{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
ABOUT AUTHORS
Bharat Lal Naik, Chaitanya Prasad Meher
Department of Pharmacology
The Pharmaceutical College (TPC), Tingipali, Barpali, Odisha
chaitanyameher84@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Diuretic are the drugs that promote the output of urine excreted by kidney. The increased excretion of water & electrolytes by the kidney is dependent on 3 different process viz. glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption & tubular secretion. Diuretic are very effective in the treatment of cardiac oedema, specifically the one related with congestive heart failure(C.H.F). They are extensively used in various type of disorders for ex. Cirrhosis of liver, Hypertension,Nephritic syndrome, diabetes insipidus, nutritional oedema, oedema of pregnancy & also to lower intraocular & cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The presented article is based on comprehensive idea about the pharmacology of various diuretic drugs.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2440
|
PharmaTutor (ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 4, Issue 10 Received On: 03/05/2016; Accepted On: 27/05/2016; Published On: 01/10/2016 How to cite this article: Naik BL, Meher CP; A Comparative Pharmacological Study of Diuretic Drugs; PharmaTutor; 2016; 4(10); 10-20 |
INTRODUCTION
All soluble constituents of blood minus the plasma proteins and lipids are filtered at the glomerulus. More than 99% of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in the tubules, about 1.5L urine is produced in 24 hours

Three different process that involve in urine formation are glomerular filtration (180L/day), tubular re-absorption (around 98%) & tubular secretion. Reabsorption occur in Proximal convoluted tubule, thick portion of ascending limb of the loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule & in cortical collecting tubule is 60-70%, 25%, 5-10%, 5% respectively.
The purpose of using diuretics is to maintain urine volume (e.g.: renal failure), to mobilize edema fluid (e.g.: heart failure,liver failure, nephrotic syndrome), to control high blood pressure. Potency of a diuretic is related to the absolute amount of drug (e.g mg/Kg) required to produce an effect. While efficacy relates to the maximum diuretic effect (usually measured in terms of urine volume/time or urine loss of Na+or NaCl/time). Diuretics may be broadly classified under the following two categories. (a) Mercurial diuretics: It contain Hg2+. These are not very much used in clinical practices due to their pronounced and marked side-effects viz., mercurialism, hypersensitivity and excessive diuresis which may lead to electrolyte depletion and vascular complications. Most of the mercurials are administered by intramuscular route and the availability of orally active diuretics has limited their use. diuretics come under this are Chlormerodrin Hg 197, Meralluride, Mercaptomerin sodium, Merethoxylline procaine Mersalyl and Mercumatilin sodium etc. (b) Non-mercurial diuretics: It is having wider applications due to fewer side-effects1. It may be classified into following type:
1. Thiazides (Benzothiadiazines),
2. Carbonic-Anhydrase Inhibitors,
3. Miscellaneous Sulphonamide Diuretics,
4. Aldosterone Inhibitors,
5. ‘Loop’ or ‘High-Ceiling’ Diuretics,
6. Purine or Xanthine Derivatives,
7. Pyrimidine Diuretics,
8. Osmotic Diuretics,
9. Acidotic Diuretics and
10. Miscellaneous Diuretics.
Diuretics are acting at different sites in the nephron. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors acting at the proximal convoluted tubule (site1 diuretics). Loop diuretics acting at the Henle’s loop (site 2 diuretics). Thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics acting at distal convoluted tubule (site 3 diuretics). Potassium-sparing diuretics acting at collecting tubule(site 4 diuretics). Osmotic diuretics act at proximal tubules, loop of henle, collecting tubule. According to type of electrolyte excreted it may be named as follows:
|
Chloruretic |
Cl- |
|
Natriuretic |
Na+ |
|
Saluretic |
Nacl |
|
Kaliuretic |
K+ |
|
Bicarbonaturetic |
HCO3- |
Some of the diuretic drugs with their pharmacological action are tabulated as below:
|
S.N |
DRUG |
MECHANISM OF ACTION |
PHARMACOKINETIC |
ADVERSE EFFECT |
CLINICAL USES |
REFERENCE |
|
1 |
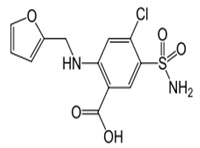
FURESEMIDE
4-chloro-2-[(furan-2 ylmethyl)amino]- 5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid |
Inhibit Na+-k+-2Cl- co-transporter of ascending loop of henle |
Administer orally, IV& IM , Plasma t½ is 1- 2 hours, Low lipid solubility, Protein binding 91–99%, |
Hypokalaemia , Metabolic alkalosis, Hypovolaemia, Hyperuricaemia, Allergy Excreted unchanged in urine 80–90 %, Volume of distribution (L/kg) 0.07–0.2% |
Used in pulmonary & cerebral Oedema, Hypertension, Hypercalcaemia of malignancy |
Tripathy et al2
|
|
2 |
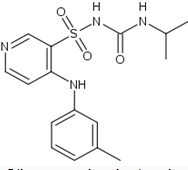
TORASEMIDE
N[(isopropylamino)carbonyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonamide |
Inhibit Na +-k+-2Cl- co- transporter of ascending loop of henle |
Administer orally, IV, plasma t½ -3.5 hours ,dose(2.5-5mg in hypertension, 5-20mg in oedema |
Hypokalaemia, Metabolic alkalosis, Hypovolaemia, Hyperuricaemia, Allergy |
Mainly used in the management of edema associated with C.H.F , used at low doses for the management of hypertension |
Dunn CJ et al 3 |
|
3 |
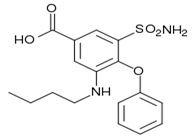
BUMETAMIDE
butylamino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoyl-benzoic acid |
Inhibit the Na+-k+-2Cl- co-transporter of ascending loop of henle. |
Use orally,IV&IM , Plasma t½ -1 hours, Bioavailability- 80 to 100% |
Hypokalaemia, Metabolic Alkalosis, Hypovolaemia, Hyperuricaemia, Allergy |
Pulmonary & cerebral Oedema, Hypertension, Hypercalcaemia of malignancy |
Rang et al4 |
|
4 |
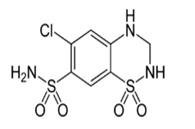
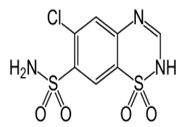
HYDROCHLOROTHAIZIDE
6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide |
Inhibit Na+-2Cl-symporter in DCT(site -3) |
Use orally, bioaviability-70%, On set of action-4-6 hours, Duration of action-8-12 hours, Excreted 95% unchanged in urine. |
