extrusion
7. Spray drying
8. Cotton Candy Process
Methods for designing Orodispersible tablets4, 7, 10
2.1.1. Compaction
a. Direct Compression by using Sugar Based Excipients
This method consists of directly compressible blend, which consists of an excipient and an active ingredient. The excipient consists of a disintegrating agent and one hydrophilic diluent selected from the polyols having less than 13 carbon atoms. Polyols most commonly used are xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol and maltitol. Directly compressible form or various ratios of compressible and powder form of polyols are used in these methods. Disintegrating agents most commonly used are Crospovidone, Croscaramellose sodium and Sodium starch glycollate. In addition to these ingredients, sweeteners and lubricants are incorporated in the formulation. Good aqueous solubility and sweeteners impart a pleasing mouth feel and good taste masking. But not all the sugar based excipients have fast dissolving action and good compressibility and/or compatibility. However, technologies were developed to make use of the sugar-based excipients in the design of fast dissolving tablets.
b. Wet/Dry Granulation using Superdisintegrants
Wet/Dry granulation techniques with superdisintegrants can be used to prepare fast dissolving tablets. Crospovidone, Croscaramellose sodium and Sodium starch glycollate are used as superdisintegrants. Active drug, diluents, binder, lubricants, glidants are used along with disintegrants. In wet granulation technique, disintegrants are added in both wet granulation step and dry blending step. Disintegrating agents have the ability to swell when exposed to GIT fluids resulting in rapid disintegration. Sweeteners and flavors are also added to dry blending step to improve palatability.
2.1.2. LYOPHILIZATION
Lyophilization can be used to create an amorphous, porous structure that commonly dissolves rapidly. The lyophilization process imparts glossy amorphous structure to the bulking agent and sometimes to the drugs, thus enhancing the dissolution characteristics of the formulation. But this method is not commonly used because of its high cost of equipment and processing. It also produces dosage forms with lack of physical resistance. The most commonly used matrix forming agents are gelatins and sugar based excipients.
2.1.3. Phase transition process
Tablets were produced by compressing a powder containing two sugar alcohols, with high and low melting points and they are subsequently heated to a temperature between their melting points. Before heating process, the tablets do not have sufficient hardness because of low compatibility. The tablet hardness was increased after heating process, due to the increase of inter particle bonds or the bonding surface area in tablets induced by phase transition of lower melting point sugar alcohol.
2.1.4. Sublimation
Tablets prepared by a water soluble material like Mannitol, give slow dissolution rates due to low porosity. Porosity can be increased by incorporating subliming agents like Urea, Ammonium bicarbonate, Ammonium carbonate, Camphor to the other tabletting ingredients and the mixture is compressed into tablets. The volatile materials are then removed by sublimation, which generates porous structures. Additionally, several solvents such as water, Cyclohexane, and Benzene can be used as pore forming agent.
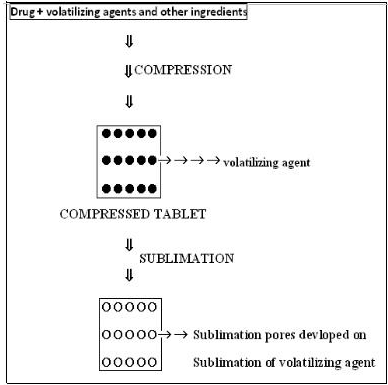
Fig no 2: - Sublimation method
2.1.5. Tablet molding
This method consists of suspending an active ingredient and a sugar into agar aqueous solution. Suspension is filled in molds to solidify into a jelly and subsequently dried. Drying can be affected by reduced pressure drying or aeration drying. Additional components like flavor, sweeteners, colors and preservatives may be added to improve taste, stability, appearance, etc.
Another method where sugar, active component, and other excipients are mixed with a small volume of volatile liquid binder to form slightly wet lump. This lump is then forced into molds and evaporated the liquid binder. Sugars, which can be used, are Mannitol or Lactose. These types of products disintegrate or dissolve within 5 to 20 seconds.
2.1.6. Mass extrusion
This technology involves softening the active blend using the solvent mixture of water-soluble Polyethylene glycol, using Methanol and expulsion of softened mass through the extruder or syringe, to get a cylindrical product and cut into even segments using heated blade to form tablets.
2.1.7. Spray drying
Compressing highly porous support matrix, produced by spray drying, with active ingredient gives fast dissolving tablets. The support matrix composed of non-hydrolyzed gelatin or hydrolyzed gelatin, bulking agent, volatizing agent like Ethanol, acidifying or alkalizing agent to maintain the net charge. Most commonly used bulking agents are Mannitol, Sorbitol, Sucrose, Lactose, etc. Croscaramellose sodium, Crospovidone, Sodium starch glycollate and a small amount of effervescent material may be added to assist in the disintegration of the tablet. Additionally sweeteners, flavors and lubricants may be added.
2.1.8. Cotton Candy process
This process is so named as it utilizes a unique spinning mechanism to produce floss-like crystalline structure, which mimic cotton candy. Cotton candy process involves formation of matrix of polysaccharides or saccharides by simultaneous action of flash melting and spinning. The matrix formed is partially recrystallized to have improved flow properties and compressibility. This candy floss matrix is then milled and blended with active ingredients and excipients and subsequently compressed to ODT. This process can accommodate high doses of drug and offers improved mechanical strength. However, high-processing temperature, limits the use of this process.
3. Important Patented Technologies for Fast Dissolving Tablets4, 7, 10
3.1. Zydis Technology
Zydis formulation is a unique freeze dried tablet in which drug is physically entrapped or dissolved within the matrix of fast dissolving carrier material. When Zydis units are put into the mouth, the freeze-dried structure disintegrates instantaneously and does not require water to aid swallowing. The Zydis matrix is composed of many materials designed to achieve a number of objectives. To impart strength and resilience during handling, polymers such as gelatin, dextran or alginates are incorporated. These form a glossy amorphous structure, which imparts strength.
To obtain crystallinity, elegance and hardness, saccharides such as mannitol or sorbitol are incorporated. Water is used in the manufacturing process to ensure production of porous units to achieve rapid disintegration while various gums are used to prevent sedimentation of dispersed drug particles in the manufacturing process. Collapse protectants such as glycine prevent the shrinkage of zydis units during freeze-drying process or on long-term storage. Zydis products are packed in blister packs to protect the formulation from moisture in the environment.
3.2. Durasolv Technology
Durasolv is the patented technology of CIMA labs. The tablets made by this technology consist of drug, filler and a lubricant. Tablets are prepared by using conventional tableting equipment and have good rigidity. These can be packaged into conventional packaging system like blisters. Durasolv is an appropriate technology for product requiring low amounts of active ingredients.
3.3. Orasolv Technology
CIMA labs have developed Orasolv Technology. In this system active medicament is taste masked. It also contains effervescent disintegrating agent. Tablets are made by direct compression technique, low compression force in order to minimize oral dissolution time.
Conventional blenders and tablet machine is used to produce the tablets. The tablets produced are soft and friable.
3.4. Flash Dose Technology
Flash dose technology has been patented by fuisz. Nurofen meltlet, a new form of ibuprofen as melt in mouth tablets prepared using flash dose technology & is the first commercial product launched by Biovail Corporation. Flash dose tablets consist of self-binding shear form matrix termed as “floss”. Shear form matrices are prepared by flash heat processing.
3.5. Wow tab Technology
Wow tab technology is patented by Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. WOW means “Without Water”. In this process, combination of low mouldable and high mouldable saccharides is used to obtain a rapidly melting, strong tablet. The active ingredient is mixed with a low mouldable saccharides (e.g. lactose, glucose, and mannitol) and granulated with a highly mouldable saccharides (e.g. Maltose, oligosaccharides) and compressed into tablet.
3.6. Flash tab Technology
Prographarm laboratories have patented the Flash tab technology. Tablet prepared by this system consists of an active ingredient in the form of micro crystals. Drug micro granules may be prepared by using the conventional techniques like coacervation, micro encapsulation and extrusion spheronisation.
3.7. LYOC Technology
This was the first freeze drying- based technology introduced for ODTs. The process involves preparation of a liquid solution or suspension of the drug containing fillers, thickening agents, surfactants, non-volatile flavoring agents, and sweeteners. This homogenous liquid is deposited in blister cavities and subjected to freeze drying. Advantages of Lyoc compared to other freeze-dried dosage forms include absence of preservatives.
3.8. ORAQUICK Technology
KV Pharmaceutical’s two proprietary taste-masking technologies, FlavorTech and Micro Mask , are utilized for developing OraQuick tablets. Micro Mask provides taste masking by incorporating a drug into matrix microspheres. The first step involved in formulating the tablet include dissolving the sugar (sucrose, mannitol, sorbitol, xylose, dextrose, fructose, or mannose), and protein (albumin or gelatin) in a suitable solvent such as water, Ethanol, Isopropyl alcohol, and Ethanol– water mixture. The porosity of the product is determined by the quantity of solvent used in the formulation. The solution of the matrix is then spray dried, yielding highly porous granules. The matrix granules are mixed with other excipients such as binder, lubricant, sweeteners, flavors, coloring agent, fillers, disintegrants, surfactants, etc. The drug can be added at this stage in the form of taste-masked granules, otherwise added first in the matrix granule. The granules or powder obtained is then compressed at low compression force to form tablets that are soft and friable but highly porous. After the tablets are compressed, they are subjected to a sintering step. Tablets are sintered in an oven, typically at temperature of about 50°C to 100°C for few minutes to an hour’s or at 90°C for about 10 min. During this step, the compressed tablets containing binder (Polyethylene glycol) in the earlier step melts and binds particles to form stronger tablet.
