 About Authors:
About Authors:
Renu1*, Shashi Kant2*, Rajendra Yadav3, Amit Kumar Tyagi4
1Faculty of Pharmacy, Shivdan Singh Institute of Technology and Management, Aligarh (U.P)
2Jubilant Chemsys Ltd, Noida,
3Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Gurukul Kangri University Haridwar,
4Department of Chemistry, Meerut College, Meerut (U.P)
*shashi.pharma83@gmail.com
ABSTRACT :
Diclofenac is currently the eighth largest-selling drug and the most frequently used NSAID (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) in the world, since its introduction in Japan in 1974. Diclofenac is among the better tolerated NSAIDs. Only major adverse effect of Diclofenac is that it causes direct and indirect irritation of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). To reduce the side effects on gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and to improve therapeutic efficacy of Diclofenac, it can be formulated in polymeric microspheres.
The use of polymeric carriers in formulations of therapeutic drug delivery systems has gained widespread application, due to their advantage of being biodegradable and biocompatible. Among the microparticulate systems, microspheres have a special importance since it is possible to target drugs and provide controlled release. Diclofenac sodium (DS), is a potent drug in the NSAID group having non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory properties, and is widely used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. In this present study, it was aimed to prepare microsphere formulations of DS using a natural biodegradable polymer as a carrier for administration to extend the duration period of the dosage form. Microsphere formulations of DS which were prepared were evaluated in vitro for particle size, yield value, encapsulation efficiency, surface morphology, and in vitro drug release.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1413
INTRODUCTION:
Microspheres are the colloidal drug delivery system. Microspheres are characteristically free-flowing powders consisting of proteins/synthetic polymers that are biodegradable in nature and ideally having a particle size less than 200mm. Biodegradable microspheres can be utilized to direct drugs to certain organs through capillary blockade. Its success depends on the size of the microspheres used and on the mode of administration (intravenous/intra-arterial). [1]
Microspheres are reported to possess high specificity and good controlled release properties were exhibited by using biodegradable polymers. [2]
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually abbreviated as NSAIDs, they reduce Pain, fever and inflammation. During the last few decades, there has been a substantial increase in the number of clinically available NSAIDs in the pharmaceutical market. NSAIDs annually account for 70 million prescriptions and 30 billion over-the-counter (OTC) medications sold in the United States alone. [3]
Diclofenac is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) which is indicated in relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and also in relief of migraines, menstrual pain. Diclofenac is used commonly to treat mild to moderate post-operative or post-traumatic pain, particularly when inflammation is also present. [4-6]
Diclofenac is among the better tolerated NSAIDs. The main adverse drug reactions associated with use of Diclofenac relate to direct and indirect irritation of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).As awareness about this side effects increases so is the increase of research to reduce side effects. To reduce the side effects on gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and to improve therapeutic efficacy of Diclofenac, research is done to formulate Diclofenac in polymeric microspheres and a satisfactory result is found. [7]
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Materials:
Drug: Diclofenac Sodium: Central Drug House New Delhi.
Polymer: Bovine serum albumin: Central Drug House New Delhi.
Chemical: Gluteraldehyde: Central Drug House New Delhi
Toluene : Qualigens Fine Chemical, Mumbai.
Acetone: Qualigens Fine Chemical, Mumbai.
Linseed oil: Qualigens Fine Chemical, Mumbai.
Instruments:
1. Magnetic stirrer: Remi Equipments, 2MLH, and Yamato LT4000.
2. Dissolution apparatus: Electro Lab, TDL- 08 L (USP).
3. U.V. Spectrometer: Shimajdu Corporation, Japan
4. Microscope: Radical, RM- 3, 20601
5. Oven: Shivaki, T-701
METHODS:
Prepare 2 ml of 25% albumin solution by dissolving 250 mg of serum in purified water. Disperse the drug in the polymer solution. Transfer the aqueous solution into a mixture of 40 ml linseed oil and 10 ml of toluene with continuous stirring at 2400 rpm. Continue stirring for 15 min. observe the particle size distribution under microscope. Add 2ml of gluteraldehyde saturated solution to the albumin solution with continuous stirring for 2 hours. Complete the cross linking process. Wash the suspension of microspheres each with toluene and with acetone. Between each washing discard the supernatant and resuspend the microspheres and at the end of washing with acetone. Suspend the microspheres in 10 ml of acetone and transfer it into a clean petridish.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Calibration curve for Diclofenac sodium in distilled water:
Prepare a solution of 100mg/ml drug in distilled water. Pipette out 1ml, 2ml, 3ml….10ml in volumetric flask and volume make up upto 10 ml by distilled water. Absorbance was taken out.