Hypokalemia, Hyperuricemia, Hyperglycemia Hyperlipidemia, Headache, Nausea/vomiting, Photosensitivity, Weight gain, Gout, Pancreatitis |
Hypertension, Congestive Heart Failure, Symptomatic edema, Diabetes, Insipidus, Renal Tubular Acidosis. |
R.A Harvey et al5 |
|
5 |
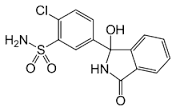
CHLOROTHAIZIDE
(RS)-2-Chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide |
Inhibit Na+-2Cl-symporter in DCT(site -3) |
Absorbed orally, Action starts within 1 hour, but the duration varies from 8–48 hours |
Nausea, Vomiting, Headache, Dizziness, Excess urine production, Dehydration, Hypoelectrolytemia |
Used to treat Edema in people with C.H.F, Cirrhosis of liver, Kidney disorders or edema caused by taking steroids or oestrogen, Used to treat hypertension |
Tripathy et al2
|
|
6 |
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE
Benzyl-1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4- benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide |
Inhibit sodium reabsorption at the beginning of the DCT. |
Oral use,Adverse interaction with alcohol, not be used by pregnant women |
Common adverse effects: Postural Hypotension, hyponatraemia, Hypokalaemia, Hypercalcaemia,Gout, Impaired glucose tolerance, impotence, fatigue, Pulmonary Oedema, Pneumonitis Rare adverse effects: Thrombocytopenia, Agranulocytosis, Photosensitivity, Rash, Pancreatitis, Renal Insufficiency |
Used for the treatment of mild heart failure, hypertension |
Satoskar et al6 |
|
7 |
CHLORTHALIDONE
(RS)-2-Chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide |
Inhibit Na+-Cl- symporter in DCT |
Oral use,dose-50-100mg/day, Duration of action is48 hours, Excreted unchanged in urine, t½ 40–50 hours |
Hypokalemia, Hypochloremia, mild metabolic alkalosis. |
Used exclusively as antihypertensive. |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
8 |
XIPAMIDE
4-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide |
Acts on kidney to reduce sodium reabsorption in DCT |
After oral administration 20 mg are reabsorbed quickly & reach the plasma cocn. Of 3 mg/l with in 1hr. Diuretic effect start after 1 hr of administration & lasts for nearly 24 hr. Plasma clearance is 30-40 ml/min. |
Hypokalaemia, Hyponatraemia, Thrombocytopenia, Leucopenia, Acute interstitial nephritis Hyperlipidemia, Orthostatic hypotension |
Used for cardiac edema caused by decompensation of heart failure, Renal edema, chronic renal disease, Hepatic edema caused by cirrhosis ascites lymphoedema, Hypertension |
Jasek et al7, Klopp et al8 |
|
9 |
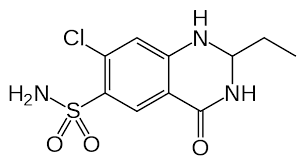
METALAZONE
7-chloro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-o-tolyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide |
Inhibit sodium-chloride symporter |
Oral use, Excreted unchanged in urine, Duration of action 12-24 hours |
Aplastic anaemia, Pancreatitis, Agranulocytosis, Angioedema, Abnormalities of water balance, electrolyte levels. |
Used mainly for edema (5–10 mg/day, rarely 20 mg), and occasionally for hypertension (2.5–5 mg/day). |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
10 |
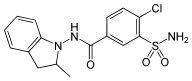
INDAPAMIDE
4-chloro-N-(2-methyl-2,3-dihydroindol-1-yl)-3-sulfamoyl-benzamide |
Inhibit Na+-Cl- symporter in DCT |
Oral use, highly lipid soluble,dose-2.5-5mg/day, duration of action-12-24 hours |
Hypokalemia, Fatigue, Orthostatic hypotension, Allergic menifestations |
Hypertension, Decompensated hypertension. |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
11 |
CLOPAMIDE
4-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethyl-1-piperidyl)-3-sulfamoyl- |
It act in kidney at PCT of nephron where it Na+-Cl- symporter |
Oral absorption 100 %, Plasma protein binding is < 50%, Plasma half life is 10 hr. |
Hypokalemia, hyperglycemia Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Loss of appetite, Blurred vision, Dizziness. |
Used in hypertension , Edema associated with heart failure |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
12 |
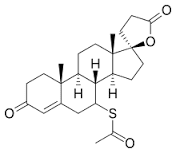
SPIRONOLACTONE
7α-Acetylthio-17α-hydroxy-3-oxopregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid γ-lactone |
It is a competitive antagonist to the mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone. The mineralocorticoid receptor is an intracellular protein in nature that can bind aldosterone. Spironolactone binds to the receptor and competitively inhibits aldosterone binding the the receptor. The inability of aldosterone to bind to its receptor prevents reabsorption of Na+& Cl-and associated water. |
The oral bioavailability from microfine powder tablet is 75%, It is highly bound to plasma proteins, Completely metabolized in liver, The most important active metabolite is Canrenone. The t½ of spironolactone is 1–2 hours, while that canrenone is ~18 hours. |
Drowsiness, Ataxia, Mental confusion, Epigastric distress and loose motions. |
Edema, Hypertension, C.H.F, It is a weak diuretic and is used only in combination with other more efficacious diuretics. |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
13 |
EPLERENONE
pregn-4-ene-7,21-dicarboxylic acid, 9,11-epoxy-17-hydroxy-3-oxo, γ-lactone, methyl ester (7α, 11α, 17α) |
It is an antagonist of the mineralocortecoid receptor. |
well absorbed orally, t½ is 4–6 hours, Plasma protein binding is 50 %, Oral bioavailability is 69% following administration of 100 mg oral tablet, Metabolism is mediated via CYP3A4,
|
Hyperkalemia, Hypotension, Dizziness, Altered renal function, Increased creatinine concentration. |
Used in moderate to severe CHF, Post-infarction left ventricular dysfunction, Hypertension, can be used as alternative to spironolactone. |
Rossi et al9 |
|
14 |
TRIAMTERENE
6-phenylpteridine-2,4,7-triamine |
It acts by blocking the epithelial sodium channel on the lumen side of the kidney collecting tubule. |
It is incompletely absorbed orally, partly bound to plasma proteins, largely metabolized in liver to an active metabolite and excreted in urine. Plasma t½ is 4 hours, effect of a single dose lasts 6–8 hours. |
Nausea, Dizziness, Muscle cramps, Rise in blood urea. Impaired glucose tolerance and photosensitivity
|
Hypertension, Edema |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
15 |
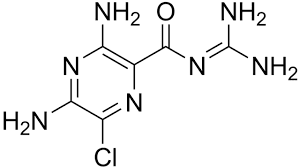
AMILORIDE
3,5-diamino-6-chloro-N-(diaminomethylene)pyrazine-2-carboxamide |
Act by directly blocking the epithelial sodium channel in the late DCT in the kidney |
Only ¼ of an oral dose is absorbed, It is not bound to plasma proteins and not metabolized, The t½ (20 hours) and duration of action are longer than triamterene. |
Nausea, Headache, Diarrhoea. |
Hypertension, C.H.F, Cystic fibrosis. |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
16 |
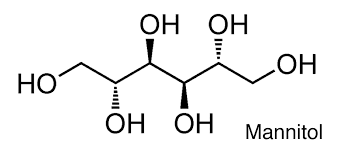
MANNITOL
(2R,3R,4R,5R)-Hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol |
It is act on the proximal tubules & inhibit both water & solute reabsorption in the kidney tubule by increasing the osmolarity of the renal tubular fluid. |
It is not absorbed orally, Has to be given i.v. as 10–20% solution, It is excreted with a t½ of 0.5–1.5 hour. |
Pulmonary congestion, Fluid & electrolyte imbalance, Dryness of mouth, Thrist, Edema, Urinary retention, Headache, Blurred vision |
Used in acute congestive heart, Glaucoma, Head injury, Shock , Severe trauma, Cardiac surgery |
Satoskar et al6 |
|
17 |
GLYCEROL
propane-1,2,3-triol |
It acts by expanding extracellular fluid & plasma volume, therefore increasing blood flow to the kidney |
Orally active osmotic diuretics, Dose: 0.5–1.5 g/kg as oral solution |
Intravenous glycerol can cause haemolysis. |
Used to reduce intraocular or intracranial tension |
Satoskar et al6 |
|
18 |
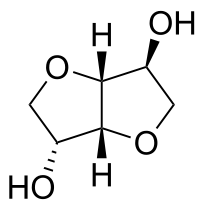
ISOSORBIDE
1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol; 1,4-Dianhydrosorbitol |
No direct effect on transport but cause shift of ions by inducing bulk water flow & changing steady state water concentration in body compartment. |
Orally active osmotic Diuretics, Dose: 0.5–1.5 g/kg as oral solution |
Hypotension, Hypovolemia, Heart failure, Pulmonary congestion, Headache, blurred vision, Nausea, vomitting |
Used to reduce intraocular or intracranial tension |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
19 |
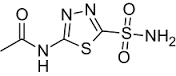
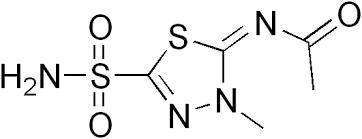
ACETAZOLAMIDE
N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide |
Inhibits CAse (type II) in PT Cells, Inhibition of CAse (type IV), The net effect is inhibition of HCO¯ (and accompanying Na+) reabsorption in PT. |
Well absorbed orally, Excreted unchanged in urine. Action of a single dose lasts 8–12 hours. |
Acidosis, Hypokalaemia, Drowsiness, Paresthesias, Fatigue, Abdominal Discomfort. Hypersensitivity reaction, Bone marrow depression. |
Glaucoma, To alkalinise urine, Epilepsy, Acute mountain sickness, Periodic paralysis |
Tripathy et al2 |
|
20 |
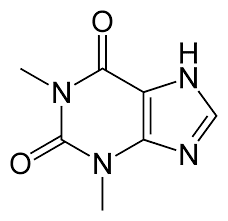
THEOPHYLLINE
1,3-Dimethyl-7H-purine-2,6-dione |
Mechanism unclear, may be related to inhibition of phosphodiesterase and/ or antagonism of adenosine receptor |
