About Author:
Sujatha Ramasamy
Scientist-B, Technology Information,
Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC)
New Delhi, India.
sujathar23@gmail.com
Introduction:
The most wonderful creation in the human body is the Brain. Brain is a very complex organ with its major role in the nervous system. The central nervous system (CNS) is made of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made of nerves. The entire human body is entangled with nerves for specific functions. Sensory nerves gathers information from all parts of the body from brain to face, ears, eyes, nose, and spinal cord and from the spinal cord to the rest of your body and sends the message to the brain. The main parts of the brain are Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Limbic System and Brain stem.
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1767
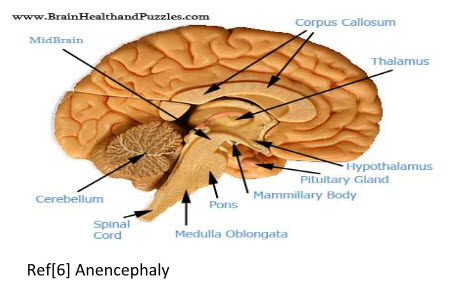
Ref[6] Anencephaly
The cerebrum or cortex is the largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. The Cerebellum or "little brain", is similar to the cerebrum in that it has two hemispheres and has a highly folded surface or cortex. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. The limbic system, often referred to as the "emotional brain", is found buried within the cerebrum. This system contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus. The brain stem is made of the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It is responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
If the brain is malformed or there is any deficit in the growth of brain, then the person is said to be mentally ill. There are several brain disorders/disease but there are a few major disorders during the stages of brain growth which are called as ‘developmental disorders’.
Developmental Disorders and its types:
Developmental disorders are defects of growth resulting in the interruption of the orderly sequence of development at any stage of brain growth.Starting at conception, the developing embryo is susceptible to many factors that affect development. During the first twelve weeks of development, the cells of the embryo and fetus are rapidly dividing and becoming the infant's muscles, bones, and organs. Exposure to disease or toxins may disrupt the process of development and can result in birth defects and developmental problems in the infant.
There may be several reasons for these defects like vascular, traumatic, metabolic, toxic, nutritional, neoplastic or infectious. These agents may lead to interruption of normal development or result in tissue destruction. The etiology is usually unknown in most cases. Birth defects can be inherited from a parent or acquired through the mother's contact with environmental factors such as drugs or infections. Birth defects of the brain, result in problems that can range from mild to severe. They can affect one part or many parts of the central nervous system.
1. Neural Tube Defects (NTD):
This is a common type of CNS malformation. A NTD is a opening in the spinal cord or brain that occurs very early in human development. The neural tube is formed during the 3rd week of pregnancy where specialized cells on the dorsal side of the fetus begin to fuse. The NTD are due to failure of a portion of the neural tube to close or reopening of the region after successful closure leading to several malformations. The last portions of the neural tube to close are the anterior and posterior neuropores. The latter closes at about the 26th day of gestation. Midline defects, which are directly related to the lack of closure of the neural tube, are among the most common of central nervous system malformations.
There are two types of NTDs: i) Open NTDs occur when the brain and/or spinal cord are exposed at birth through a defect in the skull or vertebrae (back bones). Eg. anencephaly, encephaloceles, hydranencephaly,iniencephaly, schizencephaly, and spina bifida.
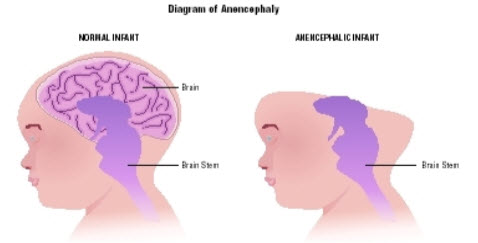
Ref[7] Anencephaly
ii) Closed NTDs are rare and occur when the spinal defect is covered by skin. eg. lipomyelomeningocele, lipomeningocele, and tethered cord.
NTD Prevention:
Researchers have found that 50-70% of NTDs can be prevented when women supplement their diet with folic acid, a water-soluble B vitamin. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends all women of childbearing age eat a diet high in folic acid or take a multivitamin with 400 micrograms of folic acid each day, especially one month prior to conception through the first three months of pregnancy.
2. Fore Brain anomalies:
Many of these types are related to mental retardation.
i)Polymicrogyria: The human brain characterized by an excessive number of small irregular convolutions (gyri) on the surface of the brain.Either the whole surface (generalized) or parts of the surface (focal) can be affected but not necessarily accompanied by mental retardation.
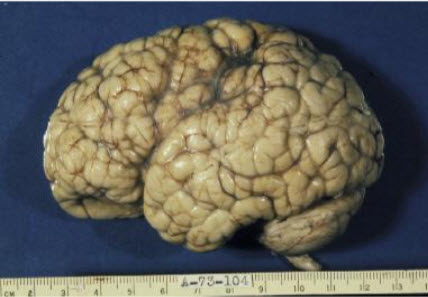
Ref[8] Polymicrogyria.
ii)Megalencephaly is a condition where the volume of brain may be abnormally large and Microcephalgy where the brain is smaller than the normal size. The latter is more common which may occur due to various reasons like chromosomal abnormalities, fetal alcohol syndrome and HIV-1 acquired in utreo.
iii) Heterotopias: Heterotopia means "out of place." Heterotopia is a condition in which nerve cells (neurons) do not migrate properly during the early development of the fetal brain, from about the 6th week to the 24th week of pregnancy. Some neurons or cluster of neurons fail to migrate to their proper position and form clumps in abnormal positions.These abnormal foci of neurons may cause seizures.
iv)Holoprosencephaly: A condition in which the cerebral hemispheres fail to divide properly. When the embryo's forebrain does not divide to form bilateral cerebral hemispheres (the left and right halves of the brain), it causes defects in the development of the face and in brain structure and function.
3.Posterior Fossa Anamolies:
i) Arnold-Chiari malformation(small posterior fossa): Abnormalities of the brainstem and cerebellum. There are 4 types found and type II which is most common. It consists of a downward displacement of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum (the opening at the base of the skull), sometimes causing non-communicating hydrocephalus as a result of obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) outflow. The cerebrospinal fluid outflow is caused by phase difference in outflow and influx of blood in the vasculature of the brain. It can cause headaches, fatigue, muscle weakness in the head and face, difficulty swallowing, dizziness, nausea, impaired coordination, and, in severe cases, paralysis.
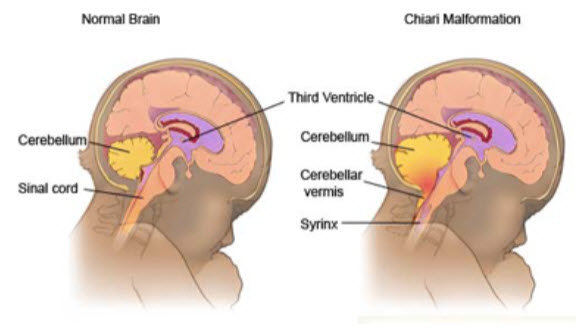
Ref[9] Arnold-Chiari malformation
ii)Dandy-Walker malformation(large posterior fossa):A congenital brain malformation involving the cerebellum and the fluid filled spaces around it.
4.Syringomyelia and Hydromyelia: These are disorders characterized by discontinuous multisegmental or confluent expansion of the ependyma-lined central canal of the cord(hydromyelia) or by formation of a fluid filled cleft like cavity in the inner portion of cord(syrimgomyelia) that may extend into the brainstem. It may affect at age.
Conclusion:
Brain, being a vital organ of the human body, plays a central role in the nervous system. Any defect of the smallest order in the brain would lead to major mishap/malfunctioning of the entire body. In view of this, utmost care is required for early detection and diagnosis of any sort of developmental disorders and it needs to be done in a timely manner. More awareness needs to be created for such brain disorders vis-a vis given to other disorders. This would ensure healthy offspring for future Indians
References:
1. chg.duke.edu/diseases/ntd.html
2. learn.chm.msu.edu/neuropath/content/developmental/dev_1.html
3. humanillnesses.com/Behavioral-Health-A-Br/Birth-Defects-and-Brain-Development.html
4. ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/periventricular-heterotopia
5. ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/polymicrogyria
6. brainhealthandpuzzles.com/diagram_of_brain.html
7. healthofchildren.com/C/Congenital-Brain-Defects.html
8. tulane.edu/som/departments/pathology/neuropg1_15.cfm
9. nursingcrib.com/nursing-notes-reviewer/medical-surgical-nursing/arnold-chiari-malformations/
10. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Developmental_disorder
11. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arnold%E2%80%93Chiari_malformation
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