Physicochemical Evaluation of the Microspheres:
Percentage drug release and drug loading:
Percentage drug release and drug loading were calculated by using following formulas.
Drug Loading (%) = Particle Content
---------------------- x 100
Theoritical Yield
Determination of the drug content:
50 mg of microspheres was dissolved in distilled water containing few drops of Con. HCl. The solution was kept over night for incubation. Then the absorbance was taken at 276.5 nm and drug content found to be 4.86 mg.
Drug Content = Concentration x Dilution factor x bath volume
-------------------------------------------
1000
Determination of size distribution of particle:
Determine the average particle size by using optical microscopy technique using calibrated eye piece micrometer. Spread minute quantity of microsphere on a glass slide and determine average size particle.
Table: 1
|
Sl. No. |
No. of particle |
Size (µ) x |
X mean |
(x-x) |
(x-x)2 |
|
1. |
42 |
16.3474 |
14.03225 |
2.3151 |
5.3597 |
|
2. |
58 |
11.7171 |
14.03225 |
2.3152 |
5.3615 |
In-Vitrorelease study:
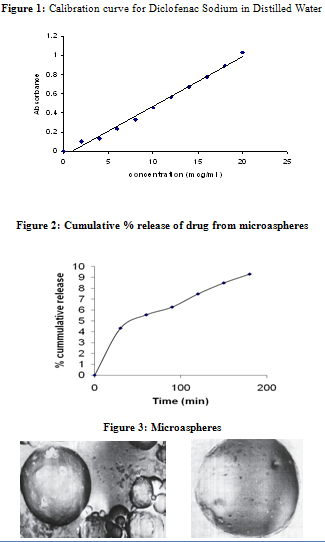
In vitro release of Diclofenac from BSA microspheres was determined in a USP Dissolution Apparatus using paddle method with six flasks in PBS at 37±0.5ºC, (Table: 2). The contents of the flasks were stirred at 100 rpm. 5 ml samples were taken and add simultaneously at 30 min intervals for the three hours and assayed by spectrophotometer at 276.5nm wavelength as mentioned above.
Amount Release = Conc x Bath Volume x Dilution Factor
------------------------------
1000
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
The objective of the present study is to prepare microspheres of bovine serum albumin by the emulsion cross-linking method. The prepared microspheres were subjected to various physicochemical evaluation and in vitro release studies. The drug release from microspheres is the most constant and prolonged drug release is diffusion followed by erosion. The characteristics of the prepared microspheres are conducive to the formulation of the sustained release drug delivery system.
In recent time some in-vivo studies are conducted to learn about the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic behavior of the drug after microencapsulation of Diclofenac. Determination of Pharmacodynamics of NSAIDs (In this case Diclofenac) is usually done in laboratory by injecting the drug formulated with microspheres into the knee joints of adjuvant induced arthritic laboratory animals.
CONCLUSION:
The Albumine microspheres are found as a good candidate for the drug delivery systems of Diclofenac. Both release and diffusion pattern shows that a sustained release form of the drug can be obtained by utilizing microsphere system of albumin. So, we may conclude they are promising drug delivery system for Diclofenac at this time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT :
The authors would like to thank Mr. Shashi Kant Mr. Rajendra Yadav for his valuable support during this work. The authors want to express his deep gratitude and appreciation to thank Mr. Amit Kumar Tyagi, Meerut College, Meerut.
REFERENCES:
1. Longo W.E, Iwata H, Lindheimer T.A, Goldberg E.P. Preparation of hydrophilic albumin microspheres using polymeric dispersions agents. J Pharm Sci, 1982; 71:1323-8
2. Daan J.A, Crommelin, Storm G. Drug Targeting in Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry. Pergamon press, 1990; 5:687-92
3. Green G.A, Cornerstone C. Understanding NSAIDs: from aspirin to COX-2, 2001; 3(5): 50-60
4. Lachman L. The Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy. 3rd Edition.
5. Chuo W.H, Tsai T.R, Hsu T.M. Preparation and In-vitro evaluation of Nifedipine-loaded microsphere cross linked by Gluteraldehyde. 1996, 56-59
6. Vyas S.P, Bhatnagar, Jain N.K, Preparation and characterization of albumin microsphere for nasal administration. Int. j. pharm. (1991); 69:1411-1413
7. Biradar S.S, Bhagavati S.T, Kuppasad I.J. Albumin microsphere: a brief overview. Int.j. Pharmacol; 2006, 4:2
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









