ABOUT AUTHORS:
AMRUTHA R.E.*, G.RAJESHWARI, A.SRILAKSHMI, G. JYOTHI REDDY, N.KRISHNA SREE, SK. AFSAR.
Department of Pharmacology
P. Rami Reddy Memorial College of Pharmacy,
Andhra Pradesh ,India.
ABSTRACT
Ethanolic extract of the roots of Zizyphus oenoplia were screened for its anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma. The parameters like the time of paralysis and the time of death were determined by using the extract at the concentrations of 10, 20and 50 mg/ml. The extract exhibited significant anthelmintic activity at highest concentration of 50 mg/ml. Albendazole (20mg/ml) was used as standard reference and distilled water as control.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1263
INTRODUCTION
Among the most widespread of all chronic infections are those caused by various species of parasitic helminths (worms).Helmintic infections are now being recognized as cause of much chronic ill health and sluggishness amongst the tropical people. Diseases caused by helminth parasites in livestock continue to be a major productivity constraint, especially in small ruminants in the tropics and sub tropic 1. In the developing world, the greatest impact of parasitic diseases,indirect and potential productivity losses 2. Infections by gastrointestinal helminth parasites of livestock are among the most common and economically important diseases 3.
Zizyphus oenoplia [Local name- Parigi, Family- Rhamnaceae] is a deciduous tree and frequently found in the hilly area of Tirumala. The purpose of the present study was to find out the antihelminthic activity of ethanolic root extract of Zizyphus oenoplia.
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
a) Collection of Plant material:
The roots of plant Zizyphus oenoplia were collected from tirumala hills, Tirupathi, A.P, India in july, 2011 and identified by assistant professor in the Department of Botany, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati. The plant was identified by routine pharmacognostical studies including organoleptic tests, and macroscopic and microscopic observations. The voucher specimen has been retained in our laboratory for future reference. The collected leaves were air-dried and pulverised using mechanical grinder.
b) Preparation of plant extract:
In the present work, the authenticated shade dried roots of the plant, approximately (500 g), were powdered to coarse particle size no. (#) 40 and subjected to continuous hot extraction with 90 % ethanol in a soxhlet extractor for 72 hrs. The total ethanol extract was filtered and concentrated to dryness at 40°C under reduced pressure in a rota evaporator. The yield of ethanol extract was found to be 100 gm (20% w/w). The extract was kept in a dessicator till the experiment. The extract was tested for presence of various phytoconstituents as per standard procedures.
c) Worms’s collection and authentification:
Indian earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Annelida) were obtained from water logged area of soil and identified at department of applied zoology. S.V.University, Tirupathi, Andhrapradesh, India.
d) Acute toxicity study
The acute toxicity study was performed according to the OPPTS(Office of prevention, pesticide and toxic substance) Up and Down procedure (Health Effect Test Guideline 2004). The different fractions were suspended using Tween 80 (0.1%) and were administered orally at the dose of 3000mg/kg. The concentration was adjusted in such a way that it did not exceed 1ml/kg b/w of the animal.
e) Anthelmintic assay
The anthelmintic assay was carried as per the method of Ajaiyeoba et al., with necessary modifications. The assay was performed on Indian adult earth worm, Pheretimaposthuma due to its anatomical and physiological resemblance with the intestinal round worm parasite of human being 4,5,6,7.Because of easy availability earth worms have been widely used for the initial evaluation of anthelmintic compounds In vitro8,9,10,11.50 ml of formulation containing different concentrations of crude extract and test standard (10, 20, 50 mg/ml) were prepared by triturating the samples with 15% tween80 and the resultant mixture were stirred using a mechanical stirrer for 30 min.Five groups of worms with five worms in each group were taken in a petridish.The time of paralysis was noted when no movement of any sort could be observed except when the worm were shaken vigorously not when dipped in warm water (45oC).
Group 1- Distilled water which served as control.
Group2- Received Albendazole at the dose of 10 mg/ml as the standard.
Group3- Received alcoholic extract at the dose of 10 mg/ml
Group4- Received alcoholic extract at the dose of 20 mg/ml
Group5- Received alcoholic extract at the dose of 50 mg/ml
METHODLOGY: Treatment sehedule of animals ,
|
GROUP |
SAMPLE |
NO OF ANIMALS |
PURPOSE |
|
|
1. |
Control |
6 |
Serve as control |
|
|
1.
|
Ethanol extract 10mg/ml |
6 |
serve as low dose |
|
|
2.
|
Ethanolic extract 20mg/ml |
6 |
serve as medium dose |
|
|
3.
|
Ethanolic extract |
6 |
serve as high dose |
|
|
4.
|
Albendazole |
6 |
Serve as standard |
|
Statistical Analysis
All the values of were expressed as mean±standard error of mean (S.E.M.) and analyzed for ANOVA and post student’s t testfor n= 6 animals Differences and were considered significant at P < 0.005 levels Vs standard groups.
RESLUTS
a) Extraction
The dried powder of Ziziphus oenoplia (50 gms) was extracted with 90% aqueous ethanol by soxhelation. The yield of aqueous ethanolic extract is 6.89g
b) Identification of Phyto chemical constituents
All extracts obtaining during successive extraction of Ziziphus Oenoplia roots were examined for the presence of various phytoconstituents by performing qualitative phytochemical tests and the results are recorded in table no:2
|
SNO |
PHYTO CHEMICALS |
ETHANOLIC EXTRACT |
|
1 |
alkaloids |
+ ve |
|
2 |
catachols |
-- ve |
|
3 |
flavanoids |
+ ve |
|
4 |
phenolic compounds |
-- ve |
|
5 |
saponins |
+ ve |
|
6 |
steroids |
+ ve |
|
7 |
tannins |
+ ve |
|
8 |
triterpinoids |
+ ve |
|
9 |
cardiac glycosides |
+ ve |
c) Results of pharmacological investigations:
Alcohol extract from the roots of Ziziphus Oenoplia were investigated for their anthelmintic, activity against Pheretima posthuma. Variousconcentrations (1%, 2.%, and 5%) of extract,were tested in the bioassay, which involveddetermination of time of paralysis and time ofdeath of the worms. Albendazole wasincluded as standard reference and distilled water as control. The anthelmintic assay wascarried as per the method of Ajaiyeoba et al. with minor modifications.The assay was performed on adult Indian earthworm, Pheretima posthuma, collected from moist soil and washed with normal saline to remove all faecal matter were used for the anthelmintic study. The earthworms of 3-5 cm inlength and 0.1-0.2 cm in width were used for all the experimental protocol. In the first set of experiment, five groups of six earthworms were released in to 20 ml of solutions of Albendazole ethanol extracts of roots of Ziziphus Oenoplia (1%, 2.% and 5% each) in distilled water. Observations were made for the timetaken to paralysis and death of individual worms. Time for paralysis was noted when no movement of any sort could be observed except when the worms were shaken vigorously. Death was concluded when the worms lost their motility followed with fading away of their body colours.
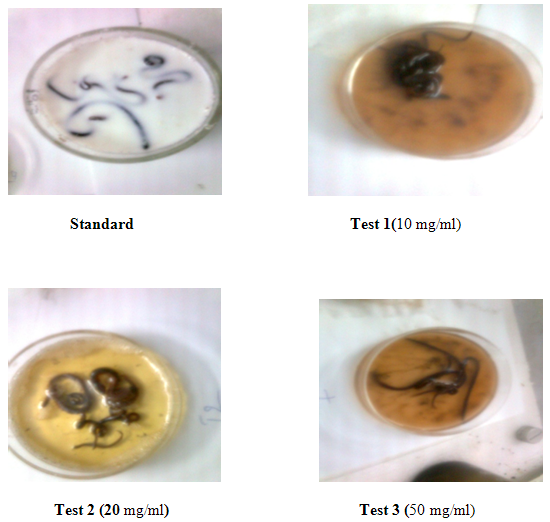

Anthelmintic activity of alcoholic extract of Ziziphus oenoplia roots Test substance concentration mg/ml Time taken for Paralysis (P) and Death (D) of worms in min (Pheretima posthuma).
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
|
Grp |
Sample |
Conc in mg/dl |
Time taken for paralysis(P ) (in min) |
Time taken for death(D) (in min) |
|
1 |
Control |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
Albendazole |
20mg/ml |
34.66 ± O.726** |
63.83±0.79** |
|
3
|
Alcohol extract |
10mg/ml
|
50.63±0.42 |
94.17±0.91 |
|
4
|
Alcohol extract |
20mg/ml
|
45.37±0.71 |
75.00±0.41 |
|
5 |
Alcohol extract |
50mg/dl |
38.15±0.13** |
68.75±0.33** |
Value are mean SEM = Standard error mean;* P < 0.05 V/S Standard groups calculated by ANAOVA followed by student’s t test. n=6
DISCUSSION
The phytochemical screening of crude alcoholic extract contains Anthraquinone, benyl isoquinone, cyclopeptidetype, Ziziphine, N,O,P,and Q new antispasmodal cyclopeptide alkaloid .
The alcoholic extract of Ziziphus oenoplia root exhibit anthelmintic activity dose dependent manner. The alcoholic extract at dose 50mg/ml caused paralysis in 38 min and death in 68 min against Pheretima posthuma compared to the reference standard Albendazole (20 mg/ml) showed the same at paralysis time 34 min and death time 63 min.
The alcoholic extract of the plant not only demonstrated paralysis, but also caused death in shorter time as compared to reference drug Albendazole. The anthelmintic potency of the prepared samples and marketed available standard drug (Albendazole).
CONCLUSION
The phytochemical screening of the ethanolic extract has revealed the presence of glycosides and steroids in alkaloids and flavonoids, tannins, carbohydrates, Antihelmintic effect due to presence of flavonoids .
Theethanolic extract showed significant anthelmintic activity when compared to reference drug Albendazole. Further, it would be interesting to isolate the possible phyto constituents which may be responsible for the activity and the mechanism of action.
REFERENCES
1. Perry, B.D., Randolph, T.F., McDermott, j.j.,nsones,K.R. and Thornton, P.K., In: Veterinary Paristology, International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya, 2002;,148.
2. Perry,B.D., Randolph, T.F., In: Veterinary Paristology, International Livestock Research
Institute,Nairobi,Kenya,1999,;84,145.
3.Monterio,A.M.,Wanyangu,S.W.,Kariuki,D.P.,Bain,R., Jackson,F.and McKeller, Q.A., Veterinary Record, 1998, 142,396.
4. Vidyarthi R.D. A text book of Zoology, S.chand and Co,New Delhi, .1967:329-370.
5. Chatterjee K.D.Parasitology.Protology and Helminthology.Cuha Ray Sree Saraswaty Press Ltd.Calcutta. .(1967):168-169.
6. Vigar Z. Atlas of Medical of Parasitology, , P.G Publishing house ,Singapore, .1984:216.
7. Thron G.W., Adams R.D., Braunwald E.,Isselbacher k. J and petersdorf R.G.Harrison”s Princples of internal Medinces, Mc Graw Hill Co., New York, 1997:.1088.
8. Sollman T, anthelmentics.Therapeutic utility of Ocimum basilcum var.album,Planta.Med 1918:.22,66,70.18.Jain M.L and Jain S.R Therapeutic utility of Ocimum basilicum var .album,planta.Med .1972:22,66-70.
9. Dash G.K., Suresh p.,Ganapaty S and Panda S.B Evaluation of Evolvolus alsinoids Linn for anthelmintic and antimicrobial activities .,J.Nat.Rem. 2002 :2(2),182-185.
10. Szeweszuk V.D., Mongelli E.R.and Pomillo A. 20.Szeweszuk V.D., Mongelli E.R.and Pomillo A.B J.Enthopharmacol .Exp.Ther.12.12 2003 :9-170.
11. Shivakar,Y.M. amd kumar V.L .Anthelmintic activity of latex of calotopis procera.Pharm.Biol.41(4) .2003:.263.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