Bioavailability is 100% in case of IV, Metabolized in liver (70%), Excreted unchanged in urine,
|
Nausea, diarrhoea, Abnormal heart rhythm, CNS excitation, seizure |
Increasing renal blood flow, Relaxing bronchial smooth muscle, COPD.
|
Rieg T et al11 , Yoshikawa et al12 |
|
21 |
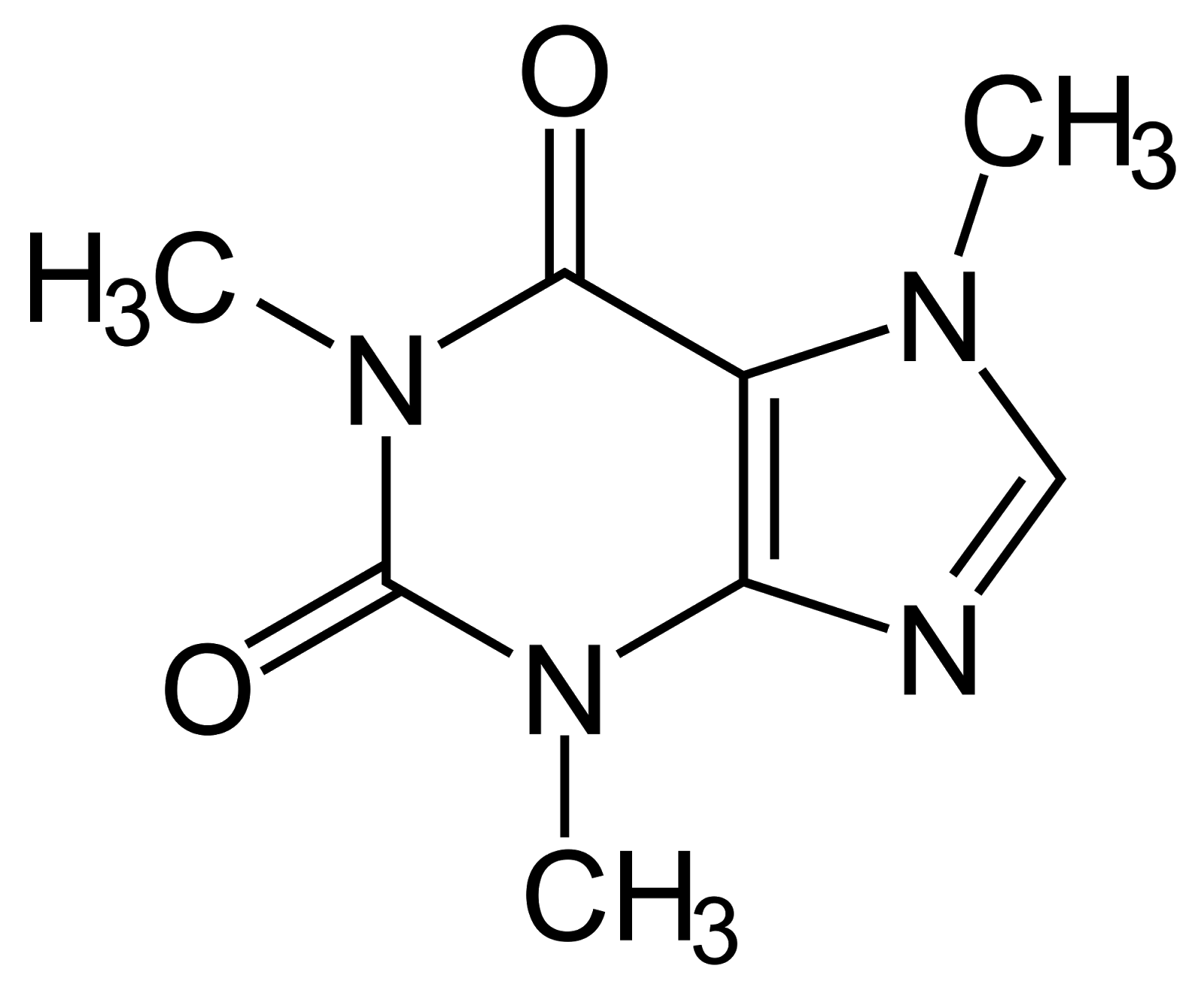
CAFFINE
1,3,7-Trimethylpurine-2,6-dione |
Mechanism unclear, may be related to inhibition of phosphodiesterase and/ or antagonism of adenosine receptor |
Metabolized in the liver, In healthy adults t1/2 is 3-7 hr, Nicotine decrease the half life by 30-50 %
|
Increase metabolic rate, Anxiety, Vasoconstriction, |
Relax smooth muscle of bronchi & is used to treat Asthma
|
Rieg T et al11 |
|
22 |
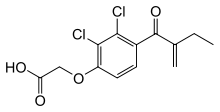
ETHACRYNIC ACID
[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic acid |
Inhibit the Na +-k+-2Cl- co transporter of ascending loop of henle (site-2) |
Oral use, t1/2-~1 hr, Metabolised ~33% in liver, Excreted in urine ~62%. |
Hypokalaemia, metabolic alkalosis, Hypovolaemia , Hyperuricaemia, Allergy |
Oedema like (pulmonary, cerebral), hypertension |
Goodman et al10 |
|
23 |
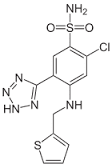
AZOSEMIDE
2-chloro-5-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-4-[(thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino]benzenesulfonamide |
It is a high ceiling diuretic. Exact mechanism is not understood But it mainly act on both medullary & cortical segment of thick ascending limb of the loop of henle. |
Oral boavailability in human is aprox. 20.4%, It’s effect is 5.5-8 time greater than furosemide. Apparent post-pseudodistribution volume is 0.0262 l/kg, In human total body clearance, renal clearance, terminal half life is 112ml/min, 41.6 ml/min, 2.03 hr respectively. |
Panic disorder, Liver disorder, Blood creatine phosphokinase increased |
Used in the treatment of oedematous states, Hypertension. |
Kim et al13 |
|
24 |
PIRETANIDE
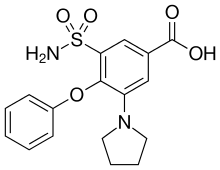
3-(aminosulfonyl)-4-phenoxy-5-pyrolidin-1-yl benzoic acid. |
Site of action is thick ascending limb of the loop of henle. |
Oral use , t1/2-~0.6-1.5 hours, Metabolised ~50% in liver, Excreted in urine ~50%. |
Excess loss of fluid & electrolyte. |
Use for the treatment of hypertension, C.H.F & edematous state caused by renal & hepatic disease. |
Goodman et al10 |
|
25 |
MUZOLIMINE
3-Amino-1-(3,4-dichloro-á-methylbenzyl)-2-pyrazolin-5-one |
It is a loop diuretic |
Effect is slow, It’s action is long lasting. |
|
Used for hypertension but was withdrawn because of severe neurological side effect. |
Reyes et al14 |
|
26 |
TRIPAMIDE
3-(aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-N-[(3aR,4S,7R,7aS)-octahydro-2H-4,7-methanoisoindol-2-yl]benzamide |
Inhibitory effect on solute reabsorption at the cortical segment of thick ascending limb of loop of henle. |
Oral use, Metabolised in liver |
Hypokalaemia, metabolic alkalosis, Hypovolaemia , Hyperuricaemia, Allergy |
Hypertension, Edema. |
Goodman et al 10 |
