 About Authors:
About Authors:
Nishant kumar singh
Research Fellow,
ICRI (Ahm) and Cranfield University
* nishantsingh.shree@gmail.com
ABSTRACT:
Over 3 decades HIV/AIDS have been a major globally accepted challenge, from endemic to a catastrophic pandemic & explodes globally. Estimates says 33.3 million HIV +ve and 2.6 million newly HIV infected people are in 2009. Since the beginning of epidemic, nearly 30 million people have died from AIDS related cause[1]. From chimpanzees to human[2] and then human to human (migration[3], MSM, HS, IDU, MTC etc) and ultimately it transformed into pandemic. After 30 years we have advanced our treatment & Medicare knowledge of HIV and AIDS. Our scientist has developed several successful targets and drugs based on them, a highly effective therapy HAART currently in use (managing viral load & cell count for better patient survival rate) showing good results. Still HIV/AIDS is incurable, WHY? It shows the need of critical thinking from the very 1st initial step i.e. TARGET. HIV itself is the target; biotech and Pharmaceutical Company must consider nanotechnology & homologous approach for CCR5. Though it seems that we have control over it but if this goes out same way, than one day just due to the HIV typical characteristic of mutation and recombination the worst Catastrophic sub Saharan-Africa epidemic will become Pandemic.[i]
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1463
INTRODUCTION
HIV/AIDS is a catastrophic illness and still a major challenge of 21st century. AIDS history is short, during 1970s “period of silence” no one was aware of deadly illness. But data suggests that current pandemic had started in late 1970s. By the time of 1980, it had already spread to continents like Europe, Australia, South America, North America and Africa. And same account for approx 100000 to 300000 infected persons[4].It was 1st reported in 1981 and at 1992 FDA receives 1st IND Submission for treatment of HIV/AIDS. Year 2009 statistics reports suggest for 33.3 million HIV+ve people who are living with HIV infection and each year around 2.6 million new cases of HIV infection whereas 1.8 million people died because of AIDS[5].
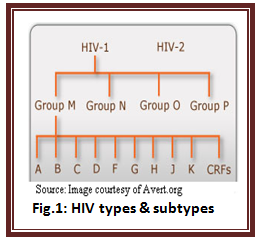
HIV/AIDS has a profound impact on HUMAN KIND by influencing social capital, population structure & national economic growth and so called as catastrophic pandemic. The impact of HIV/AIDS will go devastating until and unless the need for novel anti-HIV agent is met because HIV has a typical characteristic of mutation & recombination. Cameroonian lady was discovered with a new strain of HIV-1 in the year 2009, which was very similar to SIV (gorilla) and is classified as group P type of HIV-1[8]. Group M is itself known to have at least 9 clades (A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J and K) and all HIV-1 subtypes differs genetically[9].At present phylogenic tree shows a large number of various different natures of HIV subtypes and the same had created the need for broad classification of HIV subtypes as shown in the fig.1. This requires the need for critical evaluation of the whole knowledge on HIV/AIDS.
EPIDEMIC INCIDENCE
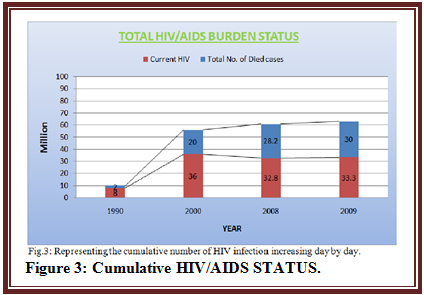
HIV/AIDS incidence rate is decreasing in all the cases weather it is the case of newer infection in children’s (MTCT) or adult (MSM, HS, IDU, low down etc) or is the case of HIV/AIDS related mortality or is the cost of treatment. The reason for same is advancement of the knowledge which leads to safer sex, AR drugs discovery, and new regimens for HAART and increased number of people receiving HIV treatment. The only case where a hike can be seen is cumulative number of HIV infection which is increasing year by year and need to be focus for betterment.
It can be calculated by the following equation: OR

The incedence of HIV/AIDS occurs mainly due to OIs and it raises with increasing age of the patient[22]. OIs such as TB(38%), BP(14%),PCP(11%),and KS(6%) in 128 patients(100%) are the vital player in HIV/AIDS morbidity or mortility incidence outcome[23]. Chemotherapy has a significant impact on mortality reduction as zidovudine reduced the incidence of AIDS about 62% in patient who took it than in those who did not(P = 0.02)[22].NHL among PWA boost up the incidence and public health burden too.Infant increased mortality in countries with high adult HIV prevelance example Zimbabwe(61%) are building up the HIVepidemic incidence burden[24]. According to latest 2010 WHO treatment guidelines, Only 36% of low-income and middle-income countries HIV infected people are receiving AR drugs [25].
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
GLOBAL TRENDS OF HIV/AIDS & 2010 FACT SHEET (UNAIDS REPORT):
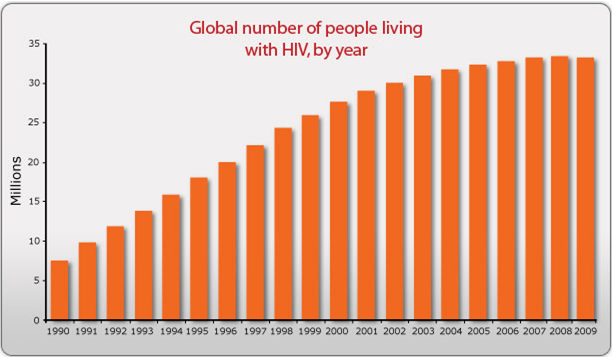
Fig.4:Representing incidence for AIDS & infectious disease[1].
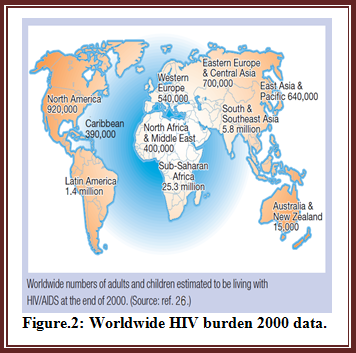
An increase of 25 million HIV +ve people since from 1990 illustrates the huge impact of HIV on human kind which had already resulted in 30 million mortality incidence over last 3 decades; it means 1 million deaths each year. Though overall cumulative burden is slow but is increasing per year.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
INCIDENCE FACT SHEET
|
S.no. |
FACTS[1] |
ESTIMATE[1] |
RANGE[1] |
|
1. |
People living with HIV/AIDS in 2009 |
33.3 million |
31.4-35.3 million |
|
2. |
Adults living with HIV/AIDS in 2009 |
30.8 million |
29.2-32.6 million |
|
3. |
Women living with HIV/AIDS in 2009 |
15.9 million |
14.8-17.2 million |
|
4. |
Children living with HIV/AIDS in 2009 |
2.5 million |
1.6-3.4 million |
|
5. |
People newly infected with HIV in 2009 |
2.6 million |
2.3-2.8 million |
|
6. |
Adults newly infected with HIV in 2009 |
2.2 million |
2.0-2.4 million |
|
7. |
AIDS deaths in 2009 |
1.8 million |
1.6-2.1 million |
|
8. |
Orphans (0-17) due to AIDS in 2009 |
16.6 million |
14.4-18.8 million |
Fig.6: Global HIV and AIDS estimates, end of 2009(Source:avert.org/worldstats).
HIV/AIDS PREVALENCE FACT SHEET WORLDWIDE (DEMOGRAPHIC DATA):
|
|
REGION |
ADULTS & CHILDEREN LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS |
ADULTS & CHILDEREN NEWLY INFECTED |
ADULT PREVELANCE* |
AIDS RELATED DEATH IN ADULTS & CHILDREN |
|
1. |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
22.5 million |
1.8 million |
5.0% |
1.3 million |
|
2. |
North Africa & Middle East |
460,000 |
75,000 |
0.2% |
24,000 |
|
3. |
South and South-East Asia |
4.1 million |
270,000 |
0.3% |
260,000 |
|
4. |
East Asia |
770,000 |
82,000 |
<0.1% |
36,000 |
|
5. |
Oceania |
57,000 |
4,500 |
0.3% |
1,400 |
|
6. |
Central & South America |
1.4 million |
92,000 |
0.5% |
58,000 |
|
7. |
Caribbean |
240,000 |
17,000 |
1.0% |
12,000 |
|
8. |
Eastern Europe & Central Asia |
1.4 million |
130,000 |
0.8% |
76,000 |
|
9. |
North America |
1.5 million |
70,000 |
0.5% |
26,000 |
|
10. |
Western & Central Europe |
820,000 |
31,000 |
0.2% |
8,500 |
|
11. |
Global Total |
33.3 million |
2.6 million |
0.8% |
1.8 million |
Fig.7:Regional statistics for HIV and AIDS end of 2009(Source: avert.org/worldstats).
HIV INFECTION & ILLNESS
This section illustrates the nature of HIV infection and its causes, processes, development, and consequences i.e. pathobiology of HIV/AIDS.
(PATHO- CLINICAL SYMPTOMS) of HIV/AIDS follows the following: -
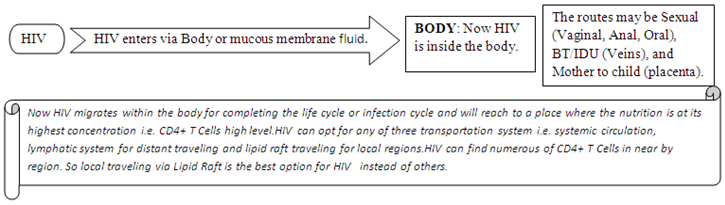
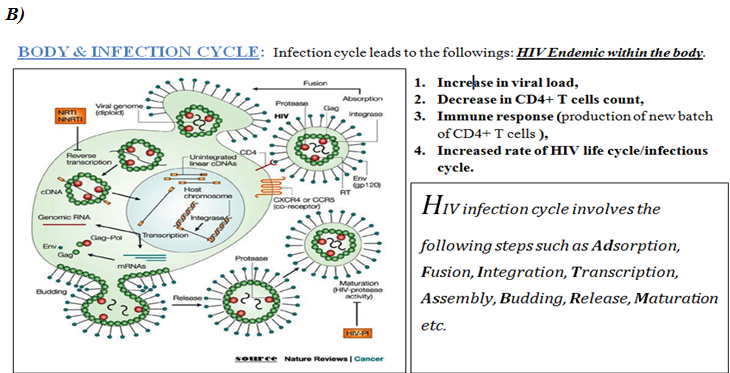
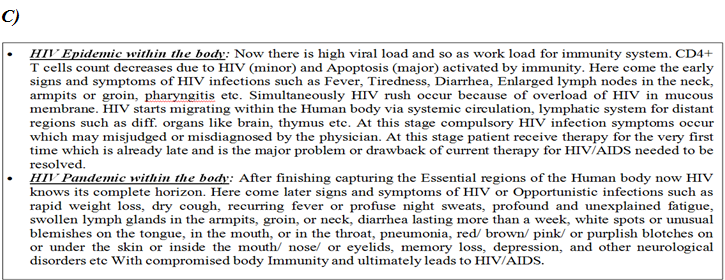
CURRENT THERAPY & IMPACT
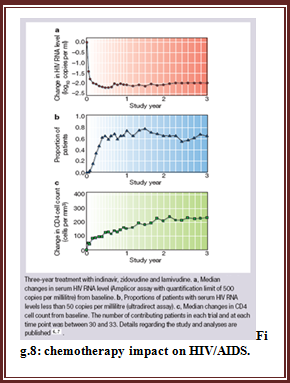
Current treatment approach for HIV infection emphasize on Highly Active Anti Retroviral Therapy i.e. HAART. This has been proved to be highly beneficial since 1996. HAART has shown remarkable improvements in QOL & general health of the patients. Its impact can be seen as given in fig.8.Though in some cases it fails to achieve optimal results and the reason can be any one of this: drug resistant HIV strain, medication intolerance because of side effects, prior (ineffective) antiretroviral therapy failure, and non adherence to HAART. Again the reason for non adherence can be noncompliance of HAART example regimen is hard to follow, side effects (liphodystrophy, dislipidemia, diarrhoea, insulin resistance, increase in cardiovascular risk) is one of the major reason, psychosocial issue.
HAART is expensive and so it is not widely available. A major fraction of patients do not have proper access to it which limits the therapy & promotes HIV illness burden globally.
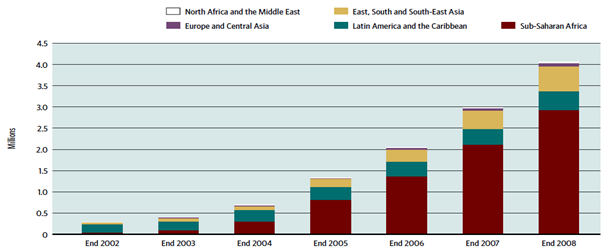
Fig.9: Number of people receiving antiretroviral therapy in low-and middle-income countries, by region, 2002-2008.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
APPROACHES TO CHALLENGE
ONGOING INITATIVES:
Several research are going on to improve current treatment options with emphasis on minimizing side effects, simplifying drug regimens with an attempt to point out best regimen sequence with all possible combinations of antiretroviral drugs for managing drug resistance. Precautionary measures to prevent opportunistic infections for individuals at risks of HIV infection such as vaccination against hepatitis A & B. Prophylactic therapy for substantial immunosuppressant patient such as: for neumocytostis jiroveci pneumonia(PCP), toxoplasmosis and Cryptococcus meningitis etc.
Discovery of an abzyme shows the potential to destroy the protein gp120 CD4+ T cell attachment site, which is common to all variants of HIV. But the side effect limits it because abzyme may destroy other proteins which are the major component of human body. Bone marrow transplant with cells that contain an unusual natural variant of CCR5 Cell surface receptors shows a high impact on HIV eradication. In Berlin, Germany a 42 year old leukaemia patient infected with HIV over a decade. Body rejection (Ag-Ab reaction) and high transplantation cost limits this approach.
Use of alternative medicine is another initiative to treat the symptoms else alter the course of disease. Such as herbal medicine, acupuncture approach but they lack the conclusive evidence. Some data suggest that the HIV/AIDS progression in adults can be reduced by the use of multivitamin and mineral supplements but again no conclusive evidence is available for morbidity or mortality reduction. The psychological benefits are the most important use of alternative medicines therapy which may improve the quality of life but have very little effect on mortality or morbidity of PLHA’s.
Chemotherapeutic approach
Various antiretroviral drugs are based on structure and replication cycle of HIV. The different target sites for treatment include enzyme (Reverse Transcriptase, Protease, Integrase enzyme), Env proteins (gp120), Vir gene, lipid raft, fusion of T cells & HIV RNA. The drugs are classified accordingly based on their target sites such as NRTI’s, NNRTI’s, PI, FI, Integrase inhibitor, Zinc finger inhibitor, antisense drugs like HGTV43 by Enzo therapeutics which is in Phase II Trial. CD4 receptor antagonist, CCR5 antagonist, Ribozyme. Ribozyme cut HIV at different stages of its infection cycle and are active against strains that are resistant to conventional anti viral therapy.
Today, therapies for the treatment of HIV/AIDS illness are focused on the reduction of viral load using that interfere with replication of virus with only a modest effect on the restoration of T cells count.
LIMITATIONS
Besides enormous benefits of HAART’s, the treatment refractory patients in response to regimens is quite high or patients showing inadequate responses to the regimens are unable to bear the toxicity and adverse effects resulted as a outcome, at the same time larger number of pills administration leads to compliance difficulty, other drugs myriad interaction and complicated schedules of dosing needs adjustment or alteration of life style pattern specially food and liquid intake habits[10]. Although successfully treated patients by HAART shows extremely low level of HIV-1 RNA load in plasma but HIV persist in their latent reservoir within the human body for sanctuaries where the AR drugs are either unable to reach or have no effect on such reservoir[11-14]. On the other side, HIV drug resistant strains emergence is a widespread and growing problem for currently available AR drugs[15]. Despite the evidence of improving immune system functions in most of the HIV +ve patients receiving CAT, its complete normalization and eradication of HIV completely from the HB is seems to be unlikely with currently available therapies. The persistence of latent HIV reservoir within HB is problematic and raises the need of lifelong treatment with AR drugs which there after may prove to be expensive and toxic for prolonged period use [16-20]. The below detectable level of viral load for HIV-1 RNA in patient plasma achieved by HAART for median of 390 days invariably rebounded within three weeks after therapy cessation[21]. There for the need for the development of a new 21st generation therapies remains at the highest priority in todays world for the betterment of human kind. Several myths regarding HAART, HIV/AIDS illness, HIV transmission etc are the major psychosocial limitations concerned with HIV/AIDS and it varies from region to region or country to country whether it is developed , developing or under developed country.
