About Author:
R. Hemalatha*
Sunder Deep Pharmacy College,
* latha.hema2004@gmail.com
Counterfeit drugs which are able to penetrate everywhere, are causing huge social and economic costs besides undermining the confidence of the common man on health care system, there is urgent need to combat the problem.
Many methods were developed till date to combat the problem such as holograms and Active/covert systems such as RFID, Taggants and 2D-encryption but still the counterfeiters are able to emulate and circumvent them. However, this problem can be successfully tackled by leveraging the now-a-days omnipresent ICT tools. By making presence of these tools mandatory by all manufacturing units and chemists and by educating people about this ubiquitous menace, this problem can be minimized.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1292
1.0 Introduction
According to WHO, counterfeit medicine is defined as1
“any product that is deliberately and fraudulently mislabeled with respect to identity and/or source. Counterfeiting can apply to both branded and generic products and counterfeit products may include products with correct ingredients or with the wrong ingredients, without active ingredients, with insufficient active ingredients or with fake packaging”
With the advent of futuristic technologies in manufacturing and packaging, the manufacturingof counterfeit medications and packaging has also become an alarmingly simple and inexpensive process fuelling their ubiquitous growth. The counterfeit drugs have been in existence for quite a long time and have made a negative impact in the recent history of industrial scale drug production in India and abroad. Globally, counterfeiting is not just limited to high value branded drugs. It now encompasses everything the pharmaceutical industry produces from high value life style, therapeutic and life saving prescription drugs to generic therapies.
Many pharmaceutical manufacturers who spend billions of dollars on research, production and marketing a particular drug are being knocked off as attenuated drugs, useless placebos or dangerous substances by counterfeits manufactured in basement laboratories throughout the world.With the gangs of organized crime and terror outfits turning to counterfeit goods to generate cash flow, the menace has grown to historic proportions.The growing trade in counterfeit products will create social and economic costs and further burden the global healthcare expenditures.
2.0 The Nature and Scope of the Problem of Counterfeits
As the counterfeits are made either without any active ingredient or insufficient quantities or with the addition of some toxic substance such that the counterfeit drug has no or has a decreased therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic value. With little or no active ingredient a person does not receive all the therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic benefit and will either not recover or will have a delayed recovery. Toxic ingredients, of course, can poison humans with fatal results. In case of infectious diseases (the major cause of disease in under developed world), the counterfeit drugs lead to selection of drug resistant pathogens, increased morbidity, mortality and a significant economic burden on the world.
No pharmaceutical product is by the way safe from counterfeiters. Although expensive medicines, such as oncology products, human growth hormone and widely prescribed life style products like erectile dysfunction drugs, are natural targets, there is still major profit to be made by counterfeiting virtually any medication as well as other products and devices used in health care like glucose monitoring solutions, mesh implants, catheters, stethoscopes and device components for assembling intra-aortic pumps, cardiovascular and orthopedic solutions.
Significant cross border price differentials often attract many small and medium pharma manufacturers to counterfeit and parallel trade. When drugs intended for a particular market at a reduced price make it into a higher price market, with the diverter pocketing the profits. There is also rapid growth in internet pharmacies. Many of the internet pharmacies are based in places other than where they appear to be located. The internet allows official drug monitoring bodies to be bypassed and provides counterfeiters with ready access to consumers and markets.
The counterfeiting may take place at various stages of production/distribution process of drugs
a)Counterfeit active / bulk ingredients
b)Counterfeit finished / diverted products
c)Counterfeit labeling / mislabeled Product
3.0 Alternatives Available to Address the Problem
Detecting counterfeit products is one of the ways the industry can combat this problem. But unfortunately, the complex and diverse trade and distribution systems through out the world can make detection difficult. On obtaining the suspect sample, the initial question is “ is this the authentic product?”. If a conclusion cannot be obtained from the packaging and other information, analysis need to be performed for comparison with the authentic product for which forensic methods are employed which include 3
a) Chemical characteristics such as i)Excipient identity, ii) Impurity profile, iii) Crystal form, iv) Morphology or particle size, v) Thermal behavior
b)Analytical profiles such as i) Major and minor components, ii) Impurities, iii)Isotopic ratios
Techniques such as infrared Spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, Thermal gravimetric analysis, microscopy and various forms of chromatography have been used to check the authenticity of samples.
However, all these methods are to be done in a well-equipped laboratory and are unavailable to the common consumer. Therefore, the trend is to develop a cost effective, simple methods that can be used by a common man.