|
27 |
QUINETHAZONE
7-chloro-2-ethyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline- |
It inhibit active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via Na-Cl cotransporter |
Onset of action 2 hr, Duration of action 18-24 hr. Time to peak effect 6 hr. |
Dizziness, Dry mouth, Nausea, Low potassium level. |
Diuretic and antihypertensive properties similar to those of the thiazides. |
Satoskar et al6 |
|
28 |
TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE
6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[e] [1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide |
Inhibit Na+/2Cl_symporter in DCT(site -3) |
Oral use , t1/2-~2.3-7.3 hours, Excreted in urine |
Hypokalemia, Hyperurecaemia, Hyperlipidimia, Hyperglycemia, Hypersensitivity, Thrombocytopenia, Volume depletion, Hyponatraemia |
Hypertension, Heart failure, Diabetes insipidus, Hypercalciurea |
Goodman et al 10 |
|
29 |
POLYTHIAZIDE
6-chloro-2-methyl-3-{[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio]methyl}-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide |
Enhance urinary excretion of both Na and H2O by specifically inhibiting Na reabsorption located in the cortical (thick) portion of the ascending limb of Henle’s loop and also in the early distal tubules. |
Normal human subjects receiving single 1mg oral dose, the mean plasma half life for absorption & elimination were 1.2 & 25.7 hr respectively, 25 % excreted unchanged in urine. |
Abdominal or stomach pain, Bleeding gum, Blurred vision, Chest pain, Blood in urine or stool. |
Long-acting diuretic and anti-hypertensive agent. As diuretic, usual, 1 to 4 mg per day As antihypertensive, 2 to 4 mg |
Hobbs et al15 |
|
30 |
METHYCLOTHIAZIDE
6-Chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide |
Enhance urinary excretion of both Na and H2O by specifically inhibiting Na reabsorption located in the cortical (thick) portion of the ascending limb of Henle’s loop and also in the early distal tubules. |
Given orally, Rapid absorption, Cross the placenta, Elimination through kidney. Duration of action 6 hr
|
Anxiety, Sweating, Severe shortness of breath, Cough with foamy mucus, Increased thrist, Drowsiness, Muscle pain, Fainting or seizure, Nausea, Vomiting. |
Diuretic and an antihypertensive agent. 2.5 to 10 mg once per day |
Asutosh et al1 |
|
31 |
CANRENONE
10,13-Dimethylspiro[2,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17,5'-oxolane]-2',3-dione |
Inhibit binding of aldosterone with mineralocorticoid receptor. |
Oral use, t1/2-~16.5 hours, |
Drowsiness, Ataxia, Mental confusion |
Oedema, hypertension, CHF |
Goodman et al10 |
|
32 |
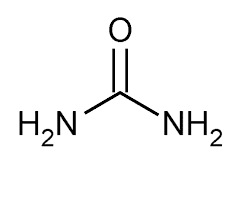
UREA
|
No direct effect on transport but cause shift of ions by inducing bulk water flow & changing steady state water concentration in body compartment. |
Used intravenously, It penetrate total body water, short half life,
|
Hypotension, Hypovolemia, Heart failure, Pulmonary congestion, Headache, blurred vision, Nausea, vomitting |