DISCUSSION
HIV/AIDS have only two possibilities:
1st possibility:
“The available resources and approaches are sufficient to cure the HIV/AIDS”.
Supporting evidence:
The Evidence of MTCT prevention and total cure of the HIV+ve infants by HAART, with a prohibition of baby milk feeding because it will lead to HIV re-exposure.
Suggestions:
Above statement throws some light to rethink on the on the concept of HIV dormancy within the body and suggest that HIV dormancy does not exist during the early times followed b HI exposure.
Also suggest that early detection of HIV is a vital factor responsible for total cure. This is already available in infants in case of MTCT but not in case of adults or children’s who experience HIV exposure during their lifetime(detection may be after the 1st occurrence of symptoms or may be latter on when HIV has already attain concentration max. within the body ).
Solution:
* Performing diagnosis based on the Sample Hiv Rna Investigation and Sample Hiv Rna Emphasized Examination technique i.e. SHRI and SHREE technique may solve the early detection of HIV within the human body.
* Based on the result obtained by the above test the suitable design of regimen may help to completely eradicate HIV from the human body.
2nd possibility:
“The available resources and approaches are insufficient to cure the HIV/AIDS and so HIV/AIDS is incurable”.
What if dormancy exists from the very 1st second of HIV exposure to a human being??
Reasons: HIVdrug resistance strains, dormancy, toxicity and side effects etc.
Problem: The only problem is Target.
Suggestion:
* Dormancy is because most of AR drugs interfere with various stages of HIV life cycle or infection cycle as a target.
*Treatment fails cause of drug remains for a short period of time while HIV may remain for centuries within the human body. As a result of this HIV dormancy occurs and patient require complex drug regimen for lifelong leading to severe toxicity. At the mean time drug resistance also leads to inefficacy of therapy or treatment which indicates complete failure with much more complications as the outcomes for the patients.
* “The big question is where and which is the target?” because only the best target can solve the problem of dormancy & drug resistance which are responsible for treatment failure and toxicity.
* The answer lies in the statement that “all HIV strains whether they are drug resistance or not, begins their life cycle with a single common step (i.e. binding with CD4+ & CCR5 followed by membrane fusion) followed by the common series of steps to complete the life cycle”. We do have marvirock as CCR5 blocker as well as abzyme for inhibition of the very 1st step of HIV life cycle.
* Then what goes wrong? Of course TARGET. In case of HIV/AIDS, HIV itself can be utilizing as a target to act upon for the treatment and cure.
STUDY LIMITATIONS
*Organs pathology in case of HIV/aids is not mentioned in the pathology section.
*Sample Hiv Rna Investigation and Sample Hiv Rna Emphasized Examination technique for early HIV detection within human body is under research process so the complete detail is not provided.
*Complete demographic HIV incidence is not covered in this study.
*Hypothesis that HIV may serve as the best target for HIV/AIDS illness lacks the supporting evidence.
CONCLUDING PRESPECTIVE
Till now HIV/aids illness is incurable and several challenges to its treatment still persist in form of numerous HIV drug resistant strains possessing typical characteristic of dormancy. Highly profound research’s in order to simplify HIV/AIDS illness is rather making it more complex and difficult to understand and so unknowingly missing noticing its complete overview. The biopharmaceutical can solve the problem by increasing the potency and decreasing the toxicity of anti HIV agent with a simplified regimen for the best suitable target for HIV/AIDS Illness.
REFERENCES
1. UNAIDS (2010) 'Unite for universal access: Overview brochure on 2011 High Level Meeting on AIDS'.
2. Weiss RA, Wrangham RW. From Pan to pandemic. Nature 1999; 397:385-6
3. Quinn TC, Fauci AS. The AIDS epidemic: demographic aspects, population biology, and virus evolution. In: Krause RM, ed. Emerging infections. New York: Academic Press, 1998:327-63.
4. Mann J. M (1989) 'AIDS: A worldwide pandemic', in Current topics in AIDS, volume 2, edited by Gottlieb M.S., Jeffries D.J., Mildvan D., Pinching, A.J., Quinn T.C., John Wiley & Sons].
5. UNAIDS (2010) 'UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic’.
6. Gulick, R. M. et al. Treatment with indinavir, zidovudine, and lamivudine in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection and prior antiretroviral therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 337, 734–739 (1997).