However, as the consumer groups have strongly advocated that it is ultimately the responsibility of the pharmaceutical company to protect their products and take all necessary measures to identify a bonafide drug. Pharmaceutical industry is trying many alternatives to protect their brands such as
a) Passiveor Overt systems i.e. Packaging that is difficult/costly to duplicate such a blister packing and ii) Holograms or Color shifting ink.
b) Active/ Covert Systems such as Radio-frequency identification (RFID) , Taggants and Tracers,2D - Encryption etc
Though the overt systems are the first defense, which can provide simplified means for consumers to deduce the authenticity of a drug. The major advantage of such passive approaches is that they can be applied at the item level. The major problem however, is that they are generally costly and not effective in the long term as often these can also be reverse engineered. For example holograms can cost as much as 10-25paise depending upon their level of sophistication and therefore can add significantly to the MRP of low end medicines that are staple of the indigenous pharmaceutical market2. Another problem is that, the hologams themselves can also be eventually duplicated by counterfeiters making the initial investment by the brand owner ineffective when such knock-offs enter the market. And, passive technologies do not provide the brand owner with an implementable supply chain management or track-trace ability.
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
4.0 Leveraging Information Technology
With the spread of Information and communication technologies (ICT) such as mobile phones almost throughout the country and even the world, advantage can be taken of the same for identification of the products from authorized sources. This will empower the end user to authenticate the product that they are using.
In this, all drugs beallocated certain unique code uptoindividual packet level coupled to Batch No. or date of manufacture. The codes may be stored in a central repository maintained by a central regulator with compatible web based software. All retailers be made to maintain authentication kiosks or computers which can be connectedto the internet through any of the available modes.
The end users shall on entering the Batch/date of manufacture and unique code will get the authenticaion of the product that they are going to purchase or people be educated toinsist on the authentication from the chemist for their own safety, besides providing necessary legal framework. Else, authentication can also be obtained by reply SMS on sending the code to a preselected number.
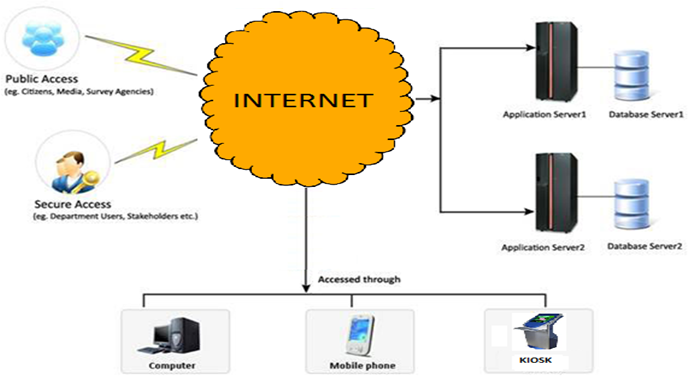
By leveraging the information technology, the disadvantages in the overt and covert systems can be overcome, which is also cost-effective. Using the technology, the manufacturer will also be able to track and trace his supply chain, thus reducing the chance for counterfeits. The cost of setting up the mechanism will by many times offset the loss of revenue due to counterfeits.
Some work in this direction has been carried out by individual companies like Helwett-Packard using cloud based solutions5. However, these solutions had to be carried out at national scale to eradicate the menace.
Finally, Weak legislation is often identified as the single most important factor driving counterfeit trade. In India the Drugs and Cosmetics amendment Bill 2007 contains stringent provisions such as a maximum penalty of life imprisonment and a fine of not less than 10lakh for those engaged in manufacturing spurious and fake drugs4. This act may be suitably amended to enforce compulsory authentication mechanism up to retailer level making it mandatory for the retailer to authenticate the product before selling the same. This type of mechanism will obviate the retailer to keep spurious products for the sake of large margins offered by counterfeiters.
Conclusion
India with its strong economy is emerging as a big player in many industries such as IT and pharmaceuticals. Given the country's image that has been portrayed abroad - a major supplier of counterfeit drugs - a genuine effort to combat this problem and to reinvent the impression and global perception India as a supplier of medicines of reliable quality, the Indian pharmaceutical industry must take measures to combat the scourge of counterfeit medicines and take the lead in ensuring the safety of its supply chain. The efforts of Indian pharmaceutical companies will be rewarding to the Pharma industry, the consumer and the Image of India as a whole.
The forensic methods cannot be used by small clinics and primary health centers to check the authenticity of the drugs they dispense,pharma companies may take advantage of the boom in Information technology and communications network to validate their supplies through the supply chains by simple and cost effective authentication mechanisms. It is in the interest of the Pharmacompanies to adopt the latest technologies as liability issues, consumer confidence and brand erosion costs are driving them to combat this ever increasing problem
References:
1. Discussion paper;:Combating Counterfeit Drugs: Building effective International collaboration – International conference – Rome, Italy 16-18 Feb, 2006.
2. MagnarLoken, and AviChaudhuri , “Countering counterfeits”, Sept., 2007
3. Mohan RK Nimmagadda, “Impact of counterfeits, parallel trade on global healthcare value chain”, Pharmabiz.com, Dec., 2007
4. P.A., Francis “Editorial: Surveying spurious drugs”, Pharambiz.com, Dec 2007
5. IYOGI TECHNICAL SERVICES, Bad Medicine : Is what you need, HP Global authentication service.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