3.9. ADVATAB Technology
The primary ingredients in the dosage form include sugar alcohols and saccharides with particle size less than 30µm along with disintegrant and lubricant. The lubricant used in the formulation is added as an external lubricant compared to conventional formulations, which contain an internal lubricant. This make tablets stronger in comparison to conventional tablets, as internal lubricants are hypothesized to decrease binding of the drug particles. The dosage forms are manufactured using conventional tableting and packaging equipments. The tablets, which can handle high drug loading and coated particles, can be packed in both bottles and pushed through blisters.
3.10. FROSTA Technology
This technology incorporates manufacture of highly plastic granules using a plastic material, a material enhancing water penetration, and a wet binder. These granules can then be compressed into tablets at low pressure, thus enabling fast disintegration upon administration.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Table no.1: List of commercially available orally disintegrating tablets4
|
Trade Name |
Active Ingredient |
Category |
Technology |
Manufacturer |
|
Feldene Fast Melt |
Piroxicam |
Anti-rheumatic |
Zydis |
Pfizer Inc. NY. USA |
|
Claritin Redi Tab |
Loratidine |
Anti-histaminic |
Zydis |
Schering Plough Corp. USA |
|
Maxallt MLT |
Rizatriptan |
Anti-migrain |
Zydis |
Merck & Co., Nj, USA. |
|
Ppcid RPD |
Famotidine |
Anti-histaminic |
Zydis |
Merck & Co., Nj, USA. |
|
Rispetdal M-tab |
Risperidone |
Schizophernia |
Zydis |
Jannsen |
|
Zubrin (pet drug) |
Tepoxalin |
Canine NSAID |
Zydis |
Schering Plough Corp. USA |
|
Zofran ODT |
Ondansetron |
Anti-emetics |
Zydis |
Glaxo Wellcome, Middlesex, UK. |
|
Klonopin Wafer |
Clonazepam |
Sedation |
Zydis |
Roche |
|
Imodium Instant Melts |
Loperamide HCl |
Anti-Diarrheal |
Zydis |
Jannsen |
|
Tempra Quicklets |
Acetaminophen |
Antipyretic |
OraSolv |
Bristol Myers Squibb, NY, USA. |
|
Remeron SolTab |
Mirtazapine |
Anti-depression |
OraSolv |
Organon Inc. |
|
Triaminc Softchews |
Various combinations |
Pediatriccold, cough and allergy |
OraSolv |
Novartis Consumer Health |
|
Zoming- ZMT |
Zolmitriptan |
Anti-migignaine |
Durasolv |
Astra Zeneca, Wilmington, USA. |
|
Alavert |
Loratadine |
Anti-histaminic |
Durasolv |
Wyeth Consumer Healthcare |
|
NuLev |
Hyoscyamines sulfate |
Anti-ulcer |
Durasolv |
Schwarz Pharma |
|
Kemsstrro |
Baclofen |
Anti-spastic analgesic |
Durasolv |
Schwarz Pharma |
|
Benadryi Fast Melt |
Diphenhydramine & Pseudophidrine. |
Anti –allergic |
WOWTAB |
Warner Lambert NJ, USA. |
|
Nasea OD |
Ramosetoron HCl |
Anti-emetics |
WOWTAB |
Yamanouchi |
|
Gaster D |
Famotidine |
Anti-ulcer |
WOWTAB |
Yamanouchi |
|
Ralivia FlashDose |
Tramadol Hcl |
Analgesics |
FlashDose |
Biovail |
|
Zolpidem ODT |
Zopidem Tartrate |
Sleep Disorders |
FlashDose |
Biovail |
|
Fluoxetine ODT |
Fluoxetine |
Anti-depression |
FlashDose |
Biovail |
|
Hyoscyamine sulfate ODT |
Hyoscyamine sulfate |
Anti-ulcer |
OraQuick |
ETHEX Corporation |
Superdisintegrants are used to improve the efficacy of Mouth Dissolving dosage forms, by decreasing their disintegration time, which in turn enhances drug dissolution rate. Disintegrants are substances or mixture of substances added that are to drug formulations to facilitates their breakup or disintegration into smaller particles that dissolve more rapidly than in the absence of disintegrants.11
Superdisintegrants are generally used at a low level in the solid dosage form, typically 1% to 10 % w/w.