7. Gulick, R. M. et al. 3-Year suppression of HIV viremia with indinavir, zidovudine and lamivudine. Ann. Intern. Med. 133, 35–39 (2000).
8. Plantier, J.C. (2009) 'A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas', Nature Medicine, 2nd August.
9. WHO (2011) 'HIV/AIDS'.
10. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1998;47(RR-5):43-82.(See updates at hivatis.org.) .
11. Chun TW, Engel D, Berrey MM, Shea T, Corey L, Fauci AS. Early establishment of a pool of latently infected, resting CD4(+) T cells during primary HIV-1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:8869-73.
12. Chun TW, Stuyver L, Mizell SB, et al. Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:13193-7.
13. Finzi D, Hermankova M, Pierson T, et al. Identification of a reservoir of HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 1997;278:1295-300.
14. Wong JK, Hezareh M, Gunthard HF, et al. Recovery of replicationcompetent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science 1997;278:1291-5.
15. Durant J, Clevenbergh P, Halfon P, et al. Drug-resistance genotyping in HIV-1 therapy: the VIRADAPT randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999;353:2195-9.
16. Furtado MR, Callaway DS, Phair JP, et al. Persistence of HIV-1 transcription in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells in patients receiving potent antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1614-22.
17. Zhang L, Ramratnam B, Tenner-Racz K, et al. Quantifying residual HIV-1 replication in patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1605-13.
18. Pomerantz RJ. Residual HIV-1 disease in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med 1999; 340:1672-4.
19. Finzi D, Blankson J, Siliciano JD, et al. Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat Med 1999;5:512-7.
20. Chun TW, Engel D, Mizell SB, et al. Effect of interleukin-2 on the pool of latently infected, resting CD4+ T cells in HIV-1-infected patients receiving highly active anti-retroviral therapy. Nat Med 1999;5:651-5.
21. Harrigan PR, Whaley M, Montaner JS. Rate of HIV-1 RNA rebound upon stopping antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 1999;13:F59-F62.
22. Peter A.selwyn, Philip algabes, et al. Clinical manifestation and predictor of disease progression in drug user with human immunodeficiency virus infection, NEJM 1992;327:1697-703.
23. Ansari N.A., Kombe A.H.,et al. Pathology and causes of death in a group of 128 predominantly HIV positive patients in Botswana,1997-1998.The Int. journal of Tuberculosis and lung disease 2001;(55-62).
24. Jacob Adetunji, Trends in under-5 mortality rates and the HIV/AIDS epidemic, Bulletin of the WHO 2000;78;1200-06(10).
25. WHO/UNAIDS/UNICEF (2010) 'Towards universal access: Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector'.
26. Avert.org/worldstats(2010)’ Worldwide HIV & AIDS Statistics ’.
ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Ab - Antibody
Ag- Antigen
AIDS- Acquired Iimmunodeficiency Syndrome
AR- Anti retroviral
ART- Anti retroviral therapy
BP- Bacterial Pneumocystis
CAT- Combinational Antiretroviral Therapy
FDA- Food and Drug Administration
FI’s- Fusion Inhibitors
HAART- Highly Active Anti Retroviral Therapy
HB- Human body
HIV- Human immunodeficiency virus
HS- Heterosexual
IDU- Injection Drug User
IF’s- Immunity Function’s
II’s- Integrase Inhibitors
IND- Investigational New Drug Application
KS- Kaposi’s sarcoma
MSM- Men sex with men
MTC/MTCT - Mother to child Transmission
NNRTI’s- Non-nucleoside reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor
NRTI’s- Nucleoside or nucleotide Reverse transcriptase Inhibitors
NHL- Non Hodgkin’s lymphoma
OI’s- Opportunistic infection’s
PCP- Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
PI’s- Protease inhibitor
PLHA’s- People living with HIV AIDS
PWA- People with AIDS
QOL- Quality of life
RNA- Ribonucleic acid
SHREE- Sample HIV RNA Emphasized Examination
SHRI- Sample HIV RNA Investigation
SIV- Simian immunodeficiency Virus
TB- Tuberculosis
WHO- World Health Organisation
ZFI’s- Zinc finger Inhibitor’s.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









