{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
ABOUT AUTHORS
P.Mounika*, Sanjit, Abhishek pandey, Dilraj Yadav
Gautham College of Pharmacy,
Bangalore – 560032
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective of the present study was to develop Bilayered tablets of Nifedipine and atenolol. Bilayered tablet contains two layers. We can formulate first layer into immediate release and second layer into sustained release for desired action. Nifedipine have half-life 2hrs make the drug suitable for immediate release. Atenolol have half-life 6-7hrs make the drug suitable for sustained release.
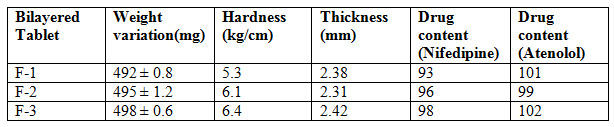
Methods: In this formulation using super disintegrants for immediate release, acacia and ethyl cellulose as a polymers for sustained release. Tablets were prepared by wet granulation method. In this study Bilayered tablets of Nifedipine and Atenolol tablets were evaluated for weight variation, hardness, thickness, drug content and In-vitro studies.
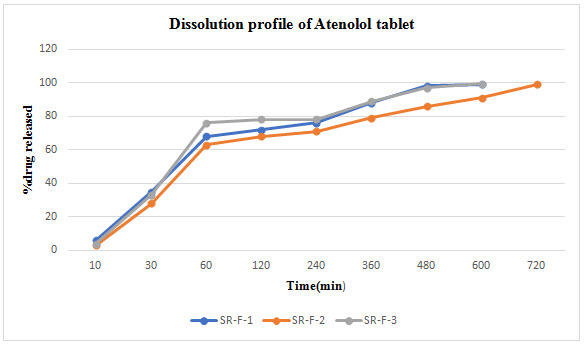
Results: Bi-layer tablet is suitable for sequential release of two drugs in combination, separate to incompatible substances and also for immediate release as initial dose and sustained release as maintenance dose. In Immediate release formulation, IR-F-3 formulation gives 98% release within 15min. For sustained effect SR-F-3, SR-F-1 gives 98% release within 8-9hrs. SR-F-2 gives 99% release within 10-11hrs for a longer period of time.
Conclusion: The combination of IF-3 and SR-F-2 suitable for formulation. This formulation is used for Bilayered tablet to combine with sustained released tablet. The evaluation parameters were estimated.
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2660
|
PharmaTutor (Print-ISSN: 2394 - 6679; e-ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 7, Issue 04 Received On: 18/03/2019; Accepted On: 23/03/2019; Published On: 01/04/2019 How to cite this article: Reddy, M., Yadav, S., Pandey, A. and Yadav, D. 2019. Formulation and Evaluation of Bilayered Tablets of Nifedipine as Immediate Release and Atenolol as Sustained Released Tablet. PharmaTutor. 7, 4 (Apr. 2019), 52-59. DOI:https://doi.org/10.29161/PT.v7.i4.2019.52 |
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nifedipine, Atenolol, Avicel PH 102, Starch, Ethyl cellulose and Acacia from Gautham college of Pharmacy
INTRODUCTION
Usually conventional dosage form produce fluctuations in plasma drug concentration levels in blood stream and tissues, with poor toxicity and therapeutic effects. The goal of designing sustained or controlled delivery system is to reduce the frequency of the dosing and increase effectiveness of the drug by localization at the site of action, reducing the dose or providing uniform drug delivery [Divya.A et al 2011]. Bi-layer tablet is suitable for sequential release of two drugs in combination, separate to incompatible substances and also for immediate release as initial dose and sustained release as maintenance dose [Shiyani et al., 2008]. In Bi-layer tablets drug release is unidirectional, if the drug can be incorporated in the upper non-adhesive layer. Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker used for the treatment of angina pectoris and hyper-tension. Nifedipine is suitable for immediate release due to its short half-life 2hrs. Nifedipine is poorly soluble in water [Pawar VK et al 2011]. The solubility of Nifedipine is enhanced by using super disintegrants such as Sodium starch glycolate, Povidone, Avicel PH 102, Micro crystalline cellulose. Immediate release layer provide therapeutically effective plasma drug concentration for a short period of time [Garg R et al 2009]. Atenolol, a cardio selective beta-1 adrenoreceptor. It belongs to antihypertensive agent and helps in reducing high blood pressure. The drug has half-life 6-7hrs which make the drug suitable for sustained release. Sustained released layer maintain uniform drug levels over a sustained period to reduce dosing intervals, side effects, increase the safety margin for highly potent drugs and thus offer better patient compliance [Guguloth M et al 2011]. Acacia, HPMC, Sodium alginate, Methyl cellulose, Ethyl cellulose used as polymers for sustained release.
PREPARATION OF IMMEDIATE RELEASE LAYER
Nifedipine is poorly soluble in water. To enhancing the solubility of Nifedipine using super disintegrants Avicel PH 102 and Starch solution in different concentrations. Starch powder acts as a disintegrating agent and diluent. Magnesium stearate acts as a lubricant [Fox CS 2010]. To get the desired tablets granules were prepared by using wet granulation method.
PREPARATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS
Atenolol has half-life 6-7hrs suitable for formulation into sustained release dosage form. To get desired action different ratios of Acacia and Ethyl cellulose are used as a polymers. Ethyl cellulose acts as a binder [Lavie CJ et al 2009]. Binder plays an important role in the sustained release formulations. Atenolol is supposed to be granulated with water. Magnesium stearate used as a lubricant. These granules were prepared by wet granulation method.
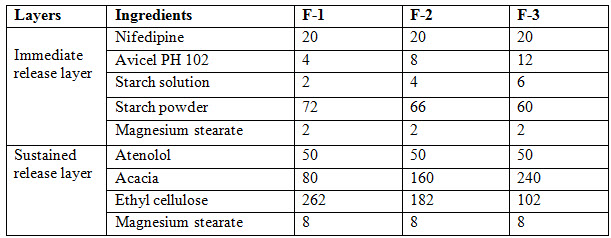
PREPARATION OF BILAYERED TABLET
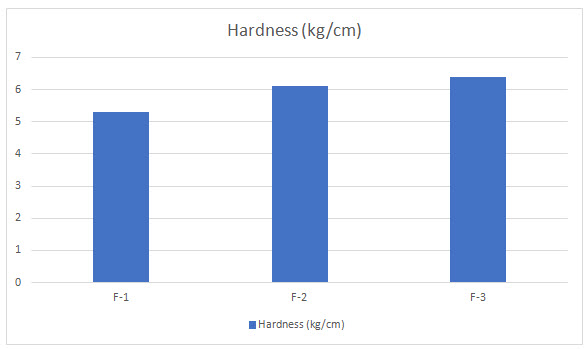
In this process, the first step sustained release granules are weighted accurately and fed in to die cavity of tablet punching machine. The next step involves immediate release granules are fed in to die cavity and compressed so that final hardness can be achieved. After preparation of tablets, the tablets are subjected for evaluation [Department of Health Statistics and Informatics 2008]. Evaluation parameters are weight variation, hardness, thickness, drug content and In-vitro studies.
Table 1 : Formulation of Immediate release layer
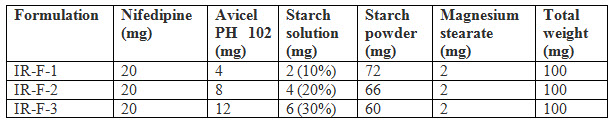
Table 2 : Formulation of Sustained release layer
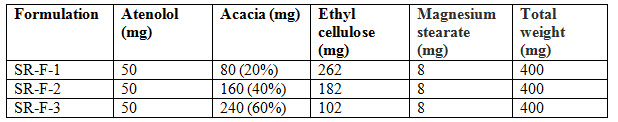
Table 3 : Formulation of Bilayered tablet
Construction of Calibration curve of Nifedipine
10mg of drug was weighted and dissolved in Phosphate buffer pH 6.8[Lim SS et al 2010]. Nifedipine concentration 2, 4, 6, 8, 10μg/ml were prepared from stock solution make up the volume with Phosphate buffer. Then λmax was determined at 235nm [Lim SS et al 2010].
Construction of Calibration curve of Atenolol
10mg of drug was weighted and dissolved in Phosphate buffer pH 6.8. Atenolol concentration 2, 4, 6, 8, 10μg/ml were prepared from stock solution make up the volume with Phosphate buffer. Then λmax was determined at 241nm [Kaushik Mukherjee et al, 2015].
In-vitro dissolution studies
Dissolution study was carried out by USP dissolution apparatus II (Paddle type), rotational speed 50rpm with 900ml 6.8pH Phosphate buffer as a dissolution medium maintainted at 37 ± 0.5°C. Samples were withdrawn for a period of 12hrs. 5ml of sample was withdrawn. By using UV/Visible spectrophotometer at 241 & 235nm for the estimation of Nifedipine and Atenolol concentration [Albadry, A et al 2017]
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Nifedipine poorly soluble in water. So in order to improve the solubility of Nifedipine super disintegrants Avicel PH 102 was used. For immediate release formulation IR-F-1, IR-F-2, IR-F-3 were prepared with different concentration ratios (5%, 10%, 20%) of Avicel. Starch gives bulkiness to the formulation. To get the sustained effect Atenolol with Acacia and Ethyl cellulose were prepared. The evaluation parameters were estimated. In Immediate release formulation, IR-F-3 formulation gives 98% release within 15min. This formulation is used for Bilayered tablet to combine with sustained released tablet. For sustained effect SR-F-3, SR-F-1 gives 98% release within 8-9hrs. SR-F-2 gives 99% release within 10-11hrs for a longer period of time. The combination of IF-3 and SR-F-2 suitable for formulation. Acacia 40% gives more retardant effect over the period of time. This may be due to increase in concentration of polymer and binder.
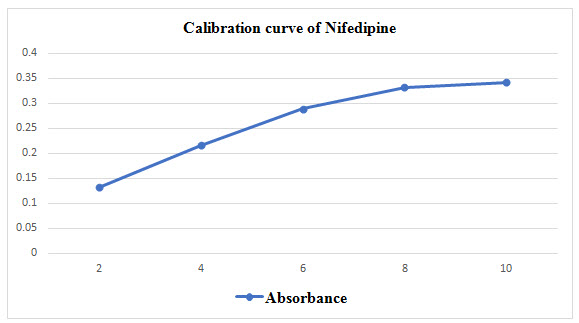
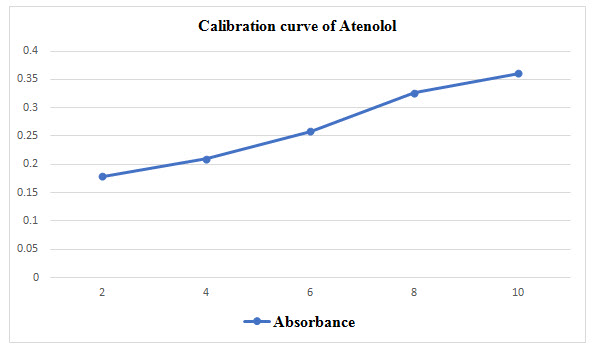
Table 4 : Dissolution profile of Nifedipine tablet
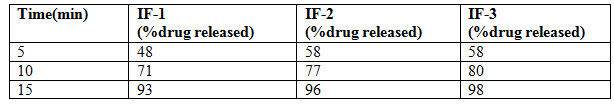
Table 5 : Dissolution profile of Atenolol tablet
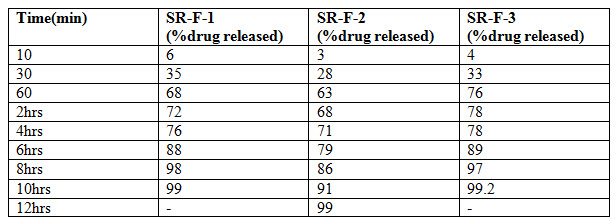
Table 6 : Evaluation parameters




CONCLUSION
The aim of this study is to Design and Evaluate Bilayered tablet of Nifedipine and Atenolol. Atenolol belongs to antihypertensive agents which helps in reducing blood pressure. In this Bilayered tablet Nifedipine released the drug for immediate action because of short duration of action. For sustained release Acacia, Ethyl cellulose are used with Atenolol. The evaluation parameters are weight variation, hardness, thickness, drug content and In-vitro studies were carried out. In-vitro dissolution studies are performed using pH 6.8 Phosphate buffer, F-2 formulation shows good sustained effect for a longer period of time up to 10-12hrs.
REFERENCES
1. Abebea A, Akselib I, Sprockela O, Kottalaa N, Cuitino AM.(2014); Review of bilayer tablet technology; Int J Pharm; 461(1-2); 549-58.
2. Albadry, A. A., W. K. Ali, F. A. Al-saady (2017); Formulation and Evaluation of Prochlorperazine Maleate Sustained Release Floating Tablet. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences; 9(2); 89-98
3. Department of Health Statistics and Informatics. Causes of death 2008: data sources and methods; Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008.
4. Divya.A, K.Kavitha (2011); Bilayered tablet technology: An over review; Journal of applied pharmaceutical science ; 1(8) ; 43-47
5. Fox CS (2010) ; Cardiovascular disease risk factors, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the Framingham heart study; Trends Cardiovasc Med ; 20(3); 90-95.
6. Garg R, Gupta GD. (2009); Preparation and evaluation of gastroretentive floating tablets of silymarin; Chem Pharm Bull ;57(6); 545-549.
7. Guguloth M, Bomma R, Veerabrahma K. (2011); Development of sustained release floating drug delivery system for norfloxacin: in vitro and in vivo evaluation; PDA J Pharm SciTechnol ; 65(3); 198-206.
8. He W, Li Y, Zhang R, Wu Z, Yin L. (2014); Gastro-floating bilayer tablets for the sustained release of metformin and immediate release of pioglitazone: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation; Int J Pharm ; 476(1-2); 223-31.
9. Kaushik Mukherjee, Subrata Chakraborty, Biswanath Sa (2015); Quick /slow biphasic release of a poorly water soluble antidiabetic drug from bi-layer tablets; Int J Pharm Pharm Sci; 7(11); 250-258
10. Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO (2009); Obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss; J Am CollCardiol; 53(21); 1925-32.
11. Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Rohani HA, et al. (2012); A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010; The Lancet ; 380(9859); 2224-2260.
12. Nakagawa T, Kondo S, Sasai Y, Kuzuya M. (2006); Preparation of floating drug delivery system by plasma technique; Chem Pharm Bull ; 54(4); 514-8.
13. Pawar VK, Kansal S, Garg G, Awasthi R, Singodia D, Kulkarni GT. (2011); Gastroretentive dosage forms: A review with special emphasis on floating drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv ; 18(2); 97-110.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