Mechanism of Superdisintegrants7
There are four major mechanisms for tablets disintegration as follows
1. Swelling
Perhaps the most widely accepted general mechanism of action for tablet disintegration is swelling. Tablets with high porosity show poor disintegration due to lack of adequate swelling force. On the other hand, sufficient swelling force is exerted in the tablet with low porosity. It isworthwhile to note that if the packing fraction is very high, fluid is unable to penetrate in the tablet and disintegration is again slows down.
2.Porosity and capillary action (Wicking)
Disintegration by capillary action is always the first step. When we put the tablet into suitableaqueous medium, the medium penetrates into the tablet and replaces the air adsorbed on the particles, which weakens the intermolecular bond and breaks the tablet into fine particles. Water uptake by tablet depends upon hydrophilicity of the drug/excipient and on tableting conditions. For these types of disintegrants, maintenance of porous structure and low interfacial tension towards aqueous fluid is necessary which helps in disintegration by creating a hydrophilic network around the drug particles.
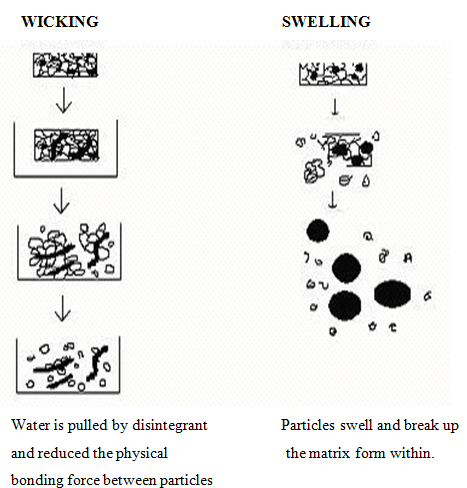
Fig no. 3: Wicking and Swelling mechanism of Superdisintegrant’s action
3. Due to disintegrating particle-particle repulsive forces
Another mechanism of disintegrant attempts to explain the swelling of tablet made with ‘non-swellable’ disintegrants. Guyot-Hermann has proposed a particle repulsion theory based on the observation that non-swelling particle also cause disintegration of tablets22. The electric repulsive forces between particles are the mechanism of disintegration that requires water. Researchers found that repulsion is secondary to wicking.
4. Due to deformation
During tablet compression, particles get deformed and these deformed particles return back to their normal structure, when they come in contact with aqueous media or water. Occasionally, the swelling capacity of starch was improved when granules were extensively deformed during compression. This increase in size of the deformed particles produces a breakup of the tablet.
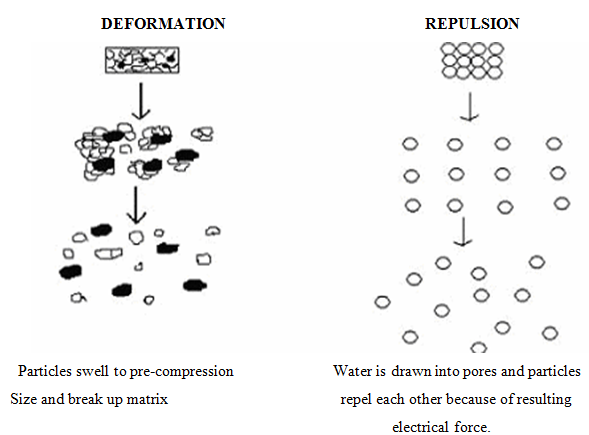
Fig no. 4: Deformation and Repulsion mechanism of Superdisintegrant’s action
Table no. 2: Classification of Superdisintegrants and their mechanism of action11.
|
Superdisintegrants
|
Example
|
Mechanism Of action
|
Special comment |
|
Crosslinked cellulose
|
Crosscarmellose , Ac-Di-Sol, Nymce ZSX, Primellose, Solutab, Vivasol, L-HPC |
Swells 4-8 folds in less than 10 seconds, Swelling and wicking both. |
Swells in two dimensions.Used in Direct compression or Starch free granulation. |
|
Crosslinked PVP
|
Crosspovidone, Crosspovidon M, Kollidon, Polyplasdone |
Swells very little and returns to original size after compression but act by capillary action. |
Water insoluble and spongy in nature, makes porous tablet.
|
|
Crosslinked starch
|
Sodium |









