 About Authors:
About Authors:
Kalpesh Ashara
Registered Pharmacist S.K.R.I.Medicines Centre, Rajkot, Gujarat, India,
M.Pharm Semester-I Student of B.K.Mody Govt.Pharmacy College Rajkot,
Department of Pharmaceutics GTU, Gujarat, India.
kalpeshashara@yahoo.com, kalpeshshr5@gmail.com*
Abstract:
Spectrophotometry is an attractive method for PKa determination in very diluted aqueous solution about 10-5 to 10-6M provided that the compound possesses PH dependent light absorption due to the presence of a chromospheres in proximity to the ionization centers. Traditionally 6 to 8 aliquot solutions of samples in identical concentrations but with different PH values are prepared & their absorption spectra are registered at single wavelength. This series of solutions can be generated by either preparing the sample in buffer solutions of known PH or titrating the sample solution e.g. alkalimetry. Then half the absorbance of maximum plotted on graph & interpolated on x-axis that will give value of PH is Pka & negative Antilog of that value at base 10 give value of ka i.e. Dissociation Constant (Pka=-logka). This exercise is carrying out in below assignment.
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1514
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Introduction:
Very dilute solution of Aspirin i.e.10ug/ml in different PH solutions gives Pka value directly from graph by use of UV absorption spectrometry & Digital PH meter by means of titrimetry, but UV-visible spectrophotometry technique is most unique because of less time consuming, reproducible than other techniques.
Materials:
API (Aspirin), 0.2MKH2PO4, 0.2MNaOH
Instrument: UV-visible spectrophotometer, two matched quartz cuvettes with 1 cm path length, Digital PH meter.
Method:
Prepare 6-8 aliquots of solutions of buffer. For preparations of buffer as IP 1996,firest take 27.18gm KH2PO4 in 100ml of volumetric flask ,dissolve then make volume up to 100ml.It will give 0.2M 100ml KH2PO4 & similar pattern freshly prepare 100ml 0.2M NaOH. Now place 50ml 0.02MKH2PO4 in 200ml volumetric flask add sufficient volume of 0.2MNaOH then make volume 200ml,so it will give 200ml specific PH buffer solution:.
|
PH |
.ml of NaOH |
|
6 |
5.6 |
|
8 |
46.1 |
|
4.2 |
3 |
For preparation of acid phosphate buffer 0.02MKH2PO4 in 200ml volumetric flask add sufficient volume of 0.2M HCl freshly prepared then add water to make volume 200ml which gives 200ml specific PH buffer solution:
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
|
PH |
.ml of NaOH |
|
2.2 |
49.5 |
|
4.0 |
0.1 |
Now with help of Digital PH meter measure the PH of prepared buffer which is found that are as follows:
|
PH of buffer |
Actual PH of Prepared Buffer by Digital PH |
|
2.2 |
2 |
|
4 |
3.5 |
|
4.2 |
6.6 |
|
6 |
7.7 |
|
8 |
9.4 |
And prepared 2:8 Aspirin: Buffer solution in which solution of aspirin is 100ug/ml, now measure the absorbance of each buffer aspirin preparation solution with help of UV-visible spectrophotometer at 226nm wavelength in which each buffer is considered as blank in each time.226nm λmax is achieved first by taking spectrum of Aspirin solution in water by UV-visible spectrophotometer then 226 nm wavelength should remain constant even by diluting the solution of solution i.e. λmax is that irrespective of concentration of substance. Here concentration of API should between in the range of 10-5to 10-6M so this method is applicable so concentration of aspirin is taking at 100µ/ml.
The absorbance of different prepared solutions is as follows:
|
2:8 Aspirin :Buffer Solution of Different PH |
Absorbance |
|
2 |
0.658 |
|
3.5 |
0.615 |
|
6.6 |
0.283 |
|
7.7 |
0.111 |
|
9.4 |
0.016 |
The maximum Absorbance is 0.658 at 2 PH. Plot a graph of Absorbance vs. PH as follow:
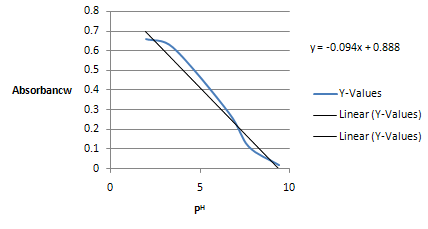
Figure: Pka determination by Spectrometry
Now from half of max absorption if plotting from graph the value of PH on x-axis directly gives value of Pka, so from equation of chart i.e. y=0.094x+0.888 the value of y=0.658/2=0.329 is taken
.y=0.094x+0.888
0.329=0.094x+0.888
0.329-0.888/0.094=x=5.95
Pka=5.95
Now Pka=-logka
5.95=-logka
Ka=-Antilog of 5.95
.ka=1 X10-6
Conclusion:
Pka determination by PH metry is time consuming process, whereas by means of Spectrophotometry is easy & reproducible method.
Acknowledgement:
I am very much thankful to Analysis Department of B.K.Mody Govt.Pharmacy College Rajkot-3, Gujarat, India especially Dr.Nilesh K.Patel, Mr.Amit J.Vyas, Mr.Ajay I. Patel, Assistant Professors B.K.Mody Govt.Pharmacy College Rajkot, Gujarat, India & Mr.Vishal Rupapara & Mr.Nalin Rabadiya M.Pharm Semester-I Student of B.K.Mody Govt.Pharmacy College Rajkot, Department of Pharmaceutics GTU, and Gujarat, India for co-operation to me in this Assignment.
References:
1. CHEM 335: Physical Biochemistry Lab pKa of a dye: UV-VIS Spectroscopy Flory Wong and Roxanne Cheung
2. “UV-Visible Spectroscopy” URL: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UV/VIS_spectroscopy> (Retrieved Apr 19 2007)
3. MERCURY’S HELP DESK | UV-VIS SPECTROMETRY jr.stryker.tripod.com/physchem/pka.html> (Retrieved Apr 19 2007)
4. Keiichiro Fuwa, B. L. Valle. “The Physical Basis of Analytical Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. The Pertinence of the Beer-Lambert Law.” Anal. Chem.; 1963; 35(8); 942-946.
5. Mukerjee, Pasupati and Bannered, Kalyan. “A Study of the Surface pH of Micelles
6. Using Solubilized Indicator Dyes” J. Phys. Chem., 68, 12, 3567 - 3574, 1964
7. Indian Pharmacopoeia1996.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