Approved to reduce intraocular pressure, intracranial pressure, Cerebral edema |
Goodman et al10 |
|
33 |
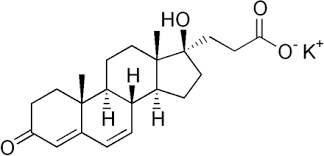
POTASSIUM CANRENOATE
potassium 3-[(8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)- |
It is an aldosterone antagonist. |
Given intravenously |
Nausea, vomiting, Confusion, Restlessness, Hallucination. |
Oedema |
Goodman et al10 |
|
34 |
METAZOLAMIDE
N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-ylidene]acetamide |
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor |
Oral use, t1/2-~14 hours, Metabolise~75%, Renal excreation of intact drug~25% |
Acidosis, drowsiness, Paresthesias , Abdominal Discomfort, Fatigue, Hypertension. |
Glaucoma, Epilepsy, periodic paralysis. |
Goodman et al10 |
|
35 |
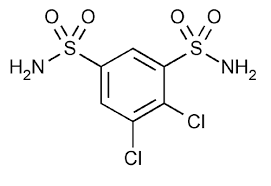
DICHLORPHENAMIDE
4,5-Dichlorobenzene-1,3-disulfonamide |
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor |
Oral use |
Dizziness, Change in the sense of test, Headache, Confusion, Weight loss, muscle pain, joint pain, Throat pain, rash |
Glaucoma, Epilepsy |
Goodman et al10 |
Selected Drug- Diuretic Interaction:
|
DRUGS |
DIURETCS |
PROBLEMS |
|
Digitalis |
Loop & thiazide |
Hypokalemia à digitalis toxicity |
|
NSAID |
Loop & thiazide |
Decrease diuretic effect |
|
Aminoglycoside |
loop |
Ototoxicity & nephrotoxicity |
|
Adrenal steroids |
Loop & thiazide |
Severe hypokalemia |
|
Chlorpropamide |
Thiazide |
Hyponatremia |
|
Lithium |
Loop & thiazide |
Increased plasma (lithium) |
|
Probenecid |
Loop & thiazide |
Decrease diuretic effect |
|
ACE inhibitors |
K+ sparing |
Hyperkalemia à Arrhythmias |
REFERENCES
1. Asutosh kar, “Medicinal chemistry”, 4th edition, page-439,451
2.K.D,Tripathy, “Essential medical pharmacology” ,seventh edition ,page no-581,582, 583,584,587,590,
3. Dunn CJ, Fitton A, Brogden RN (January 1995). "Torasemide. An update of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy".Drugs 49 (1): 121–42
4. Rang & dale’s pharmacology,H.P.Rang,M.M.Dale,J.M.Ritter, R.J Flower,7th edition ,page no. 354
5. R.A.Harvey, Pharmacology, 5th edition.page-283
6.R.S.Satoskar,S.D.bhandarkar,S.Sainapure, Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutic, page no.543,540,545
7. Jasek.W,ed.(2007).austria-codex (in german)1 (2007/2008 ed.).vienna,pp-600-603
8. Klopp.T, ed.(2007). Arzenemittel-interaktionen (in german) (2007/2008 ed.)
9.Rossi S,editor,Australian medicines hand book 2006,adelade.
10. Goodman & Gilman” The Pharmacological basis of therapeutics,10thedition,Page no-767,770,774
11. Rieg T, J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2005,Apr,313(1)403-9.Epub 2004 Dec 8.
12. Yoshika H(Apr 2007), first line therapy for theophylline associated seizure, Acta neurol scand 115 (4 suppl): 57-61
13. Suh, OK, Kim SH, Biopharm Drug Dispose,2003 Oct;24(7): 275-97.
14. reyes A.J,” Clinicopharmacologicalreappraisal of the potency of diuretics” cardiovascular dru & therapy 7:23-28.
15. Hobbs DC,Clin pharmacol ther,1978 feb:23(2):241-6
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE