{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
ABOUT AUTHORS
Suleman S. khoja, Parthkumar H. Chauhan, Maulik N. Patel, Harsha D. Jani
Department of Quality Assurance,
Shivam Pharmaceutical Studies and Research Centre, Anand, Gujarat.
premukhoja@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Cinnarizine and Dimenhydrinate combination are active contain and approved by CDSCO The two substances belong to different groups of medicines. Cinnarizine is a part of a group called calcium antagonists. Dimenhydrinate belongs to a group called antihistamines Also used in Treatment of vertigo symptoms of various origins. exhibits anti-emetic and antivertiginous effects through influencing the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the region of the 4th ventricle. Dimenhydrinate thus acts predominantly on the central vestibular system. Due to its calcium antagonistic properties, cinnarizine acts mainly as a vestibular sedative through inhibition of the calcium influx into the vestibular sensory cells. Cinnarizine thus acts predominantly on the peripheral vestibular system. Both cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate are known to be effective in the treatment of vertigo. The combination product is more effective than the individual compounds in the population studied. The product has not been evaluated in motion sickness. Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of cinnarizine and diphenhydramine are reached in humans within 2 - 4 hours. metabolised in the liver. Cinnarizine is mainly eliminated via the faeces (40-60%) and to a lower extent also in urine, mainly in the form of metabolites conjugated with glucuronic acid. The major route of elimination of diphenhydramine is in the urine
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2441
|
PharmaTutor (ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 4, Issue 10 Received On: 02/05/2016; Accepted On: 07/06/2016; Published On: 01/10/2016 How to cite this article: Khoja SS, Chauhan PH, Patel MN, Jani HD; A Review on chemistry and Pharmacological activity of Cinnarizine and Dimenhydrinate combine dosage form; PharmaTutor; 2016; 4(10); 26-30 |
INTRODUCTION
Cinnarizine is an antihistamine and a calcium channel blocker classified as a selective antagonist of T-type voltage-operated calcium ion channels, because its binding blocks the channels and keeps them inert. In treatment of nausea and motion sickness it was previously hypothesized that cinnarizine exerts its effects by inhibiting the calcium currents in voltage gated channels in type II vestibular hair cells within the inner ear
Dimenhydrinate is an antiemetics drug combination that contains diphenhydramine andtheophylline. It is not effective in the treatment of nausea associated with cancer chemotherapy. Dimenhydrinate directly inhibits the stimulation of certain nerves in the brain and inner ear to suppress nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and vertigo. diphenhydramine and dimenhydinate both reduce vestibular neuronal excitation due to angular or linear acceleration motions [1-3]
Tablet contain two active substances; cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate. The two substances belong to different groups of medicines. Cinnarizine is a part of a group called calcium antagonists. Dimenhydrinate belongs to a group called antihistamines. Both substances work by reducing symptoms of vertigo (a feeling of dizziness or “spinning”) and nausea (feeling sick). When these two substances are used together they are more effective than when each one is used on their own.[4]
Therapeutic indications Treatment of vertigo symptoms of various origins.
Contraindications Diphenhydramine is completely excreted renally, and patients with severe renal impairment were excluded from the clinical development programme. combination should not be used by patients with a creatinine clearance of ≤ 25 ml/min (severe renal impairment). Since both active components of combination are extensively metabolised by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, the plasma concentrations of the unchanged drugs and their half-lives will increase in patients with severe hepatic impairment. This has been shown for diphenhydramine in patients with cirrhosis. Combination should therefore not be used by patients with severe hepatic impairment. Combination is contra-indicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the active substances, diphenhydramine or other antihistamines of similar structure or to any of the excipients. Combination should not be used in patients with angle-closure glaucoma, convulsions, suspicion of raised intracranial pressure, alcohol abuse or urine retention due to urethroprostatic disorders.
Special warnings and precautions for use combination does not reduce blood pressure significantly, however, it should be used with caution in hypotensive patients. Combination should be taken after meals to minimise any gastric irritation. combination should be used with caution in patients with conditions that might be aggravated by anticholinergic therapy, e.g. raised intra-ocular pressure, pyloro-duodenal obstruction, prostatic hypertrophy, hypertension, hyperthyroidism or severe coronary heart disease. Caution should be exercised when administering combination to patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction The anticholinergic and sedative effects of combination may be potentiated by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Procarbazine may enhance the effect of comibination. In common with other antihistamines, combination may potentiate the sedative effects of CNS depressants including alcohol, barbiturates, narcotic analgesics and tranquillisers. Patients should be advised to avoid alcoholic drinks. Combination may also enhance the effects of antihypertensives, ephedrine and anticholinergics such as atropine and tricyclic antidepressants. Combination may mask ototoxic symptoms associated with amino glycosidic antibiotics and mask the response of the skin to allergic skin tests. The concomitant administration of medicines that prolong the QT interval of the ECG (such as Class Ia and Class III anti-arrhythmics) should be avoided. The information about potential pharmacokinetic interactions with cinnarizine and diphenhydramine and other medicinal products is limited. Diphenhydramine inhibits CYP2D6 mediated metabolism and caution is advised if drug combination is combined with substrates of this enzyme, especially those with narrow therapeutic range Pregnancy and lactation Pregnancy: The safety of combination in human pregnancy has not been established. Animal studies are insufficient with respect to effects on pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development and postnatal development.The teratogenic risk of the single actives dimenhydrinate/diphenhydramine and cinnarizine is low. No teratogenic effects were observed in animal studies. Dimenhydrinate may have an oxytocic effect and may shorten labour. Combination should not be used during pregnancy. Lactation: Dimenhydrinate and cinnarizine are excreted in human breast milk. Combine drug should not be taken by women who are breast feeding. Effects on ability to drive and use machines. This combination may cause drowsiness, especially at the start of treatment. Patients affected in this way should not drive or operate machinery.
Overdose Symptoms of overdosage with drug combination include drowsiness, dizziness and ataxia with anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth, flushing of the face, dilated pupils, tachycardia, pyrexia, headache and urinary retention. Convulsions, hallucinations, excitement, respiratory depression, hypertension, tremor and coma may occur, particularly in cases of massive overdosage. Management of overdose: General supportive measures should be used to treat respiratory insufficiency or circulatory failure. Gastric lavage with isotonic sodium chloride solution is recommended. Body temperature should be closely monitored, since pyrexia may occur as a consequence of antihistamine intoxication, especially in children. Cramp-like symptoms may be controlled by careful application of a short-acting barbiturate. In cases of marked central-anticholinergic effects, physostigmine (after physostigmine test) should be administered slowly intravenously (or, if necessary, intramuscularly) : 0.03mg/kg body weight (adults max. 2mg, children max. 0.5 mg). Dimenhydrinate is dialyzable, however treatment of overdosage by this measure is considered as unsatisfactory. Sufficient elimination can be achieved by means of haemoperfusion using activated charcoal. No data are available concerning the dialysability of cinnarizine.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: cinnarizine and Dimenhydrinate, the chlorotheophylline salt of diphenhydramine, acts as antihistamine with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties, exerting parasympatholytic and centrally-depressant effects. The substance exhibits anti-emetic and antivertiginous effects through influencing the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the region of the 4th ventricle. Dimenhydrinate thus acts predominantly on the central vestibular system. Due to its calcium antagonistic properties, cinnarizine acts mainly as a vestibular sedative through inhibition of the calcium influx into the vestibular sensory cells. Cinnarizine thus acts predominantly on the peripheral vestibular system.
Both cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate are known to be effective in the treatment of vertigo. The combination product is more effective than the individual compounds in the population studied. The product has not been evaluated in motion sickness.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption and distribution: Dimenhydrinate rapidly releases its diphenhydramine moiety after oral administration. Diphenhydramine and cinnarizine are rapidly absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of cinnarizine and diphenhydramine are reached in humans within 2 - 4 hours. The plasma elimination half-lives of both substances range from 4 to 5 hours, when given either alone or as the combination product.
Metabolism: Cinnarizine and diphenhydramine are extensively metabolised in the liver. The metabolism of cinnarizine involves ring hydroxylation reactions that are in part catalysed by CYP2D6 and N desalkylation reactions of low CYP-enzyme specificity. The main pathway in the diphenhydramine metabolism is the sequential N-demethylation of the tertiary amine. Studies in human liver microsomes in vitro indicate the involvement of various CYP-enzymes, including CYP2D6.
Elimination: Cinnarizine is mainly eliminated via the faeces (40-60%) and to a lower extent also in urine, mainly in the form of metabolites conjugated with glucuronic acid. The major route of elimination of diphenhydramine is in the urine, mainly in the form of metabolites, with the deaminated compound, diphenylmethoxy acetic acid, being the predominant metabolite (40-60%).
Preclinical safety data :Preclinical data revealed no specific hazard for humans based on repeated dose toxicity studies with the combination of cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate, fertility studies with cinnarizine or dimenhydrinate, and embryo/foetal development studies with dimenhydrinate. Doses were well in excess of the maximum human dose. Studies in dogs, rabbits and rats gave no evidence for teratogenic effects of cinnarizine. In one study in rats, cinnarizine decreased litter size, increased the number of resorbed foetuses and decreased the birth weight of pups. The genotoxic and carcinogenic potential of the cinnarizine/dimenhydrinate combination has not fully been evaluated.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
List of excipients
cellulose, microcrystalline, maize starch, talc, hypromellose, silica, colloidal anhydrous, magnesium stearate, cross carmellose sodium
Shelf life: 3 years
Special precautions for storage: This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
CLINICAL ASPECTS INDICATIONS
Treatment :vertigo
DOSE AND DOSE SCHEDULE
Adults: 1 tablet three times daily, to be taken unchewed with some liquid after meals.
Children and adolescents under the age of 18 years: Not recommended.
Elderly:Dosage as for adults. Renal impairment: combine Tablets should be used with caution in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Tablets should not be used by patients with a creatinine clearance of < 25mL/min (severe renal impairment).Hepatic impairment: No studies in patients with hepatic impairment are available.Cinnarizine and Dimenhydrinate 20mg/40mg Tablets should not be used by patients with severe hepatic impairment. In general, the duration of treatment should not exceed four weeks. The physician shall decide whether longer treatment is required. The dose and dose schedule is satisfactory.
Chemistry of Cinnarizine and Dimenhydrinate [5-11]
Drug profile of Cinnarizine
Description of Cinnarizine
|
Sr. No. |
Parameters |
|
|
Name of Drug |
Cinnarizine |
|
|
1 |
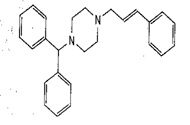
Chemical Structure |
|
|
2 |
IUPAC name |
(E)-1-(Diphenylmethyl)-4-(3-phenylprop2enyl)piperazine.
|
|
3 |
Chemical Formula
|
C26H28N2 |
|
4 |
Molecular Weight
|
368.51 g.mol-1
|
|
5 |
Appearance
|
White or almost Powder.
|
|
6 |
Solubility |
Soluble in Acetone freely soluble in methylene choloride,Dicholoromethane |
|
7 |
Melting range |
118-122 °C |
|
8 |
Therapeutic Category
|
Antihistamine |
|
9 |
pKa
|
8.4 |
|
10 |
Storage
|
Protect from light |
Drug profile of Dimenhydrinate
Description of Dimenhydrinate
|
Sr.No |
PARAMETER |
|
|
Name of Drug |
Dimenhydrinate |
|
|
1 |
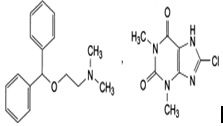
Chemical Structure |
|
|
2 |
IUPAC name |
Diphenhydramine[2(diphenylmethoxy)-N,N-dimethylethylamine8-chlorotheophylline (8-chloro-3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione
|
|
3 |
Chemical Formula
|
C17H21NO,C7H7ClN4O2 |
|
4 |
Molecular Weight
|
469.96 g.mol-1
|
|
5 |
Appearance
|
A white or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals |
|
6 |
Solubility |
slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol |
|
7 |
Melting range |
102-106°C |
|
8 |
Therapeutic Category |
Antihistamine
|
|
9 |
pKa |
8.87 |
|
10 |
Storage
|
Preserve in well closed containers |
Various combination available
|
Sr.No |
Formulation |
Manufactured by |
|
A |
Spinfree |
Intas Pharma |
|
B |
Stugeron plus |
Johnson and Johnson |
|
C |
Dizitac |
Sun Pharma |
|
D |
Diziron d tablet |
Gelnmark pharmaceutical ltd |
|
E |
Vomivert |
Mankind Pharma ltd |
REFERENCES
1. Central drug standard control organization, August 2015 ,http://cdsco.nic.in/writereaddata/LIST%20OF%20APPROVED%20DRUG%20FROM%2001.htm
2. Drug bank Dimenhydrinate,August 2015; http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00985
3. Drug bank Cinnarizine,August 2015; http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00568
4. Medplus,August 2015, http://www.medplusmart.com/compositionProducts/Cinnarizine-20-MG-and-Dimenhydrinate-40-MG/21345
5. Indian Pharmacopoeia; Indian Pharmaceutical Commission, Ghaziabad; 7th Edn;Volume II; 2014; 1397-1399.
6. British pharmacopoeia; 7th Edn; The Stationary Office, London Medicines and Healthcare Product Regulatory Agency; 2015; Vol I; 559.
7. European Pharmacopeia 8.0; European Directorate for the quality of Medicine; 1892-1893
8. Heda AA, Sonawane AR, Naranje GH and Puranik PK; A Rapid Determination of Cinnarizine in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form by LC; E-Journal of Chemistry; 2010; 7(3); 1080-1084 .
9. Jadhav GY, Galgatte UC and Chaudhari PD; Estimation of Dimenhydrinate in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form; Indo-American journal of pharmaceutical research..2013;3(9);7001-7007.
10. Francas Gernot.Pellet- type controlled- release preparation containing cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate for combating vertigo; India patents 1682/MUMNP/2007; 2007
11. Renate Kessler. combination of cinnarizine and at least one benzodiazepine compound as active principle besides usual pharmaceutical adjuvants and/or carrier substances. USPTO; US4734412A;1988.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE